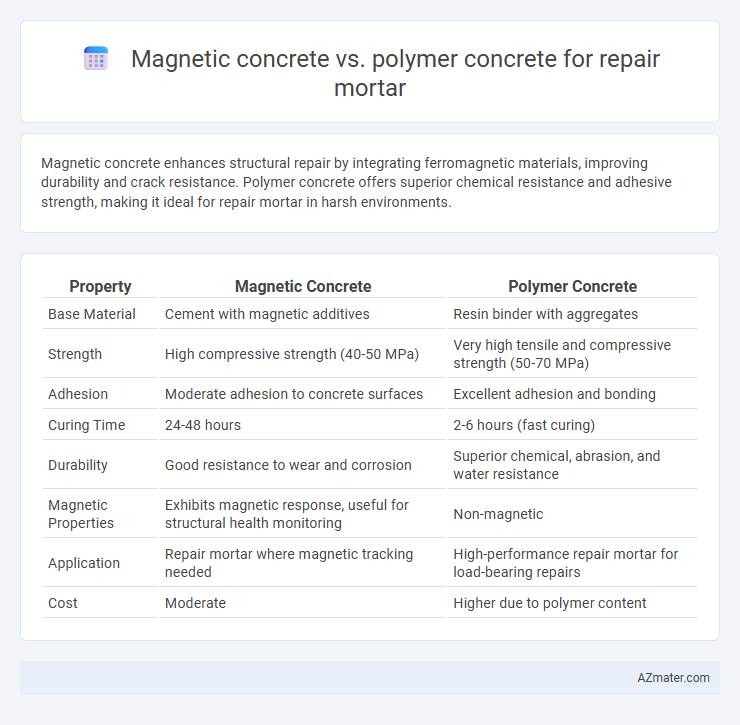
Magnetic concrete enhances structural repair by integrating ferromagnetic materials, improving durability and crack resistance. Polymer concrete offers superior chemical resistance and adhesive strength, making it ideal for repair mortar in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Magnetic Concrete | Polymer Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Base Material | Cement with magnetic additives | Resin binder with aggregates |
| Strength | High compressive strength (40-50 MPa) | Very high tensile and compressive strength (50-70 MPa) |
| Adhesion | Moderate adhesion to concrete surfaces | Excellent adhesion and bonding |
| Curing Time | 24-48 hours | 2-6 hours (fast curing) |
| Durability | Good resistance to wear and corrosion | Superior chemical, abrasion, and water resistance |
| Magnetic Properties | Exhibits magnetic response, useful for structural health monitoring | Non-magnetic |
| Application | Repair mortar where magnetic tracking needed | High-performance repair mortar for load-bearing repairs |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to polymer content |
Introduction to Repair Mortar: Magnetic vs Polymer Concrete
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic materials to enhance mechanical strength and enable self-sensing capabilities, making it ideal for structural health monitoring in repair mortar applications. Polymer concrete uses polymer resins as binders, offering superior chemical resistance and faster curing times, which improve durability and adhesion on deteriorated surfaces. Both materials provide distinct advantages in repair mortar, with magnetic concrete focusing on smart functionality and polymer concrete emphasizing resilient, rapid repairs.
Material Composition: Magnetic Concrete Explained
Magnetic concrete incorporates iron oxide and ferromagnetic particles within a standard cement matrix, enhancing its magnetic properties and mechanical strength for repair mortar applications. Polymer concrete replaces traditional cement with polymer binders such as epoxy or polyester, offering improved chemical resistance and adhesion but lacks magnetic features. The iron-rich composition in magnetic concrete enables unique functionalities like self-sensing and enhanced durability under dynamic loads, differentiating it from polymer-based repair mortars.
Material Composition: Polymer Concrete Overview
Polymer concrete consists of aggregates bound by a polymer resin, typically epoxy, polyester, or vinyl ester, providing superior adhesion and chemical resistance compared to traditional cementitious materials. Its composition allows for rapid curing, high tensile strength, and excellent durability in harsh environments, making it ideal for repair mortar applications that demand longevity and minimal maintenance. Unlike magnetic concrete, polymer concrete does not contain magnetic particles but excels in structural integrity and bonding with existing concrete surfaces.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Magnetic concrete exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to polymer concrete, including higher compressive strength and improved tensile resistance due to the incorporation of magnetic particles that enhance bonding and structural integrity. Polymer concrete offers excellent chemical resistance and flexibility but generally falls short in load-bearing capacity and durability under high-stress conditions. Studies indicate magnetic concrete's mechanical performance makes it more suitable for repair mortar applications requiring enhanced strength and longevity.
Durability and Long-Term Performance
Magnetic concrete exhibits enhanced durability through improved crack resistance and self-healing properties, making it ideal for long-term structural repair. Polymer concrete offers superior chemical resistance and strong adhesion to existing substrates, ensuring robust performance in corrosive environments. Both materials provide extended service life for repair mortar applications, but magnetic concrete excels in dynamic load conditions while polymer concrete is preferred for chemical durability.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Suitability
Magnetic concrete exhibits enhanced chemical resistance due to the incorporation of magnetic particles that improve impermeability and durability against acidic and alkaline substances, making it suitable for industrial repair applications. Polymer concrete offers superior environmental suitability, featuring high resistance to freeze-thaw cycles, UV radiation, and moisture ingress, which is ideal for outdoor or harsh climate repairs. Both materials provide strong repair mortar solutions, but polymer concrete excels in environmental adaptability while magnetic concrete offers enhanced chemical resilience.
Application Techniques and Workability
Magnetic concrete repair mortar requires precise application techniques, often involving specialized electromagnetic curing methods to enhance bonding and durability, which can be critical in infrastructure repairs exposed to heavy loads. Polymer concrete offers superior workability with excellent adhesion and rapid curing properties, making it ideal for patching and resurfacing in both vertical and horizontal applications. The workability of polymer concrete facilitates easier mixing and placement, while magnetic concrete demands more controlled handling to maintain its unique magnetic-induced structural benefits.
Cost Analysis: Magnetic Concrete vs Polymer Concrete
Magnetic concrete typically incurs higher initial costs due to the incorporation of magnetic particles and specialized materials, whereas polymer concrete demands premium resins and additives that elevate its price. Lifecycle expenses favor magnetic concrete by reducing maintenance frequency through enhanced durability and self-sensing capabilities, while polymer concrete may require more frequent repairs under harsh environmental conditions. Comprehensive cost analysis must weigh upfront investment against long-term performance, with magnetic concrete offering potential savings in structural health monitoring and extended service life.
Ideal Use Cases for Each Material
Magnetic concrete is ideal for repair mortar applications where enhanced structural bonding and electromagnetic shielding are required, making it suitable for infrastructure exposed to vibrations or electromagnetic interference. Polymer concrete excels in environments demanding high chemical resistance, fast curing times, and superior adhesion to existing surfaces, particularly in industrial flooring or corrosive settings. Selecting between magnetic and polymer concrete depends on specific project needs such as mechanical performance, cure speed, and environmental exposure conditions.
Future Trends and Research in Repair Mortars
Future trends in repair mortars emphasize the integration of magnetic concrete and polymer concrete to enhance durability and self-healing properties in infrastructure maintenance. Research is increasingly focused on the development of magnetically responsive nanoparticles within polymer concrete to improve crack detection and repair efficiency. Advanced formulations combining magnetic powders with polymer matrices demonstrate promising potential for smart repair mortars in critical construction and civil engineering applications.
Infographic: Magnetic concrete vs Polymer concrete for Repair mortar
 azmater.com
azmater.com