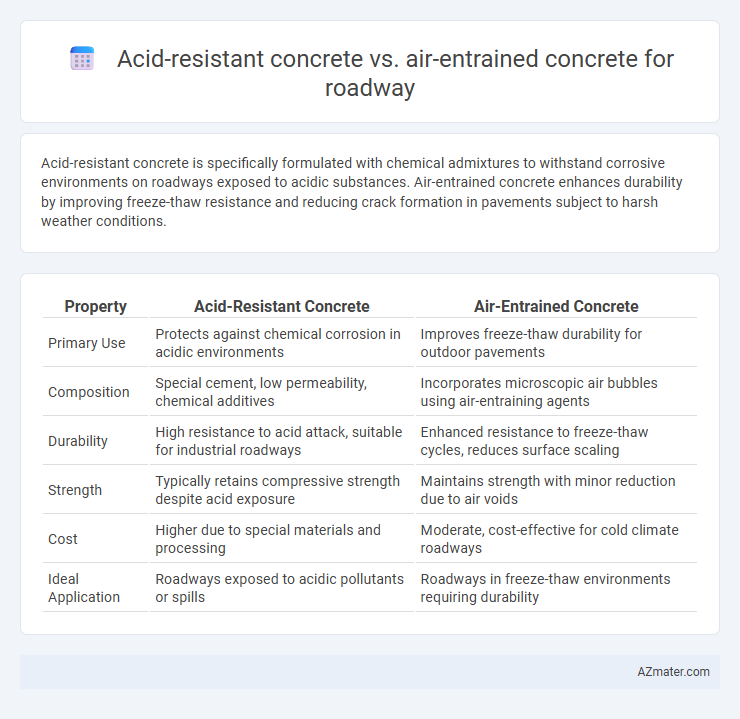
Acid-resistant concrete is specifically formulated with chemical admixtures to withstand corrosive environments on roadways exposed to acidic substances. Air-entrained concrete enhances durability by improving freeze-thaw resistance and reducing crack formation in pavements subject to harsh weather conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acid-Resistant Concrete | Air-Entrained Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Protects against chemical corrosion in acidic environments | Improves freeze-thaw durability for outdoor pavements |
| Composition | Special cement, low permeability, chemical additives | Incorporates microscopic air bubbles using air-entraining agents |
| Durability | High resistance to acid attack, suitable for industrial roadways | Enhanced resistance to freeze-thaw cycles, reduces surface scaling |
| Strength | Typically retains compressive strength despite acid exposure | Maintains strength with minor reduction due to air voids |
| Cost | Higher due to special materials and processing | Moderate, cost-effective for cold climate roadways |
| Ideal Application | Roadways exposed to acidic pollutants or spills | Roadways in freeze-thaw environments requiring durability |
Introduction to Specialty Concrete for Roadways
Acid-resistant concrete incorporates chemical-resistant aggregates and binders designed to withstand harsh acidic environments, making it ideal for roadways exposed to industrial pollutants or chemical spills. Air-entrained concrete contains microscopic air bubbles that improve freeze-thaw durability and resistance to deicing salts, enhancing longevity in cold climates. Choosing between acid-resistant and air-entrained concrete depends on specific environmental exposures and roadway conditions requiring specialty performance characteristics.
Key Properties of Acid-Resistant Concrete
Acid-resistant concrete is designed with low permeability and enhanced chemical stability using specialized cement and aggregates to withstand harsh acidic environments often encountered in industrial roadways. It features high-density microstructure and incorporates additives such as silica fume or polymer modifiers, significantly improving resistance to acid attack and increasing durability. Unlike air-entrained concrete, which primarily enhances freeze-thaw resistance through microscopic air bubbles, acid-resistant concrete prioritizes chemical resistance, making it essential for road surfaces exposed to sulfate or chemical corrosion.
Key Properties of Air-Entrained Concrete
Air-entrained concrete contains microscopic air bubbles that enhance its freeze-thaw durability and resistance to scaling, making it ideal for roadways exposed to deicing salts. Its improved workability and reduced permeability help prevent water infiltration and subsequent damage in cold climates. These key properties significantly extend pavement lifespan by minimizing cracking and surface deterioration.
Chemical Resistance in Roadway Applications
Acid-resistant concrete is specifically designed to withstand severe chemical attacks from acidic substances commonly found in industrial roadway environments, ensuring prolonged durability and structural integrity. In contrast, air-entrained concrete incorporates microscopic air bubbles that improve freeze-thaw resistance but offers limited protection against chemical corrosion in roadways exposed to harsh chemical agents. Selecting acid-resistant concrete is crucial for roadways subjected to acidic runoff, spills, or industrial waste to prevent surface degradation and maintain long-term performance.
Durability Against Freeze-Thaw Cycles
Acid-resistant concrete offers enhanced chemical stability but may lack the optimized pore structure to resist freeze-thaw damage effectively. Air-entrained concrete incorporates microscopic air bubbles that improve freeze-thaw durability by providing space for ice expansion, significantly reducing cracking and scaling in roadway applications. For roads exposed to deicing salts and fluctuating temperatures, air-entrained concrete exhibits superior longevity against freeze-thaw cycles compared to acid-resistant concrete.
Performance in Aggressive Environmental Conditions
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior durability in aggressive environments by resisting chemical degradation from acids, making it ideal for industrial or polluted roadway applications. Air-entrained concrete enhances freeze-thaw resistance through microscopic air bubbles, improving performance in cold climates but with limited chemical resistance. Selecting the appropriate concrete depends on specific environmental challenges, such as exposure to acidic substances versus freeze-thaw cycles.
Comparative Cost Analysis
Acid-resistant concrete generally incurs higher initial costs due to specialized materials like silica fume and acid-proof aggregates, which enhance durability against chemical attack in industrial or polluted roadway environments. Air-entrained concrete, commonly used for freeze-thaw durability in colder climates, often has lower upfront expenses but may require more frequent maintenance or early replacement in acidic environments, potentially increasing lifecycle costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership, acid-resistant concrete provides better long-term value on roadways exposed to corrosive substances, while air-entrained concrete is cost-effective primarily for improved frost resistance in non-acidic conditions.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior chemical durability, minimizing surface degradation and reducing maintenance frequency in environments exposed to acidic pollutants or industrial runoff. Air-entrained concrete enhances freeze-thaw resistance by incorporating microscopic air bubbles, which improve longevity in cold climates but may require regular inspection to manage potential scaling or surface wear. Choosing between acid-resistant and air-entrained concrete depends on specific environmental stressors, with acid-resistant variants emphasizing chemical stability and air-entrained types prioritizing durability against physical weathering.
Suitable Use Cases for Each Concrete Type
Acid-resistant concrete is ideal for roadways exposed to chemical spills, industrial areas, or environments with acidic rain, providing enhanced durability and protection against corrosive substances. Air-entrained concrete is suitable for cold climates where freeze-thaw cycles occur frequently, improving resistance to scaling and cracking by incorporating microscopic air bubbles that enhance durability. Selection depends on environmental stressors; acid-resistant concrete ensures longevity against chemical erosion, while air-entrained concrete prevents damage from freeze-thaw weathering in pavement applications.
Final Recommendations for Roadway Projects
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior durability in environments exposed to chemical spills or acidic rain, protecting roadways from degradation and extending their service life. Air-entrained concrete enhances freeze-thaw resistance, making it ideal for roadways in colder climates subject to frequent temperature fluctuations and deicing salts. For roadway projects, selecting acid-resistant concrete is recommended in industrial or highly polluted areas, while air-entrained concrete is preferred in regions with harsh winter conditions to ensure structural integrity and longevity.
Infographic: Acid-resistant concrete vs Air-entrained concrete for Roadway
 azmater.com
azmater.com