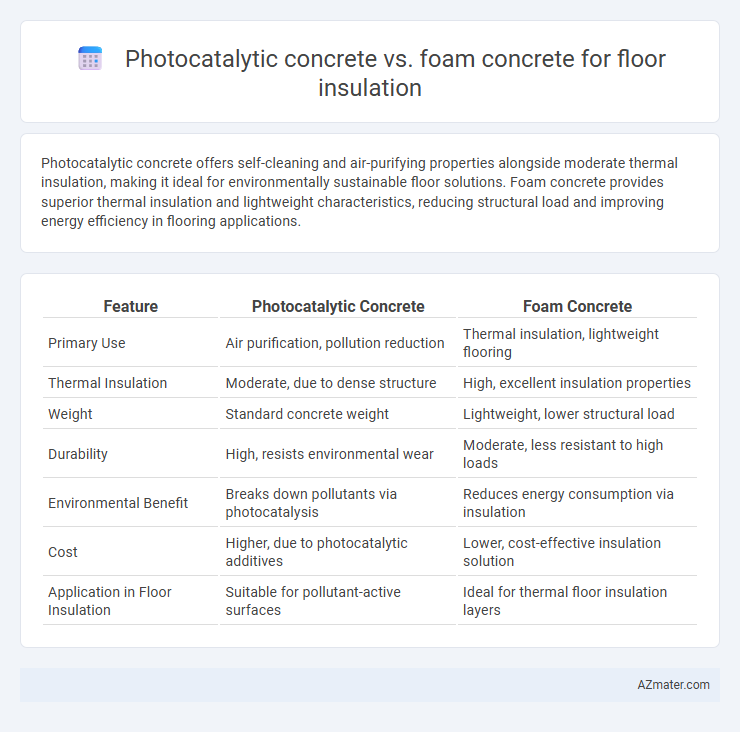
Photocatalytic concrete offers self-cleaning and air-purifying properties alongside moderate thermal insulation, making it ideal for environmentally sustainable floor solutions. Foam concrete provides superior thermal insulation and lightweight characteristics, reducing structural load and improving energy efficiency in flooring applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Photocatalytic Concrete | Foam Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Air purification, pollution reduction | Thermal insulation, lightweight flooring |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate, due to dense structure | High, excellent insulation properties |
| Weight | Standard concrete weight | Lightweight, lower structural load |
| Durability | High, resists environmental wear | Moderate, less resistant to high loads |
| Environmental Benefit | Breaks down pollutants via photocatalysis | Reduces energy consumption via insulation |
| Cost | Higher, due to photocatalytic additives | Lower, cost-effective insulation solution |
| Application in Floor Insulation | Suitable for pollutant-active surfaces | Ideal for thermal floor insulation layers |
Introduction to Innovative Concrete Materials
Photocatalytic concrete incorporates titanium dioxide nanoparticles that actively reduce air pollutants by triggering chemical reactions under sunlight, enhancing environmental sustainability in urban flooring. Foam concrete, characterized by its lightweight cellular structure with entrapped air bubbles, provides superior thermal insulation and sound absorption, making it ideal for energy-efficient building floors. Both materials represent innovative advancements in concrete technology, targeting improved environmental impact and enhanced insulation performance in modern construction practices.
Overview of Photocatalytic Concrete
Photocatalytic concrete incorporates titanium dioxide nanoparticles that activate under UV light to break down pollutants and reduce harmful emissions, offering an eco-friendly solution for floor insulation. This type of concrete also exhibits self-cleaning properties, minimizing maintenance while enhancing durability and air quality within indoor environments. Its innovative photocatalytic reaction not only insulates effectively but also contributes to sustainable building practices by improving urban pollution control.
Understanding Foam Concrete for Floor Insulation
Foam concrete offers excellent thermal insulation due to its lightweight and porous structure, making it ideal for floor insulation in both residential and commercial buildings. Its low density reduces heat transfer while providing sound absorption and fire resistance properties. Compared to photocatalytic concrete, foam concrete is more effective in insulating floors but lacks the self-cleaning and air-purifying benefits brought by photocatalytic additives.
Thermal Insulation Properties: Photocatalytic vs Foam Concrete
Photocatalytic concrete enhances thermal insulation through its porous surface that facilitates air circulation and reduces heat absorption, leveraging titanium dioxide's self-cleaning and UV-resistant properties to maintain insulation efficiency over time. Foam concrete provides superior thermal insulation due to its lightweight, aerated structure filled with air bubbles that significantly reduce heat transfer and improve energy efficiency in flooring applications. While foam concrete excels in consistent thermal insulation performance, photocatalytic concrete offers the added benefit of maintaining thermal properties alongside environmental purification and durability.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Photocatalytic concrete enhances energy efficiency by reducing surface pollutants and lowering urban heat island effects through its self-cleaning and air-purifying properties, contributing to cooler building environments and decreased cooling demands. Foam concrete offers superior thermal insulation due to its lightweight, porous structure, significantly reducing heat transfer and energy consumption for heating and cooling in floors. Environmentally, photocatalytic concrete promotes air quality and longevity with minimal maintenance, while foam concrete lowers material usage and energy costs during production, making both options sustainable but suited for different energy-saving priorities in floor insulation.
Durability and Longevity in Floor Applications
Photocatalytic concrete offers enhanced durability with its self-cleaning and pollutant-degrading properties, reducing surface wear and extending lifespan in floor applications. Foam concrete provides excellent insulation but may have lower compressive strength and long-term durability compared to photocatalytic options. For floor insulation, photocatalytic concrete ensures prolonged performance under heavy use, while foam concrete primarily benefits thermal insulation with moderate longevity.
Cost Comparison: Installation and Maintenance
Photocatalytic concrete for floor insulation typically incurs higher initial installation costs due to advanced material composition and specialized application processes, whereas foam concrete offers a more economical installation with quicker curing times. Maintenance expenses for photocatalytic concrete tend to be lower over time because of its self-cleaning properties and resistance to pollutants, reducing the need for frequent cleaning and repairs. Foam concrete requires periodic inspection and potential sealing to maintain insulating effectiveness, which can increase cumulative maintenance costs despite its lower upfront price.
Mold Resistance and Indoor Air Quality
Photocatalytic concrete enhances mold resistance by breaking down organic contaminants and preventing microbial growth on floor surfaces, thus maintaining superior indoor air quality. Foam concrete, while providing good thermal insulation, is more prone to moisture retention, which can promote mold development and compromise indoor air quality. Selecting photocatalytic concrete for floor insulation ensures both effective mold inhibition and improved air purity in indoor environments.
Suitability for Residential and Commercial Projects
Photocatalytic concrete offers superior durability and self-cleaning properties, making it highly suitable for commercial projects with high foot traffic and pollution exposure. Foam concrete provides excellent thermal insulation and lightweight characteristics, ideal for residential applications where energy efficiency and ease of installation are prioritized. Both materials enhance floor insulation, but foam concrete is generally preferred for homes due to its cost-effectiveness and thermal performance, while photocatalytic concrete excels in commercial environments requiring long-term maintenance reduction.
Final Recommendations and Best Use Cases
Photocatalytic concrete offers superior air purification and self-cleaning properties, making it ideal for urban floors exposed to heavy pollution and pedestrian traffic. Foam concrete provides excellent thermal insulation and lightweight characteristics, suited for subfloor applications and buildings prioritizing energy efficiency. Final recommendations suggest photocatalytic concrete for outdoor walkways and public spaces, while foam concrete is best for indoor insulation where thermal performance is critical.
Infographic: Photocatalytic concrete vs Foam concrete for Floor insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com