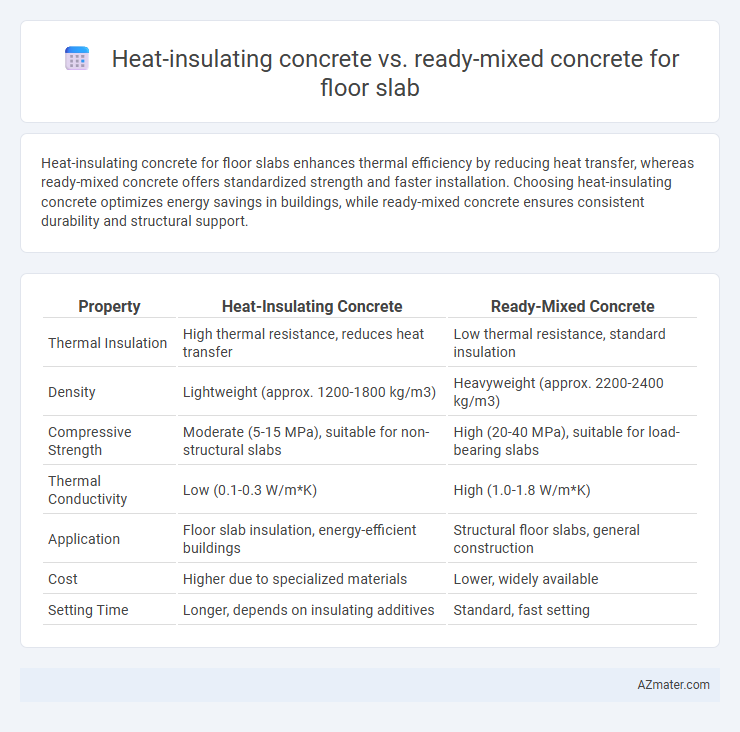
Heat-insulating concrete for floor slabs enhances thermal efficiency by reducing heat transfer, whereas ready-mixed concrete offers standardized strength and faster installation. Choosing heat-insulating concrete optimizes energy savings in buildings, while ready-mixed concrete ensures consistent durability and structural support.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Heat-Insulating Concrete | Ready-Mixed Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | High thermal resistance, reduces heat transfer | Low thermal resistance, standard insulation |
| Density | Lightweight (approx. 1200-1800 kg/m3) | Heavyweight (approx. 2200-2400 kg/m3) |
| Compressive Strength | Moderate (5-15 MPa), suitable for non-structural slabs | High (20-40 MPa), suitable for load-bearing slabs |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (0.1-0.3 W/m*K) | High (1.0-1.8 W/m*K) |
| Application | Floor slab insulation, energy-efficient buildings | Structural floor slabs, general construction |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized materials | Lower, widely available |
| Setting Time | Longer, depends on insulating additives | Standard, fast setting |
Introduction to Floor Slab Concrete Options
Heat-insulating concrete enhances thermal performance by integrating insulating materials, ideal for floor slabs requiring energy efficiency and temperature regulation. Ready-mixed concrete offers consistent quality and rapid installation, commonly used for standard floor slabs without special thermal insulation needs. Selecting between heat-insulating and ready-mixed concrete depends on specific project requirements such as thermal insulation, load-bearing capacity, and budget constraints.
Defining Heat-Insulating Concrete
Heat-insulating concrete is a specialized type of concrete designed to reduce thermal conductivity, enhancing energy efficiency in floor slabs by maintaining indoor temperatures and minimizing heat loss. Unlike standard ready-mixed concrete, heat-insulating concrete incorporates lightweight aggregates or insulating materials such as expanded polystyrene beads, perlite, or vermiculite, which provide superior thermal resistance. This characteristic makes heat-insulating concrete ideal for floor slabs requiring enhanced thermal performance, particularly in cold climates or energy-conscious building designs.
Understanding Ready-Mixed Concrete
Ready-mixed concrete for floor slabs offers consistent quality and precise mix proportions controlled at batching plants, ensuring optimal strength and durability. It reduces on-site labor and waste, facilitating faster construction timelines compared to heat-insulating concrete, which integrates insulating materials for thermal performance but may have variable mix consistency. Understanding the formulation and logistics of ready-mixed concrete is crucial for achieving structural integrity and meeting project specifications in floor slab applications.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Heat-insulating concrete for floor slabs significantly reduces thermal conductivity, typically achieving values as low as 0.15 W/m*K compared to ready-mixed concrete's range of 1.4 to 2.0 W/m*K, enhancing building energy efficiency. This specialized concrete incorporates lightweight aggregates or insulating additives, which improve thermal resistance and reduce heat loss through floor slabs. Ready-mixed concrete provides structural strength but lacks thermal insulation, leading to higher heat transfer and increased energy demands for heating or cooling.
Structural Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity
Heat-insulating concrete for floor slabs incorporates lightweight aggregates and insulating materials, resulting in lower density and reduced thermal conductivity but generally exhibits lower compressive strength compared to ready-mixed concrete. Ready-mixed concrete offers higher structural strength and load-bearing capacity due to its dense composition and optimized mix design, making it suitable for heavy load applications and high-stress environments. Selecting between the two depends on balancing thermal performance with structural requirements, where ready-mixed concrete is preferred for maximum strength and heat-insulating concrete for energy efficiency.
Installation Process and Workability
Heat-insulating concrete for floor slabs requires careful layering and placement to maintain thermal barrier properties, often needing specialized handling and curing to prevent thermal bridging. Ready-mixed concrete offers superior workability with consistent mix quality delivered directly to the site, enabling quicker installation and reduced labor. The installation process for heat-insulating concrete typically involves additional steps such as integrating insulation aggregates or panels, whereas ready-mixed concrete involves straightforward pouring and finishing, optimizing construction timelines.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-Term
Heat-insulating concrete generally incurs higher initial costs than ready-mixed concrete due to specialized materials and production processes. However, its enhanced thermal performance can significantly reduce long-term energy expenses by minimizing heat loss through the floor slab. Over the lifespan of a building, the investment in heat-insulating concrete often results in lower total operational costs compared to traditional ready-mixed concrete.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Heat-insulating concrete offers superior thermal resistance with embedded insulating materials that reduce heat loss and enhance energy efficiency in floor slabs, leading to long-term durability under temperature fluctuations. Ready-mixed concrete provides consistent quality and faster installation but may require additional insulation layers to achieve similar thermal performance, potentially increasing maintenance efforts. Maintenance demands for heat-insulating concrete are generally lower due to its resistance to cracking and moisture penetration, whereas ready-mixed concrete slabs might need more frequent repairs and sealing to maintain integrity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Heat-insulating concrete for floor slabs significantly reduces energy consumption by enhancing thermal efficiency, lowering heating and cooling demands compared to traditional ready-mixed concrete. Its composition often incorporates recycled or environmentally friendly materials, contributing to reduced carbon emissions and resource conservation in construction projects. Ready-mixed concrete, while widely used for structural strength and uniformity, typically has a higher environmental footprint due to energy-intensive production processes and limited thermal performance.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Your Floor Slab
Heat-insulating concrete offers superior thermal resistance, reducing energy costs and improving indoor comfort compared to traditional ready-mixed concrete, which is optimized for strength and durability. For floor slabs, selecting heat-insulating concrete is ideal in climates requiring enhanced thermal performance, while ready-mixed concrete suits standard load-bearing applications with faster installation and consistent quality. Evaluating project-specific factors like thermal insulation needs, load requirements, and budget ensures the right concrete choice for optimal floor slab performance.
Infographic: Heat-insulating concrete vs Ready-mixed concrete for Floor slab
 azmater.com
azmater.com