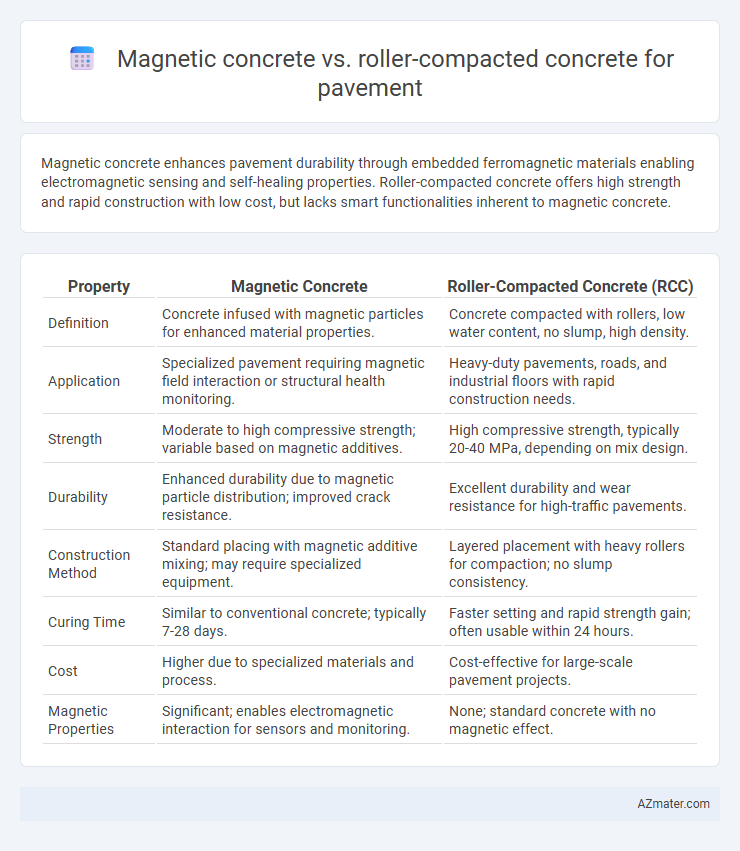
Magnetic concrete enhances pavement durability through embedded ferromagnetic materials enabling electromagnetic sensing and self-healing properties. Roller-compacted concrete offers high strength and rapid construction with low cost, but lacks smart functionalities inherent to magnetic concrete.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Magnetic Concrete | Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete infused with magnetic particles for enhanced material properties. | Concrete compacted with rollers, low water content, no slump, high density. |
| Application | Specialized pavement requiring magnetic field interaction or structural health monitoring. | Heavy-duty pavements, roads, and industrial floors with rapid construction needs. |
| Strength | Moderate to high compressive strength; variable based on magnetic additives. | High compressive strength, typically 20-40 MPa, depending on mix design. |
| Durability | Enhanced durability due to magnetic particle distribution; improved crack resistance. | Excellent durability and wear resistance for high-traffic pavements. |
| Construction Method | Standard placing with magnetic additive mixing; may require specialized equipment. | Layered placement with heavy rollers for compaction; no slump consistency. |
| Curing Time | Similar to conventional concrete; typically 7-28 days. | Faster setting and rapid strength gain; often usable within 24 hours. |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized materials and process. | Cost-effective for large-scale pavement projects. |
| Magnetic Properties | Significant; enables electromagnetic interaction for sensors and monitoring. | None; standard concrete with no magnetic effect. |
Introduction to Magnetic Concrete and Roller-Compacted Concrete
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic materials to enhance electromagnetic properties and enable structural health monitoring, while roller-compacted concrete (RCC) is a zero-slump concrete mixture placed with asphalt pavers and compacted by rollers, commonly used for pavement due to its high strength and rapid construction capabilities. RCC offers durable, cost-effective solutions for heavy-load pavements with low water content, whereas magnetic concrete focuses on integrating smart sensing features within the pavement structure. Both types improve infrastructure performance, with RCC emphasizing mechanical strength and magnetic concrete advancing functional monitoring.
Composition and Material Properties
Magnetic concrete integrates ferromagnetic particles such as iron oxide or steel slag into traditional concrete mix, enhancing electromagnetic properties while maintaining compressive strength around 30-40 MPa, suitable for specialized pavement applications requiring magnetic responsiveness. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC), composed of conventional Portland cement, aggregates, and minimal water, achieves higher density and compressive strength typically ranging from 25-50 MPa through compaction with heavy rollers, providing superior durability and load-bearing capacity for heavy-traffic pavements. The key differentiation lies in magnetic concrete's embedded magnetic materials that allow unique functionalities, whereas RCC focuses on optimized mechanical properties and rapid construction without the need for steel reinforcement.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic particles mixed into the cement matrix, requiring precise control during mixing to ensure uniform distribution of magnetic materials, whereas roller-compacted concrete (RCC) uses a drier mix with low water content, designed for high compaction through heavy rollers rather than conventional finishing tools. Manufacturing magnetic concrete involves specialized batching equipment to integrate magnetic additives without compromising structural integrity, while RCC production emphasizes continuous, rapid mixing and placement techniques optimized for large-scale pavement projects. The critical distinction lies in magnetic concrete's need for enhanced homogeneity to maintain magnetic properties, contrasting with RCC's focus on achieving optimal density and strength through mechanical compaction.
Key Engineering Applications in Pavement
Magnetic concrete enhances pavement durability by integrating ferromagnetic materials, which improve crack resistance and enable electromagnetic heating for rapid snow and ice melting, crucial for cold-region applications. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) provides high load-bearing capacity and quick construction with lower cement content, making it ideal for heavy-traffic pavements like highways and industrial areas. Both materials offer distinct engineering advantages: magnetic concrete excels in renewable energy integration and maintenance, while RCC optimizes cost-efficiency and structural strength in pavement engineering.
Installation Techniques and Equipment
Magnetic concrete installation requires specialized electromagnetic equipment to align magnetic particles, enhancing pavement durability and crack resistance. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) utilizes conventional paving machines and vibratory rollers, allowing for faster placement and compaction on large pavement projects. The choice between magnetic concrete and RCC hinges on project scale and desired material properties, with magnetic concrete demanding advanced technology and RCC offering efficiency with standard construction equipment.
Structural Performance and Load-Bearing Capacity
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic materials that enhance its load-bearing capacity by improving internal stress distribution and crack resistance, resulting in superior structural performance compared to conventional roller-compacted concrete (RCC). Roller-compacted concrete offers high compressive strength and rapid construction benefits but generally exhibits lower tensile strength and durability under cyclic loading conditions. Studies indicate magnetic concrete's enhanced microstructural bonding leads to increased pavement lifespan and reduced maintenance costs in heavy-load applications.
Durability and Longevity in Pavement Use
Magnetic concrete integrates magnetic particles that enhance crack resistance and self-healing properties, significantly improving durability and extending pavement lifespan under heavy traffic conditions. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers excellent structural strength and rapid construction with a dense, low-slump mix that resists wear and weathering effectively over time. While RCC is widely used for highway and airport pavements due to its high compressive strength, magnetic concrete shows promising potential for reducing maintenance costs by mitigating micro-cracks and thermal expansion damage.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Magnetic concrete incorporates iron oxide particles that enable electromagnetic activation, reducing the need for traditional chemical additives and lowering carbon emissions during production. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers environmental benefits through its low water content and reduced cement use, which decreases carbon footprint and energy consumption compared to conventional concrete. Both materials enhance sustainability in pavement construction by improving durability and reducing maintenance frequency, thus minimizing resource use over the pavement lifecycle.
Cost Analysis and Economic Benefits
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic materials that enhance durability and offer potential energy savings through embedded electromagnetic systems, often resulting in higher initial costs compared to traditional roller-compacted concrete (RCC). RCC is favored for its cost-effectiveness, rapid construction time, and lower material expenses, making it economically advantageous for large-scale pavement projects. Long-term maintenance savings and improved performance of magnetic concrete can offset upfront costs, whereas RCC provides immediate budget relief with proven structural reliability.
Future Trends in Concrete Pavement Technologies
Magnetic concrete enhances pavement durability and self-sensing capabilities through embedded ferromagnetic particles, enabling real-time structural health monitoring. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers rapid construction and superior load-bearing capacity, favored for large-scale infrastructure projects with sustainable resource use. Emerging trends combine smart materials like magnetic concrete with RCC methods to optimize performance, reduce maintenance costs, and support intelligent transportation systems.
Infographic: Magnetic concrete vs Roller-compacted concrete for Pavement
 azmater.com
azmater.com