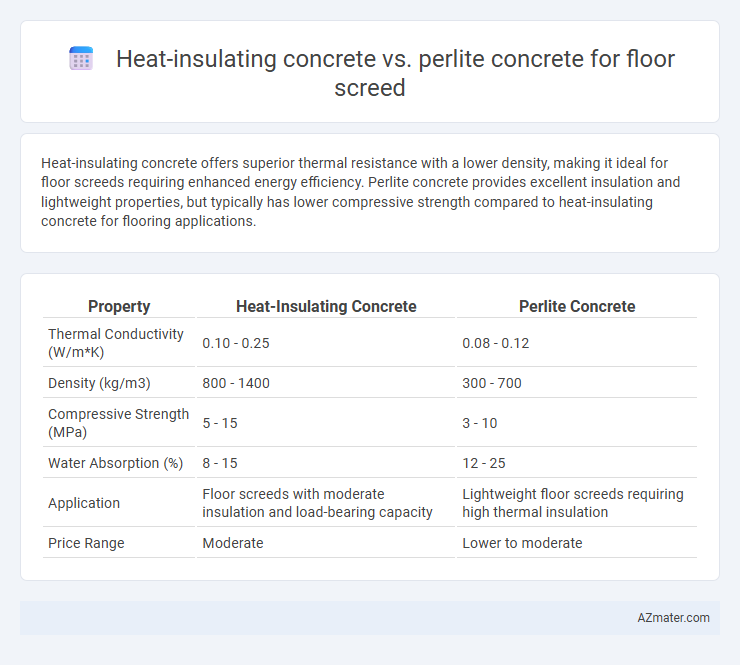
Heat-insulating concrete offers superior thermal resistance with a lower density, making it ideal for floor screeds requiring enhanced energy efficiency. Perlite concrete provides excellent insulation and lightweight properties, but typically has lower compressive strength compared to heat-insulating concrete for flooring applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Heat-Insulating Concrete | Perlite Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m*K) | 0.10 - 0.25 | 0.08 - 0.12 |
| Density (kg/m3) | 800 - 1400 | 300 - 700 |
| Compressive Strength (MPa) | 5 - 15 | 3 - 10 |
| Water Absorption (%) | 8 - 15 | 12 - 25 |
| Application | Floor screeds with moderate insulation and load-bearing capacity | Lightweight floor screeds requiring high thermal insulation |
| Price Range | Moderate | Lower to moderate |
Introduction to Floor Screed Insulation
Heat-insulating concrete incorporates materials like expanded polystyrene or foam beads to reduce thermal conductivity, offering effective floor screed insulation by minimizing heat loss and enhancing energy efficiency. Perlite concrete uses lightweight expanded volcanic glass aggregates, delivering excellent thermal insulation, fire resistance, and moisture control under screeds. Both materials improve thermal comfort and durability in floor systems, but their specific thermal conductivity values and moisture performance dictate choice based on project requirements.
What Is Heat-Insulating Concrete?
Heat-insulating concrete is a specialized building material formulated with lightweight aggregates such as expanded polystyrene beads, perlite, or vermiculite to enhance thermal insulation properties while maintaining structural integrity. This type of concrete reduces heat transfer, making it ideal for floor screeds in energy-efficient buildings by improving indoor temperature regulation and reducing heating and cooling costs. Compared to perlite concrete, heat-insulating concrete often incorporates a mix of insulating materials for optimized thermal resistance and mechanical performance in flooring applications.
Overview of Perlite Concrete
Perlite concrete, made from lightweight expanded volcanic glass, offers excellent thermal insulation and fire resistance properties, making it an ideal choice for floor screeds requiring energy efficiency and safety. Its porous structure provides superior moisture resistance compared to traditional heat-insulating concrete, reducing the risk of mold and structural damage. The material also exhibits good compressive strength while maintaining low density, optimizing both insulation and durability in floor applications.
Key Thermal Properties Comparison
Heat-insulating concrete offers superior thermal resistance with a typical thermal conductivity range of 0.1 to 0.3 W/m*K, significantly reducing heat transfer in floor screeds. Perlite concrete, characterized by its lightweight and porous structure, generally exhibits even lower thermal conductivity values around 0.05 to 0.15 W/m*K, enhancing insulation performance. Both materials contribute to energy efficiency but Perlite concrete's lower density and thermal conductivity make it particularly effective for minimizing heat loss in flooring applications.
Strength and Durability Differences
Heat-insulating concrete typically offers higher compressive strength compared to perlite concrete, making it more suitable for floor screeds requiring robust load-bearing capacity. Perlite concrete, while excellent for thermal insulation due to its lightweight and porous structure, often exhibits lower strength and reduced durability under heavy mechanical stress. Durability in heat-insulating concrete is enhanced by its denser matrix, providing better resistance to wear, moisture ingress, and cracking over time in floor screed applications.
Installation Methods and Workability
Heat-insulating concrete for floor screed offers a dense mix requiring precise water-cement ratios and vibration techniques to achieve optimal compaction and minimal voids, ensuring robust thermal insulation and structural integrity. Perlite concrete, characterized by lightweight expanded perlite aggregates, allows easier workability with reduced slump and less settlement risk, facilitating quicker manual or pump installation while maintaining thermal resistance. Both materials demand careful curing, but perlite concrete's lower density and enhanced flowability often result in faster setting times and simplified on-site application.
Cost Analysis: Heat-Insulating vs Perlite Concrete
Heat-insulating concrete generally incurs higher initial material costs compared to perlite concrete due to advanced additives and enhanced thermal properties. Perlite concrete offers a cost-effective solution with lower raw material expenses and simpler manufacturing processes, making it favorable for budget-conscious floor screeds. Long-term energy savings from heat-insulating concrete can offset higher upfront costs, but immediate project budgets often favor the economical perlite alternative.
Moisture Resistance and Longevity
Heat-insulating concrete offers moderate moisture resistance but can be prone to water absorption over time, potentially reducing its longevity in damp floor screed applications. Perlite concrete boasts superior moisture resistance due to its lightweight, porous structure that inhibits water retention, enhancing durability and lifespan in floor screeds exposed to moisture. Choosing perlite concrete for floor screeds improves long-term performance by minimizing moisture-related damage compared to traditional heat-insulating concrete.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Heat-insulating concrete typically incorporates synthetic foaming agents or chemical additives, which may lead to higher embodied energy and increased carbon emissions during production compared to Perlite concrete. Perlite concrete uses naturally occurring expanded volcanic glass, offering superior sustainability due to its low thermal conductivity, recyclability, and minimal environmental footprint. Choosing Perlite concrete for floor screed contributes to reduced resource consumption and enhanced energy efficiency in building construction, aligning with sustainable building practices.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Project
Heat-insulating concrete offers superior thermal resistance and structural strength, making it ideal for floor screeds in energy-efficient buildings requiring durability. Perlite concrete provides excellent lightweight insulation and moisture resistance, suitable for floors needing enhanced thermal performance with reduced load. Selecting the right material depends on your project's thermal requirements, load-bearing capacity, and moisture exposure to achieve optimal floor screed performance.
Infographic: Heat-insulating concrete vs Perlite concrete for Floor screed
 azmater.com
azmater.com