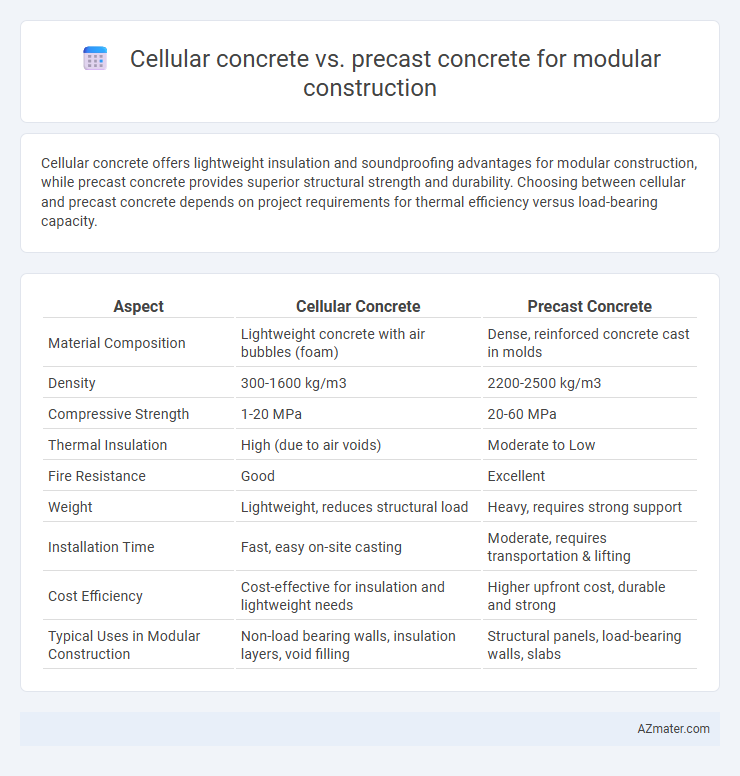
Cellular concrete offers lightweight insulation and soundproofing advantages for modular construction, while precast concrete provides superior structural strength and durability. Choosing between cellular and precast concrete depends on project requirements for thermal efficiency versus load-bearing capacity.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cellular Concrete | Precast Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Lightweight concrete with air bubbles (foam) | Dense, reinforced concrete cast in molds |
| Density | 300-1600 kg/m3 | 2200-2500 kg/m3 |
| Compressive Strength | 1-20 MPa | 20-60 MPa |
| Thermal Insulation | High (due to air voids) | Moderate to Low |
| Fire Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces structural load | Heavy, requires strong support |
| Installation Time | Fast, easy on-site casting | Moderate, requires transportation & lifting |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for insulation and lightweight needs | Higher upfront cost, durable and strong |
| Typical Uses in Modular Construction | Non-load bearing walls, insulation layers, void filling | Structural panels, load-bearing walls, slabs |
Overview of Cellular Concrete and Precast Concrete
Cellular concrete, known for its lightweight and insulating properties, is produced by introducing air bubbles into the cement mix, resulting in a material with reduced density and enhanced thermal performance. Precast concrete involves casting concrete elements in a controlled factory environment before transporting them to the construction site, offering superior quality control, increased durability, and faster assembly times for modular construction. Both materials contribute to efficiency in modular construction but differ significantly in weight, insulation capabilities, and manufacturing processes.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Cellular concrete consists of cement, water, and pre-formed foam bubbles that create a lightweight, porous structure, while precast concrete is made from a mix of cement, aggregates, water, and admixtures cast in molds for uniform density and strength. The manufacturing process of cellular concrete involves mixing foam into the slurry, allowing it to cure into a low-density material ideal for insulation and reduced weight. Precast concrete production includes batching, molding, curing in controlled environments, and quality checks that result in high-strength, durable components suitable for modular construction's structural demands.
Structural Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity
Cellular concrete offers lower density and thermal insulation but has reduced structural strength and load-bearing capacity compared to precast concrete, making it less suitable for heavy load applications in modular construction. Precast concrete provides superior compressive strength typically ranging from 25 to 50 MPa, enabling it to support significant structural loads and ensure long-term durability in modular frameworks. The choice between these materials depends on the balance needed between weight reduction and the required structural performance in building design.
Insulation and Thermal Performance
Cellular concrete offers superior insulation properties due to its high air content, resulting in lower thermal conductivity values typically around 0.1 to 0.2 W/m*K, which enhances energy efficiency in modular construction. Precast concrete, while robust and durable, generally exhibits higher thermal conductivity, approximately 1.0 to 1.4 W/m*K, necessitating additional insulation measures to meet thermal performance standards. Integrating cellular concrete panels in modular units reduces HVAC loads and contributes to improved indoor thermal comfort compared to standard precast concrete components.
Speed and Efficiency in Modular Construction
Cellular concrete offers superior speed in modular construction due to its lightweight properties and ease of on-site forming, significantly reducing curing time compared to traditional methods. Precast concrete panels provide high efficiency through factory-controlled quality and rapid on-site assembly, minimizing labor costs and construction delays. Combining cellular concrete's quick setting with precast concrete's precision can optimize modular construction timelines and overall project efficiency.
Cost Comparison and Budget Considerations
Cellular concrete offers significant cost advantages in modular construction due to its lightweight properties, reducing transportation and crane expenses while providing superior thermal insulation that can lower long-term energy costs. Precast concrete, though typically more expensive upfront due to manufacturing and curing processes, delivers higher structural strength and faster on-site assembly, potentially decreasing labor and project timeline expenses. Budget considerations must weigh the initial material and production costs against lifecycle savings, project scale, and specific design requirements to determine the most cost-effective choice for modular construction.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Cellular concrete offers superior sustainability benefits in modular construction due to its lightweight nature, which reduces transportation emissions and energy consumption during installation. Its excellent thermal insulation properties contribute to lower energy use in buildings, enhancing environmental performance compared to traditional precast concrete. Precast concrete, while durable and reusable, generally has a higher carbon footprint due to energy-intensive manufacturing processes and heavier transportation demands.
Flexibility in Design and Customization
Cellular concrete offers superior flexibility in design for modular construction due to its lightweight, easy-to-shape properties, enabling intricate molds and curved forms that precast concrete struggles to achieve. Precast concrete provides consistent quality and faster production but is limited in customization by rigid mold designs and heavier weight constraints. For projects emphasizing unique architectural features and adaptive layouts, cellular concrete allows greater customization without compromising structural integrity.
Transportation and On-Site Installation
Cellular concrete offers significant advantages in transportation due to its lightweight nature, reducing fuel costs and enabling easier handling compared to precast concrete's heavier and bulkier panels. On-site installation of cellular concrete is more flexible, allowing for pouring and shaping directly at the construction site, whereas precast concrete requires precise placement and heavy machinery for lifting and positioning. The faster curing time of cellular concrete also minimizes downtime, enhancing efficiency in modular construction projects.
Long-Term Durability and Maintenance
Cellular concrete offers excellent thermal insulation and lightweight properties, but its long-term durability can be compromised by moisture absorption and lower compressive strength compared to precast concrete. Precast concrete demonstrates superior resistance to weathering, cracking, and chemical exposure, ensuring minimal maintenance over extended periods in modular construction. Choosing precast concrete enhances structural integrity and reduces lifecycle costs due to its robustness and consistent quality control during manufacturing.
Infographic: Cellular concrete vs Precast concrete for Modular construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com