Reactive powder concrete offers superior compressive strength and durability for industrial flooring, making it ideal for heavy-load applications. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances tensile strength and crack resistance, improving impact resistance and flexibility in industrial environments.
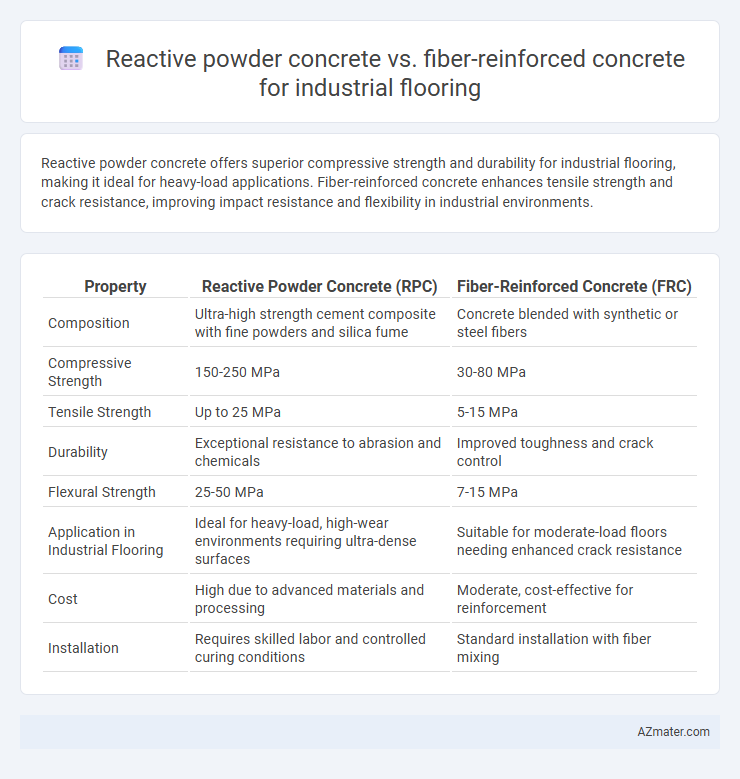
Table of Comparison
| Property | Reactive Powder Concrete (RPC) | Fiber-Reinforced Concrete (FRC) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Ultra-high strength cement composite with fine powders and silica fume | Concrete blended with synthetic or steel fibers |
| Compressive Strength | 150-250 MPa | 30-80 MPa |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 25 MPa | 5-15 MPa |
| Durability | Exceptional resistance to abrasion and chemicals | Improved toughness and crack control |
| Flexural Strength | 25-50 MPa | 7-15 MPa |
| Application in Industrial Flooring | Ideal for heavy-load, high-wear environments requiring ultra-dense surfaces | Suitable for moderate-load floors needing enhanced crack resistance |
| Cost | High due to advanced materials and processing | Moderate, cost-effective for reinforcement |
| Installation | Requires skilled labor and controlled curing conditions | Standard installation with fiber mixing |
Introduction to Advanced Concrete Technologies
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) offers superior compressive strength up to 200 MPa and exceptional durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty industrial flooring exposed to intense wear and chemical attacks. Fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) improves tensile strength and crack resistance through the addition of steel, glass, or synthetic fibers, enhancing impact resistance and reducing maintenance costs in industrial environments. Both advanced concrete technologies extend service life and performance, with RPC emphasizing high density and microstructure refinement, while FRC focuses on toughness and flexibility.
Key Properties of Reactive Powder Concrete (RPC)
Reactive Powder Concrete (RPC) exhibits exceptional compressive strength exceeding 200 MPa, significantly outperforming Fiber-Reinforced Concrete (FRC) in load-bearing capacity for industrial flooring. Its ultra-high density and low porosity enhance durability and resistance to chemical attack, making it ideal for harsh industrial environments. The fine particle packing and optimized mix design result in superior abrasion resistance and minimal shrinkage, critical properties that ensure long-term performance and reduced maintenance.
Overview of Fiber-Reinforced Concrete (FRC)
Fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) enhances industrial flooring durability by incorporating various fibers such as steel, glass, or synthetic polymers to improve tensile strength, crack resistance, and impact toughness. This composite material addresses common flooring challenges like shrinkage cracking and surface wear, providing superior performance in heavy traffic and harsh environments. FRC's improved load distribution and resistance to thermal and chemical stresses make it a preferred choice over conventional concrete in industrial applications.
Comparative Mechanical Strength: RPC vs FRC
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) exhibits higher compressive strength, often exceeding 200 MPa, compared to fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC), which typically ranges between 40 to 80 MPa depending on fiber type and dosage. RPC's ultra-fine particles and optimized mix design contribute to superior durability and wear resistance, making it ideal for heavy industrial flooring subjected to intense mechanical loads. In contrast, FRC offers enhanced tensile strength and crack control due to fiber inclusion, improving impact resistance and flexural performance, but it generally cannot match RPC's exceptional compressive capabilities.
Durability and Wear Resistance in Industrial Flooring
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) exhibits superior durability and wear resistance for industrial flooring due to its ultra-high compressive strength and dense microstructure, minimizing porosity and surface wear. Fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) enhances tensile strength and crack resistance through the integration of steel or synthetic fibers, improving impact resistance and toughness under heavy industrial loads. Both materials provide long-lasting flooring solutions, but RPC offers exceptional surface hardness and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for high-traffic, heavy-wear industrial environments.
Flexural and Impact Performance
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) exhibits superior flexural strength and impact resistance compared to traditional fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC), making it ideal for industrial flooring subjected to heavy dynamic loads. The ultra-high compressive strength and dense microstructure of RPC enhance durability and crack resistance, improving long-term performance under repeated impact stresses. While FRC offers improved toughness and post-crack behavior due to fiber dispersion, RPC's optimized particle packing and steel microfibers deliver exceptional flexural modulus and impact energy absorption for demanding industrial environments.
Installation Techniques and Workability
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) offers superior strength and durability for industrial flooring but requires precise mixing, pressing, and heat treatment during installation to achieve optimal performance, demanding skilled labor and controlled conditions. Fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) improves workability with enhanced crack resistance and easier placement due to the distribution of synthetic or steel fibers, allowing for faster, less labor-intensive installation on large surfaces. Both materials provide high performance, but RPC's complex curing process contrasts with FRC's straightforward mixing and finishing techniques, affecting project timelines and labor costs.
Cost Analysis: Material and Lifecycle Expenses
Reactive powder concrete typically has higher initial material costs due to its fine powders and special additives but offers superior compressive strength and durability, leading to reduced maintenance expenses over its lifecycle. Fiber-reinforced concrete incurs moderate material costs by incorporating various fiber types such as steel, synthetic, or glass fibers that improve tensile strength and crack resistance, potentially lowering repair costs in industrial flooring applications. Lifecycle expenses for reactive powder concrete can be lower overall when factoring in its enhanced wear resistance and longevity, while fiber-reinforced concrete provides cost-effective performance where moderate durability is sufficient.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) offers superior durability and reduced material usage, leading to lower carbon emissions in industrial flooring applications compared to traditional concretes. Fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) enhances crack resistance and extends service life, minimizing maintenance frequency and resource consumption, contributing positively to sustainability. Both materials improve industrial flooring resilience, but RPC's dense microstructure provides greater long-term environmental benefits through enhanced energy efficiency and reduced raw material extraction.
Choosing the Best Solution for Industrial Flooring Applications
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) offers exceptional compressive strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy-load industrial flooring where high wear resistance is critical, while fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) enhances tensile strength and crack control, improving impact resistance and toughness for dynamic industrial environments. Selecting the best solution depends on specific industrial flooring requirements, with RPC favored for maximum structural performance and FRC preferred for flexibility and reduced maintenance costs. The decision should consider factors such as load intensity, exposure conditions, installation complexity, and long-term maintenance to optimize performance and cost-efficiency.
Infographic: Reactive powder concrete vs Fiber-reinforced concrete for Industrial flooring
 azmater.com
azmater.com