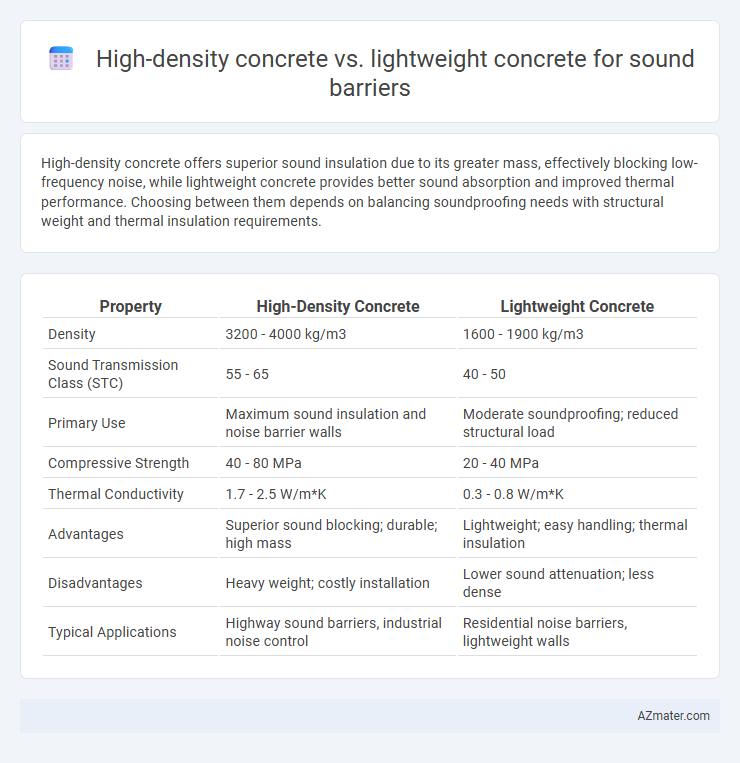
High-density concrete offers superior sound insulation due to its greater mass, effectively blocking low-frequency noise, while lightweight concrete provides better sound absorption and improved thermal performance. Choosing between them depends on balancing soundproofing needs with structural weight and thermal insulation requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | High-Density Concrete | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 3200 - 4000 kg/m3 | 1600 - 1900 kg/m3 |
| Sound Transmission Class (STC) | 55 - 65 | 40 - 50 |
| Primary Use | Maximum sound insulation and noise barrier walls | Moderate soundproofing; reduced structural load |
| Compressive Strength | 40 - 80 MPa | 20 - 40 MPa |
| Thermal Conductivity | 1.7 - 2.5 W/m*K | 0.3 - 0.8 W/m*K |
| Advantages | Superior sound blocking; durable; high mass | Lightweight; easy handling; thermal insulation |
| Disadvantages | Heavy weight; costly installation | Lower sound attenuation; less dense |
| Typical Applications | Highway sound barriers, industrial noise control | Residential noise barriers, lightweight walls |
Introduction to Concrete Sound Barriers
High-density concrete, with its increased mass and density, effectively dampens low-frequency sounds, making it ideal for sound barriers near highways or industrial zones. Lightweight concrete, characterized by its porous structure and reduced weight, provides sound absorption benefits by trapping sound waves within its cellular makeup, suitable for areas requiring noise reduction without heavy structural load. Both materials serve distinct acoustic purposes, optimizing sound barrier design based on frequency range and structural requirements.
Defining High-Density Concrete
High-density concrete is a specialized material composed of heavyweight aggregates such as barite, magnetite, or hematite, resulting in a density typically above 2400 kg/m3, which enhances its sound attenuation properties. This increased density allows high-density concrete sound barriers to effectively reduce low-frequency noise transmission compared to lightweight concrete, which has a lower density and porous structure. The superior mass and damping capacity of high-density concrete make it a preferred choice for applications requiring enhanced acoustic insulation in transportation and industrial noise mitigation.
Defining Lightweight Concrete
Lightweight concrete is a type of concrete characterized by its reduced density, typically ranging from 800 to 1,800 kg/m3, achieved by incorporating lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or perlite. It offers superior sound absorption qualities compared to high-density concrete, which generally weighs around 2,400 kg/m3 and relies on mass to block sound transmission. For sound barriers, lightweight concrete enhances noise reduction by minimizing sound reflection and promoting energy dissipation through its porous structure.
Key Properties Affecting Sound Insulation
High-density concrete, with its greater mass and density typically above 2400 kg/m3, provides superior sound insulation by effectively blocking airborne noise through mass law principles. Lightweight concrete, characterized by densities ranging from 800 to 1800 kg/m3, offers improved sound absorption due to its porous structure but is less effective at reducing transmitted sound levels compared to high-density variants. The key properties affecting sound insulation include density, porosity, and internal damping capacity, where high-density concrete excels in mass and damping while lightweight concrete contributes to absorption and vibration reduction.
Acoustic Performance Comparison
High-density concrete exhibits superior sound attenuation due to its increased mass and density, effectively reducing sound transmission loss compared to lightweight concrete. Lightweight concrete, although easier to handle and install, typically offers lower acoustic insulation because of its porous structure and reduced mass. Selecting high-density concrete for sound barriers ensures enhanced acoustic performance, particularly in mitigating low-frequency noise and achieving higher Sound Transmission Class (STC) ratings.
Structural Considerations and Durability
High-density concrete offers superior sound insulation due to its increased mass, making it ideal for sound barriers requiring robust noise attenuation and high compressive strength, often exceeding 4000 psi. Lightweight concrete, while easier to handle and install because of its reduced density (typically 1350-1850 kg/m3), may deliver lower soundproofing performance and can be more susceptible to moisture-related durability issues unless properly treated. Structural considerations must balance the load-bearing capacity and long-term resilience, with high-density concrete providing enhanced durability against environmental stresses and impact, whereas lightweight concrete demands additional reinforcement or protective measures to maintain integrity over time.
Installation and Maintenance Factors
High-density concrete offers superior sound attenuation for barriers but requires specialized equipment and skilled labor during installation due to its significant weight, increasing time and costs. Lightweight concrete, being easier to handle and transport, simplifies installation and reduces labor expenses, though it may require more frequent maintenance to address potential surface wear and acoustic degradation. Maintenance for high-density concrete sound barriers typically involves periodic inspections for cracking and structural integrity, while lightweight concrete barriers demand additional sealing and repair to maintain acoustic performance over time.
Cost Analysis: High-Density vs Lightweight
High-density concrete typically incurs higher material and transportation costs due to its increased weight and use of heavy aggregates like barite or magnetite, making it more expensive than lightweight concrete. Lightweight concrete, made with materials such as expanded shale or clay, offers reduced transportation and handling expenses, contributing to lower overall project costs. However, the superior sound attenuation properties of high-density concrete may justify its higher cost in applications demanding maximum noise reduction.
Environmental Impact Assessment
High-density concrete exhibits superior sound insulation due to its mass but often involves higher embodied energy and carbon emissions from its cement and aggregate components, impacting environmental sustainability negatively in sound barrier applications. Lightweight concrete reduces structural load and resource consumption, resulting in lower carbon footprints and enhanced sustainability, although it may require additional thickness or treatments to meet equivalent acoustic performance. Environmental Impact Assessments for sound barriers must balance the trade-offs between the material's acoustic efficiency and lifecycle emissions, considering factors such as raw material sourcing, production energy, and end-of-life recyclability.
Best Applications for Each Concrete Type
High-density concrete excels in sound barrier applications where maximum noise reduction is needed, such as along highways and industrial zones, due to its superior mass and sound attenuation properties. Lightweight concrete is best suited for sound barriers in residential areas or structures requiring ease of installation and reduced structural load while still providing effective noise control. Selecting the appropriate concrete type depends on balancing sound insulation performance with structural and logistical considerations.
Infographic: High-density concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Sound barrier
 azmater.com
azmater.com