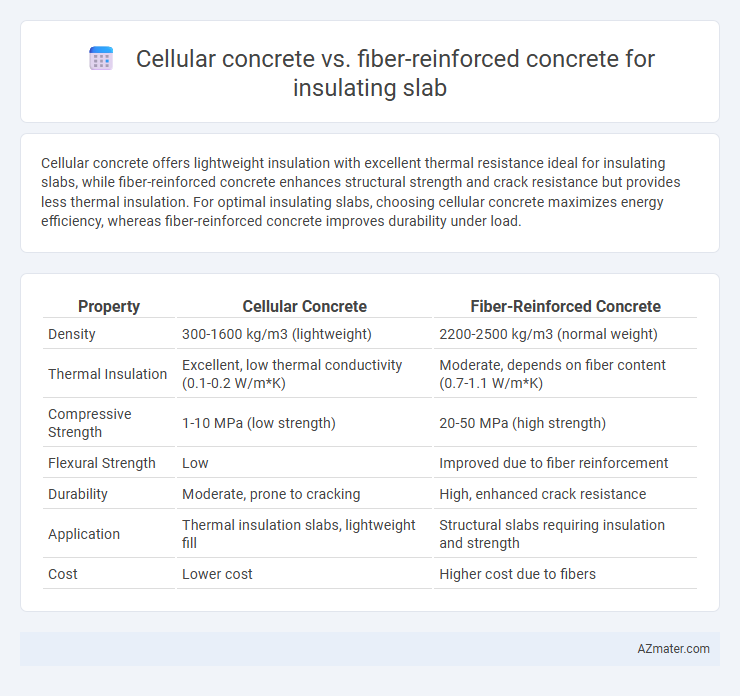
Cellular concrete offers lightweight insulation with excellent thermal resistance ideal for insulating slabs, while fiber-reinforced concrete enhances structural strength and crack resistance but provides less thermal insulation. For optimal insulating slabs, choosing cellular concrete maximizes energy efficiency, whereas fiber-reinforced concrete improves durability under load.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cellular Concrete | Fiber-Reinforced Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 300-1600 kg/m3 (lightweight) | 2200-2500 kg/m3 (normal weight) |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent, low thermal conductivity (0.1-0.2 W/m*K) | Moderate, depends on fiber content (0.7-1.1 W/m*K) |
| Compressive Strength | 1-10 MPa (low strength) | 20-50 MPa (high strength) |
| Flexural Strength | Low | Improved due to fiber reinforcement |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to cracking | High, enhanced crack resistance |
| Application | Thermal insulation slabs, lightweight fill | Structural slabs requiring insulation and strength |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to fibers |
Overview of Insulating Slab Materials
Cellular concrete and fiber-reinforced concrete are prominent insulating slab materials offering distinct thermal and structural advantages. Cellular concrete, characterized by its lightweight, porous structure with entrained air bubbles, provides excellent thermal insulation and fire resistance, making it suitable for energy-efficient slab applications. Fiber-reinforced concrete incorporates fibers such as steel, glass, or synthetic materials to enhance mechanical strength and crack resistance, while maintaining moderate insulation properties depending on the fiber type and matrix composition.
What is Cellular Concrete?
Cellular concrete is a lightweight insulating material composed of cement, water, and pre-formed foam that creates air-filled voids, reducing density and enhancing thermal insulation properties. Its porous structure provides excellent thermal resistance, making it highly effective for insulating slabs compared to traditional concrete types. This material also offers fire resistance and sound absorption, contributing to energy-efficient building designs.
Understanding Fiber-Reinforced Concrete
Fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) enhances insulating slabs by incorporating synthetic or steel fibers, which improve tensile strength, crack resistance, and durability compared to traditional cellular concrete. The fibers create a network that controls shrinkage and flexural stress, making FRC ideal for structural applications requiring higher load-bearing capacity alongside thermal insulation. This composite material balances insulation properties with enhanced mechanical performance, offering a versatile solution for energy-efficient building envelopes.
Material Composition Comparison
Cellular concrete consists of cement, water, and pre-formed foam that creates air bubbles, resulting in lightweight, highly insulating material with low thermal conductivity. Fiber-reinforced concrete incorporates fibrous materials such as glass, steel, or synthetic fibers into a traditional cement matrix to enhance tensile strength and crack resistance but offers comparatively lower insulation properties. The key material composition difference lies in cellular concrete's high air void content for thermal insulation versus fiber-reinforced concrete's embedded fibers aimed at structural performance improvement.
Thermal Insulation Capabilities
Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation due to its lightweight, porous structure, which significantly reduces heat transfer in insulating slabs. Fiber-reinforced concrete, while enhancing tensile strength and durability, provides limited improvement in thermal insulation compared to cellular concrete. For projects prioritizing energy efficiency and insulation performance, cellular concrete remains the optimal choice.
Strength and Structural Performance
Cellular concrete offers excellent thermal insulation with a lower compressive strength typically ranging between 3 to 8 MPa, making it suitable for non-load-bearing insulating slabs. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances structural performance by significantly improving tensile strength, crack resistance, and durability, achieving compressive strengths often exceeding 25 MPa, which supports load-bearing applications. For insulating slabs requiring a balance of moderate strength and thermal efficiency, fiber-reinforced concrete provides superior mechanical properties, while cellular concrete prioritizes insulation but with limited load capacity.
Durability and Longevity
Cellular concrete offers excellent thermal insulation with moderate durability due to its lightweight, aerated structure, making it suitable for non-load-bearing insulating slabs. Fiber-reinforced concrete significantly enhances durability and longevity through improved tensile strength and crack resistance, ideal for slabs exposed to mechanical stress and environmental wear. Selecting fiber-reinforced concrete ensures longer service life and reduced maintenance in insulating slab applications demanding structural resilience.
Installation and Workability
Cellular concrete offers superior workability due to its lightweight and flowable consistency, allowing easy pumping and placement in insulating slab applications. Fiber-reinforced concrete, while denser, requires more careful mixing and placing to ensure even fiber distribution and avoid clumping, which can affect the slab's uniformity and insulation performance. Installation of cellular concrete is faster and less labor-intensive, making it preferable for large-scale insulating slabs where speed and ease of handling are critical factors.
Cost Considerations
Cellular concrete typically offers lower initial costs for insulating slabs due to its lightweight and ease of installation, reducing labor and transportation expenses. Fiber-reinforced concrete, while more expensive upfront because of the added cost of fibers and mixing complexity, provides enhanced durability and crack resistance, potentially lowering long-term maintenance costs. Evaluating overall project budgets requires balancing cellular concrete's cost efficiency against fiber-reinforced concrete's superior structural performance and lifespan benefits.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation due to its lightweight, air-entrained structure, significantly reducing energy consumption in buildings and lowering carbon footprints compared to conventional materials. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances structural durability and reduces cracking, extending the lifespan of insulating slabs and minimizing resource consumption for repairs and replacements. Both materials contribute to sustainable construction; however, cellular concrete's lower embodied energy and better thermal performance make it a preferred choice for environmentally conscious insulating slab applications.
Infographic: Cellular concrete vs Fiber-reinforced concrete for Insulating slab
 azmater.com
azmater.com