Precast concrete offers enhanced quality control and faster construction for dams, while mass concrete provides superior thermal stability and cost-effectiveness for large-volume structures. Selecting between precast and mass concrete depends on project scale, structural requirements, and environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
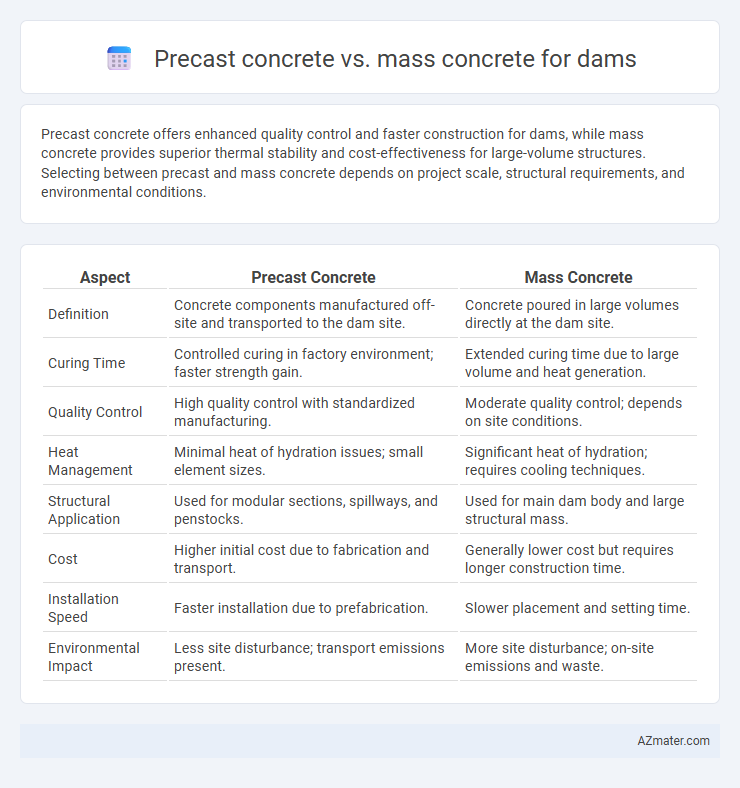
| Aspect | Precast Concrete | Mass Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete components manufactured off-site and transported to the dam site. | Concrete poured in large volumes directly at the dam site. |
| Curing Time | Controlled curing in factory environment; faster strength gain. | Extended curing time due to large volume and heat generation. |
| Quality Control | High quality control with standardized manufacturing. | Moderate quality control; depends on site conditions. |
| Heat Management | Minimal heat of hydration issues; small element sizes. | Significant heat of hydration; requires cooling techniques. |
| Structural Application | Used for modular sections, spillways, and penstocks. | Used for main dam body and large structural mass. |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to fabrication and transport. | Generally lower cost but requires longer construction time. |
| Installation Speed | Faster installation due to prefabrication. | Slower placement and setting time. |
| Environmental Impact | Less site disturbance; transport emissions present. | More site disturbance; on-site emissions and waste. |
Introduction to Dam Construction Methods
Precast concrete in dam construction offers modular components manufactured off-site, ensuring quality control and reducing on-site labor and construction time compared to traditional mass concrete methods. Mass concrete involves placing large volumes of concrete in situ, requiring careful temperature control to avoid thermal cracking during curing, making it suitable for massive dam structures like gravity dams. Selecting between precast and mass concrete depends on factors such as project scale, structural requirements, construction timeline, and cost considerations.
Overview of Precast Concrete in Dam Engineering
Precast concrete in dam engineering offers enhanced quality control, faster construction times, and improved durability compared to traditional mass concrete methods. Prefabricated precast components are manufactured in controlled environments, ensuring consistent strength and reducing on-site labor and curing times. This approach optimizes structural performance and enables modular construction, which is particularly beneficial for complex dam geometries and rapid project timelines.
Understanding Mass Concrete in Dam Structures
Mass concrete in dam structures typically involves large volumes of concrete poured in a single placement without joints, ensuring structural integrity and durability under immense water pressure. It relies heavily on controlling heat generation during curing to prevent thermal cracking, using low-heat cement and cooling techniques, making it distinct from precast concrete elements. Understanding the thermal and mechanical properties of mass concrete is critical for the long-term performance and stability of gravity and arch dams.
Key Differences Between Precast and Mass Concrete
Precast concrete for dams involves factory-made components that are manufactured under controlled conditions, ensuring uniform quality and faster construction timelines, while mass concrete is poured in large volumes on-site, designed to handle significant thermal stresses through slow curing. Key differences include the degree of quality control, with precast offering precise dimensional accuracy and reduced on-site labor, whereas mass concrete relies heavily on temperature management to prevent cracking during hydration. Precast concrete typically enables modular construction and faster assembly, while mass concrete offers the advantage of monolithic structures capable of withstanding immense hydraulic forces.
Structural Performance Comparison
Precast concrete offers superior quality control and uniformity, resulting in enhanced durability and reduced permeability compared to mass concrete in dam construction. The modular nature of precast elements allows for faster installation and better resistance to shrinkage and thermal cracking, increasing overall structural integrity. Mass concrete, while cost-efficient for large volumes, often faces challenges with thermal gradients and requires extensive curing to prevent structural weaknesses.
Construction Speed and Efficiency
Precast concrete significantly accelerates dam construction by enabling off-site fabrication under controlled conditions, which minimizes weather-related delays and ensures consistent quality. Mass concrete requires extensive curing times and complex on-site formwork, often slowing down the construction schedule and demanding more labor-intensive processes. Utilizing precast units enhances overall efficiency, reduces project timelines, and improves resource management compared to traditional mass concrete methods.
Cost Analysis: Precast vs Mass Concrete
Precast concrete offers reduced labor costs and faster installation times compared to mass concrete, resulting in lower overall expenditure for dam construction. Mass concrete requires significant on-site formwork and curing time, increasing project duration and associated costs. However, economies of scale in mass concrete production can offset initial expenses in large-volume dam projects, making cost-effectiveness dependent on project size and logistical considerations.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Precast concrete for dams offers enhanced durability due to controlled factory conditions that minimize defects and ensure uniformity, reducing permeability and resistance to chemical attack. Mass concrete, while robust, is prone to thermal cracking and variable curing conditions that can compromise long-term durability and increase maintenance needs. Maintenance considerations favor precast elements, as their modular nature allows for easier inspection, repair, and replacement compared to the monolithic structure of mass concrete.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Precast concrete for dam construction offers reduced environmental impact by minimizing on-site waste and lowering carbon emissions through controlled factory production, enhancing resource efficiency. Mass concrete requires extensive energy consumption for curing and generates higher greenhouse gases due to prolonged cement hydration processes, posing sustainability challenges. Utilizing precast elements supports sustainable dam infrastructure by promoting recyclability and reducing the overall carbon footprint compared to traditional mass concrete methods.
Choosing the Right Method for Dam Projects
Precast concrete offers faster construction times and higher quality control for dam projects due to factory production, making it ideal for modular designs and repetitive elements. Mass concrete provides superior durability and thermal stability for large-scale, monolithic dam structures requiring extensive volume and heat dissipation management. Selecting the right method depends on project scale, environmental conditions, cost constraints, and structural requirements specific to the dam type and location.
Infographic: Precast concrete vs Mass concrete for Dam
 azmater.com
azmater.com