Polymer-modified concrete enhances adhesion, flexibility, and durability, making it ideal for repair mortar in dynamic or crack-prone environments. Rapid-hardening concrete provides fast strength gain within hours, suitable for urgent repairs requiring early load application.
Table of Comparison
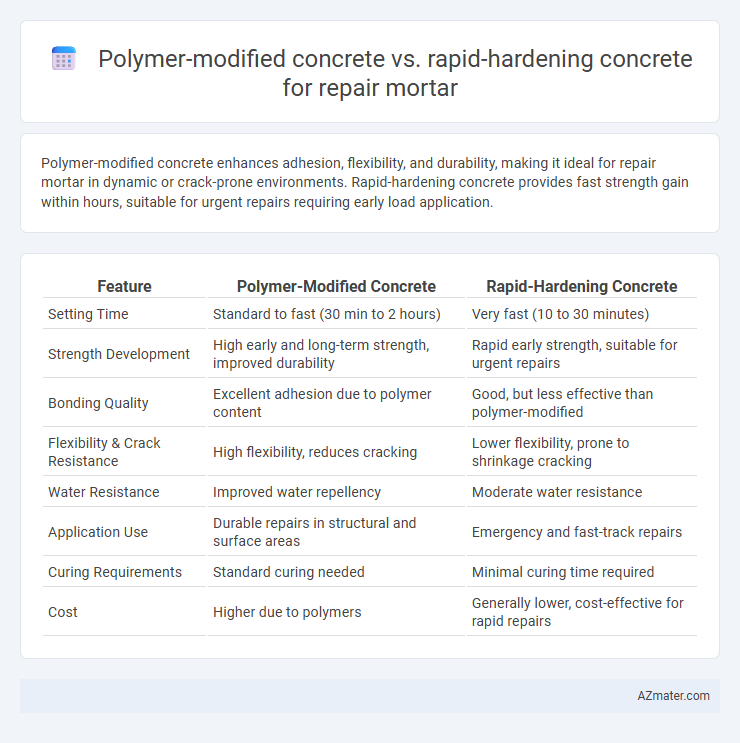
| Feature | Polymer-Modified Concrete | Rapid-Hardening Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Setting Time | Standard to fast (30 min to 2 hours) | Very fast (10 to 30 minutes) |
| Strength Development | High early and long-term strength, improved durability | Rapid early strength, suitable for urgent repairs |
| Bonding Quality | Excellent adhesion due to polymer content | Good, but less effective than polymer-modified |
| Flexibility & Crack Resistance | High flexibility, reduces cracking | Lower flexibility, prone to shrinkage cracking |
| Water Resistance | Improved water repellency | Moderate water resistance |
| Application Use | Durable repairs in structural and surface areas | Emergency and fast-track repairs |
| Curing Requirements | Standard curing needed | Minimal curing time required |
| Cost | Higher due to polymers | Generally lower, cost-effective for rapid repairs |
Introduction to Repair Mortars
Repair mortars are specialized materials designed to restore the integrity and durability of damaged concrete structures. Polymer-modified concrete enhances adhesion, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals by incorporating polymers, making it ideal for durable repairs in dynamic environments. Rapid-hardening concrete offers fast strength development and early load-bearing capacity, suitable for urgent repairs requiring quick turnaround times.
Overview of Polymer-Modified Concrete
Polymer-modified concrete (PMC) enhances traditional concrete by incorporating polymers such as acrylics, styrene-butadiene rubber, or epoxy, improving adhesion, flexibility, and resistance to cracking. PMC exhibits superior bond strength to existing substrates, increased durability against chemical attacks, and reduced permeability compared to conventional concrete. These properties make polymer-modified concrete ideal for structural repair mortars requiring long-term performance and resistance to environmental stressors.
Understanding Rapid-Hardening Concrete
Rapid-hardening concrete is engineered with special cement types and admixtures that accelerate its setting and strength gain, enabling it to reach high compressive strength within hours. This characteristic is crucial for repair mortar applications where minimizing downtime and restoring structural integrity quickly is essential. Compared to polymer-modified concrete, rapid-hardening concrete offers faster load-bearing capacity but may have reduced flexibility and crack resistance, impacting performance in dynamic or high-stress environments.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Polymer-modified concrete exhibits enhanced adhesion, flexibility, and chemical resistance due to the incorporation of polymer resins, making it ideal for durable repair mortar applications subject to dynamic loads and environmental exposure. Rapid-hardening concrete achieves significantly faster compressive strength gain, often reaching over 20 MPa within hours, which is crucial for emergency repairs requiring quick return to service. While polymer-modified concrete offers improved durability and crack resistance, rapid-hardening concrete provides superior early strength development, necessitating selection based on project-specific performance criteria such as curing time and mechanical demands.
Setting Time and Workability
Polymer-modified concrete exhibits enhanced workability due to the incorporation of polymers, allowing for improved adhesion and flexibility in repair mortar applications, while its setting time can be adjusted to moderate durations based on polymer type. Rapid-hardening concrete features significantly accelerated setting times, often achieving initial set within 30 minutes to 2 hours, making it ideal for urgent repairs requiring fast strength gain but potentially reducing workability window. Choosing between the two depends on balancing the need for quick setting in emergency repairs with the enhanced durability and ease of application offered by polymer-modified concrete.
Bond Strength and Adhesion Performance
Polymer-modified concrete exhibits superior bond strength and adhesion performance compared to rapid-hardening concrete, primarily due to the incorporation of polymer additives that enhance flexibility and reduce shrinkage. Rapid-hardening concrete achieves its strength quickly but often lacks the durability and adhesion necessary for long-term repair applications. The improved interfacial bonding of polymer-modified concrete ensures better resistance to environmental stresses and mechanical loading in repair mortar contexts.
Durability and Long-Term Performance
Polymer-modified concrete enhances durability and long-term performance in repair mortars by improving adhesion, reducing permeability, and providing superior resistance to chemical attacks and freeze-thaw cycles. Rapid-hardening concrete offers quicker strength gain but may be more susceptible to shrinkage and cracking over time, potentially compromising its durability in aggressive environments. Selecting polymer-modified concrete for repair mortars ensures greater longevity and sustained structural integrity in demanding conditions.
Resistance to Chemical and Environmental Factors
Polymer-modified concrete offers superior resistance to chemical attacks such as sulfates, chlorides, and acids due to its enhanced impermeability and adhesion properties, making it ideal for repair mortar applications exposed to harsh environments. Rapid-hardening concrete provides faster strength gain but generally exhibits lower long-term resistance to chemical and environmental degradation compared to polymer-modified alternatives. For durable repair mortar, polymer-modified concrete ensures extended service life by effectively mitigating damage from aggressive substances and fluctuating weather conditions.
Cost Analysis and Application Scenarios
Polymer-modified concrete offers enhanced adhesion and durability at a higher initial cost compared to rapid-hardening concrete, which is more cost-effective for urgent repairs requiring quick strength gain. Polymer-modified variants are ideal for structural repairs in aggressive environments where long-term performance justifies the investment, while rapid-hardening concrete suits time-sensitive applications like emergency patching or cold-weather repairs. Cost analysis reveals that despite the premium price, polymer-modified concrete reduces lifecycle expenses through superior resistance to cracking and chemical attack, whereas rapid-hardening mixes minimize downtime and labor costs in fast-track projects.
Selecting the Right Repair Mortar: Polymer vs Rapid-Hardening
Polymer-modified concrete offers enhanced adhesion, flexibility, and durability, making it ideal for structural repairs exposed to dynamic loads or moisture. Rapid-hardening concrete excels in applications requiring quick turnaround times and early strength gain, such as emergency repairs and fast reopening of infrastructure. Selecting the right repair mortar depends on project-specific requirements, including setting time, environmental conditions, and desired mechanical properties.
Infographic: Polymer-modified concrete vs Rapid-hardening concrete for Repair mortar
 azmater.com
azmater.com