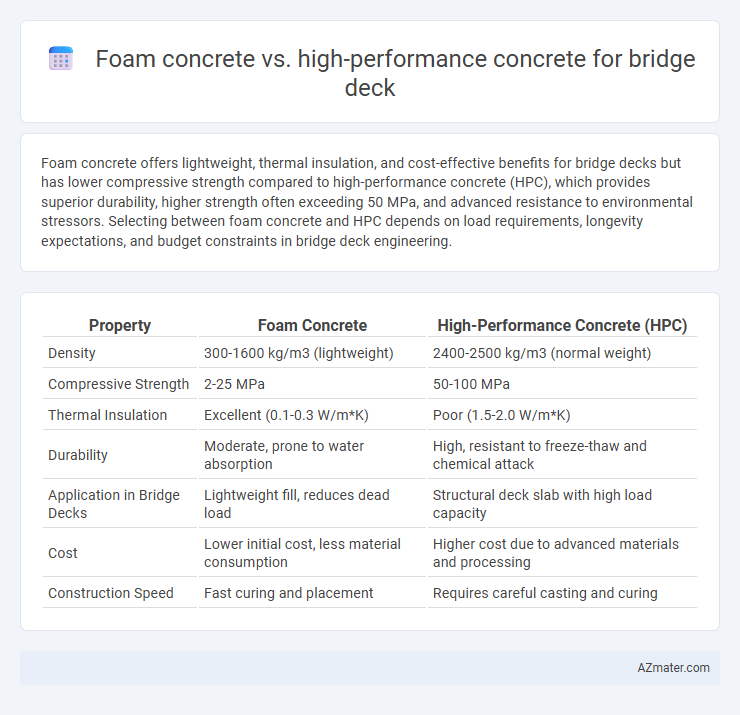
Foam concrete offers lightweight, thermal insulation, and cost-effective benefits for bridge decks but has lower compressive strength compared to high-performance concrete (HPC), which provides superior durability, higher strength often exceeding 50 MPa, and advanced resistance to environmental stressors. Selecting between foam concrete and HPC depends on load requirements, longevity expectations, and budget constraints in bridge deck engineering.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Foam Concrete | High-Performance Concrete (HPC) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 300-1600 kg/m3 (lightweight) | 2400-2500 kg/m3 (normal weight) |
| Compressive Strength | 2-25 MPa | 50-100 MPa |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent (0.1-0.3 W/m*K) | Poor (1.5-2.0 W/m*K) |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to water absorption | High, resistant to freeze-thaw and chemical attack |
| Application in Bridge Decks | Lightweight fill, reduces dead load | Structural deck slab with high load capacity |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, less material consumption | Higher cost due to advanced materials and processing |
| Construction Speed | Fast curing and placement | Requires careful casting and curing |
Introduction to Bridge Deck Materials
Bridge deck materials significantly influence durability, load capacity, and maintenance frequency of bridges. Foam concrete offers lightweight properties and excellent thermal insulation, reducing dead loads on bridge structures and enhancing energy efficiency. High-performance concrete provides superior strength, durability, and resistance to environmental stressors, making it ideal for heavy traffic loads and harsh climates in bridge deck applications.
Overview of Foam Concrete
Foam concrete is a lightweight, aerated material composed of cement, water, and pre-formed foam, offering excellent thermal insulation and reduced self-weight for bridge decks. Its low density ranges from 400 to 1600 kg/m3, significantly decreasing dead loads on bridge structures compared to traditional concretes. This material provides good workability and rapid installation, enhancing construction efficiency while maintaining adequate compressive strength for non-structural bridge deck layers.
Overview of High-Performance Concrete
High-performance concrete (HPC) used in bridge decks exhibits superior strength, durability, and resistance to environmental stressors compared to traditional mix designs. HPC's optimized mix includes supplementary cementitious materials, low water-cement ratio, and chemical admixtures, enhancing its flexural and compressive strength essential for heavy traffic loads. This advanced concrete type significantly minimizes permeability and improves freeze-thaw resistance, extending the lifespan and reducing maintenance costs of bridge structures.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Foam concrete exhibits low density and excellent thermal insulation, making it lightweight and reducing dead load on bridge decks, while high-performance concrete (HPC) offers superior compressive strength, durability, and resistance to freeze-thaw cycles critical for structural integrity. HPC typically achieves compressive strengths above 50 MPa with low permeability, enhancing longevity and load-bearing capacity, whereas foam concrete's high porosity results in lower strength but improved crack resistance and energy absorption. The choice depends on balancing structural demands with weight reduction and thermal management, where HPC suits high-stress applications and foam concrete benefits decks requiring lightweight and insulating properties.
Structural Performance in Bridge Decks
Foam concrete exhibits lower density and reduced compressive strength compared to high-performance concrete (HPC), making HPC more suitable for bridge decks requiring superior load-bearing capacity and durability. HPC offers enhanced toughness, superior abrasion resistance, and improved fatigue performance, which are critical for withstanding repeated traffic loads and environmental stressors. The optimized mix design of HPC results in higher modulus of elasticity and reduced permeability, directly contributing to the long-term structural integrity and reduced maintenance of bridge decks.
Durability and Longevity
Foam concrete offers enhanced durability for bridge decks due to its lightweight and high thermal insulation properties, reducing stress and cracking over time. High-performance concrete (HPC) exhibits superior strength, resistance to chemical attack, and low permeability, significantly extending the lifespan of bridge decks in harsh environments. The longevity of HPC surpasses foam concrete when subjected to heavy traffic loads and aggressive weather conditions, making it the preferred material for critical infrastructure requiring maximum durability.
Weight and Load Considerations
Foam concrete offers significant weight reduction compared to traditional High-performance concrete, making it ideal for bridge decks where minimizing dead load is critical. High-performance concrete provides superior compressive strength and durability, supporting heavier traffic loads while withstanding harsh environmental conditions. Selecting between the two depends on balancing the need for lightweight materials to reduce structural load and the demand for high strength to ensure longevity and safety.
Cost Analysis and Economic Factors
Foam concrete offers significant cost savings for bridge decks due to its lightweight nature, reducing foundation and transportation expenses compared to traditional high-performance concrete (HPC). While HPC ensures superior durability and strength, its higher material and labor costs can impact overall project budgets, making foam concrete a more economical choice for non-critical load-bearing applications. Evaluating lifecycle costs, including maintenance and longevity, is crucial, as HPC may provide better long-term economic benefits despite higher initial investments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Foam concrete offers significant environmental benefits for bridge decks due to its reduced density and lower cement content, resulting in decreased carbon emissions during production compared to high-performance concrete (HPC). HPC provides superior durability and strength, extending the lifespan of bridge decks and minimizing the frequency of repairs and replacements, thereby reducing long-term environmental impact. Selecting foam concrete enhances sustainability through lightweight construction and resource efficiency, while HPC supports sustainability by improving structural resilience and lifecycle performance.
Best Applications and Recommendations
Foam concrete, characterized by its lightweight and excellent thermal insulation, is best suited for bridge deck applications requiring reduced structural load and enhanced insulation properties, such as pedestrian bridges or secondary roadways. High-performance concrete (HPC), known for its superior durability, high compressive strength, and resistance to environmental stresses, is ideal for primary bridge decks exposed to heavy traffic and harsh conditions. For optimal long-term performance, foam concrete is recommended where weight reduction is critical, while HPC should be selected for high-load-bearing bridge decks demanding maximum strength and durability.
Infographic: Foam concrete vs High-performance concrete for Bridge deck
 azmater.com
azmater.com