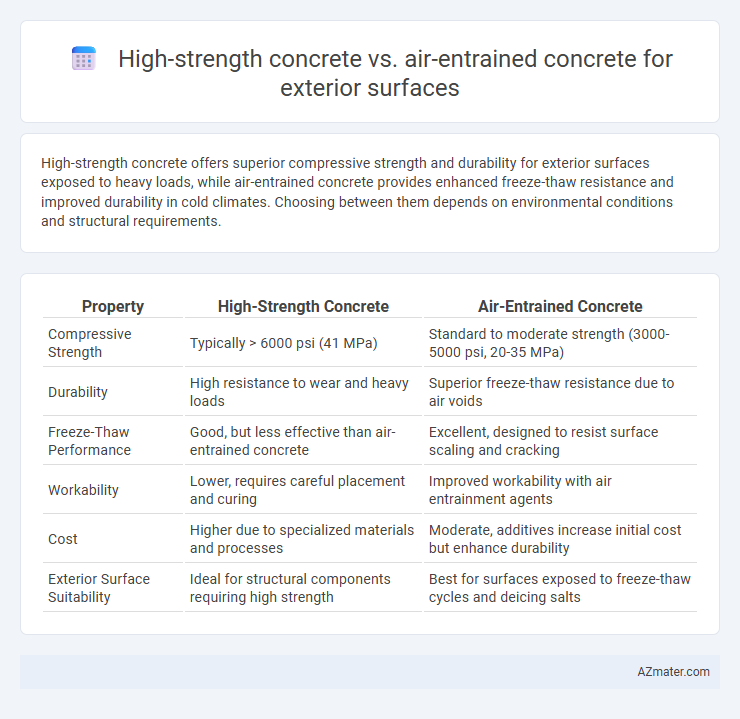
High-strength concrete offers superior compressive strength and durability for exterior surfaces exposed to heavy loads, while air-entrained concrete provides enhanced freeze-thaw resistance and improved durability in cold climates. Choosing between them depends on environmental conditions and structural requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | High-Strength Concrete | Air-Entrained Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Compressive Strength | Typically > 6000 psi (41 MPa) | Standard to moderate strength (3000-5000 psi, 20-35 MPa) |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and heavy loads | Superior freeze-thaw resistance due to air voids |
| Freeze-Thaw Performance | Good, but less effective than air-entrained concrete | Excellent, designed to resist surface scaling and cracking |
| Workability | Lower, requires careful placement and curing | Improved workability with air entrainment agents |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized materials and processes | Moderate, additives increase initial cost but enhance durability |
| Exterior Surface Suitability | Ideal for structural components requiring high strength | Best for surfaces exposed to freeze-thaw cycles and deicing salts |
Introduction to High-Strength and Air-Entrained Concrete
High-strength concrete features a compressive strength typically exceeding 6,000 psi, making it ideal for exterior surfaces requiring enhanced durability and load-bearing capacity. Air-entrained concrete contains microscopic air bubbles that improve freeze-thaw resistance, crucial for exterior applications exposed to harsh weather conditions. Selecting between these concretes depends on structural demands and environmental exposure, emphasizing performance characteristics like strength or durability against climate-induced stresses.
Key Material Properties: Strength vs Durability
High-strength concrete exhibits superior compressive strength, often exceeding 6,000 psi, making it ideal for structural applications requiring load-bearing capacity. Air-entrained concrete enhances durability by incorporating microscopic air bubbles that improve freeze-thaw resistance and reduce permeability, essential for exterior surfaces exposed to harsh weather conditions. While high-strength concrete prioritizes strength, air-entrained concrete balances moderate strength with enhanced durability against environmental stressors.
Climate Considerations for Exterior Surfaces
High-strength concrete offers superior durability and compressive strength, making it ideal for exterior surfaces exposed to heavy loads and harsh environmental conditions. Air-entrained concrete enhances freeze-thaw resistance by incorporating microscopic air bubbles that prevent cracking in climates with frequent temperature fluctuations and moisture exposure. For cold or wet climates, air-entrained concrete provides better protection against frost damage, while high-strength concrete suits hotter, drier regions requiring structural resilience and long-term performance.
Resistance to Freeze-Thaw Cycles
High-strength concrete offers superior compressive strength but often lacks adequate freeze-thaw resistance due to its dense microstructure that can trap water, leading to internal damage during freeze-thaw cycles. Air-entrained concrete is specifically designed with microscopic air pockets that act as pressure relief zones, significantly enhancing durability and resistance to freeze-thaw damage on exterior surfaces. For environments with severe freeze-thaw exposure, air-entrained concrete provides a more reliable solution in preventing cracking and surface scaling.
Workability and Ease of Placement
High-strength concrete offers superior compressive strength but often exhibits lower workability, making placement on exterior surfaces more challenging without specialized admixtures or techniques. Air-entrained concrete improves workability and ease of placement by incorporating microscopic air bubbles that enhance flow and resistance to freeze-thaw cycles. For exterior applications, air-entrained concrete is generally preferred when ease of placement and durability against weathering are critical factors.
Performance in Heavy Traffic or Load-Bearing Areas
High-strength concrete offers superior compressive strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy traffic or load-bearing exterior surfaces where resistance to mechanical stress is critical. Air-entrained concrete enhances freeze-thaw resistance through microscopic air bubbles, reducing surface scaling but typically exhibits lower compressive strength compared to high-strength mixes. For exterior pavements subjected to intense loading, high-strength concrete provides better long-term structural integrity, while air-entrained concrete is preferred in climates with frequent freeze-thaw cycles to prevent surface deterioration.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Lifecycle Costs
High-strength concrete offers a higher initial cost due to specialized materials and mixing processes, but its durability reduces maintenance expenses and extends lifecycle, resulting in lower long-term costs for exterior surfaces. Air-entrained concrete has a comparatively lower upfront cost but may incur higher lifecycle costs owing to potential freeze-thaw damage and required repairs in harsh weather conditions. Evaluating total ownership costs reveals that high-strength concrete provides greater cost efficiency for exterior applications exposed to extreme environmental stress.
Maintenance and Longevity of Exterior Concrete
High-strength concrete offers superior compressive strength and durability, enabling it to withstand heavy loads and resist abrasion on exterior surfaces, which reduces maintenance frequency and extends service life. Air-entrained concrete contains microscopic air bubbles that improve freeze-thaw resistance, minimizing cracking and scaling in cold climates, thereby enhancing longevity and reducing repair costs. Choosing between the two depends on environmental conditions and specific performance requirements, with air-entrained concrete preferred in freeze-prone areas and high-strength concrete suitable for high-stress exterior applications.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
High-strength concrete offers increased durability and reduced material usage, leading to lower carbon emissions over its lifecycle, making it a sustainable choice for exterior surfaces. Air-entrained concrete enhances freeze-thaw resistance, reducing maintenance and repair needs in cold climates, which contributes to environmental conservation through extended service life. Selecting either type depends on local environmental conditions and sustainability goals, with high-strength concrete favoring structural efficiency and air-entrained concrete supporting resilience in harsh weather.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Your Exterior Project
High-strength concrete offers superior compressive strength ideal for load-bearing exterior surfaces requiring enhanced durability and resistance to heavy traffic or structural stress. Air-entrained concrete provides excellent freeze-thaw resistance by incorporating microscopic air bubbles that improve durability in cold climates, making it suitable for exterior surfaces exposed to frequent temperature fluctuations. Choosing the right concrete depends on project-specific factors such as exposure to mechanical loads versus climatic conditions, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the exterior surface.
Infographic: High-strength concrete vs Air-entrained concrete for Exterior surface
 azmater.com
azmater.com