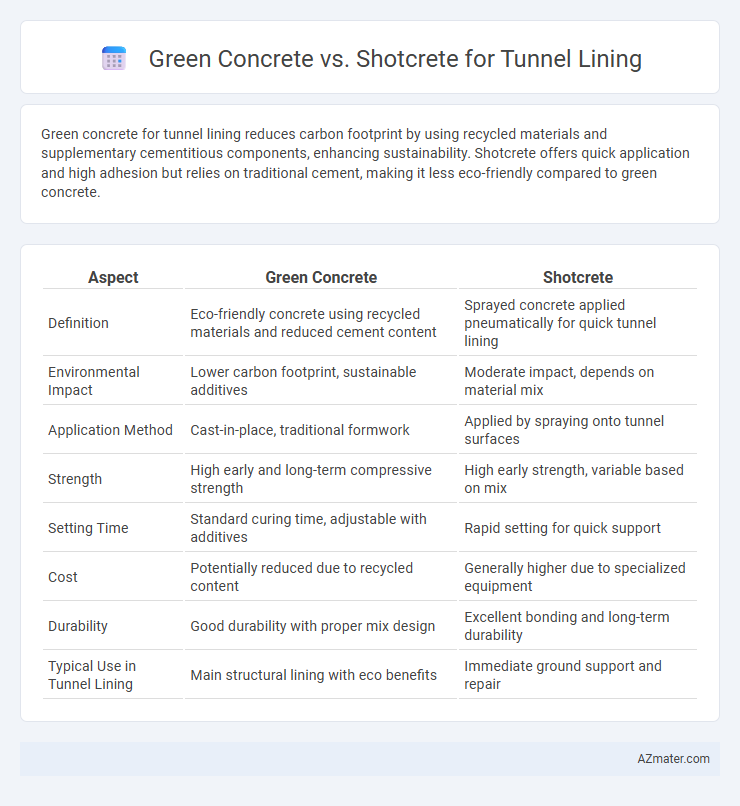
Green concrete for tunnel lining reduces carbon footprint by using recycled materials and supplementary cementitious components, enhancing sustainability. Shotcrete offers quick application and high adhesion but relies on traditional cement, making it less eco-friendly compared to green concrete.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Green Concrete | Shotcrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Eco-friendly concrete using recycled materials and reduced cement content | Sprayed concrete applied pneumatically for quick tunnel lining |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, sustainable additives | Moderate impact, depends on material mix |
| Application Method | Cast-in-place, traditional formwork | Applied by spraying onto tunnel surfaces |
| Strength | High early and long-term compressive strength | High early strength, variable based on mix |
| Setting Time | Standard curing time, adjustable with additives | Rapid setting for quick support |
| Cost | Potentially reduced due to recycled content | Generally higher due to specialized equipment |
| Durability | Good durability with proper mix design | Excellent bonding and long-term durability |
| Typical Use in Tunnel Lining | Main structural lining with eco benefits | Immediate ground support and repair |
Introduction to Tunnel Lining Solutions
Green concrete and shotcrete both serve as essential tunnel lining solutions, offering distinct advantages in structural support and environmental impact. Green concrete incorporates industrial byproducts like fly ash and slag to reduce carbon emissions while maintaining durability, making it a sustainable choice for tunnel lining. Shotcrete, a sprayed concrete method, provides rapid application and strong adhesion on uneven surfaces, ensuring effective reinforcement and minimizing construction time in tunnel lining projects.
What is Green Concrete?
Green concrete is an eco-friendly building material that incorporates recycled waste materials and industrial by-products such as fly ash, slag, and silica fume to reduce the carbon footprint associated with traditional concrete production. It offers enhanced durability, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and improved thermal insulation, making it a sustainable choice for tunnel lining applications. In contrast, shotcrete, a sprayed concrete mixture applied pneumatically, emphasizes rapid application and high adhesion but may not inherently include the same environmental benefits as green concrete.
Understanding Shotcrete Technology
Shotcrete technology involves the pneumatically applied concrete mix, which ensures rapid placement and strong adhesion to tunnel surfaces, making it ideal for lining complex geometries in tunnel construction. Green concrete, characterized by its eco-friendly composition using recycled materials and reduced carbon emissions, offers sustainability benefits but may require adjustments in mix design to match the performance of traditional shotcrete. Understanding the critical role of shotcrete technology in tunnel lining highlights its advantages in adaptability, structural strength, and accelerated construction timelines compared to green concrete alternatives.
Material Composition: Green Concrete vs Shotcrete
Green concrete for tunnel lining incorporates recycled materials like fly ash, slag, and silica fume, reducing cement content while maintaining strength and durability. Shotcrete, a pneumatically applied concrete, typically uses a mix of Portland cement, aggregates, water, and admixtures, optimized for rapid setting and high adhesion on tunnel surfaces. The sustainable composition of green concrete minimizes carbon footprint, whereas shotcrete offers enhanced workability and quick application crucial for tunnel stabilization.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Green concrete for tunnel lining significantly reduces carbon emissions by incorporating recycled materials and industrial byproducts such as fly ash, lowering cement consumption and enhancing sustainability. Shotcrete, while advantageous for its fast application and strong adhesion in tunnel excavation, typically relies on conventional cement mixes with higher embodied energy, resulting in a larger environmental footprint. Sustainable tunnel lining solutions prioritize green concrete formulations to minimize resource depletion and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, thereby promoting eco-friendly infrastructure development.
Mechanical Properties and Strength Comparison
Green concrete for tunnel lining exhibits comparable compressive strength to traditional shotcrete but offers enhanced durability and lower carbon footprint through supplementary cementitious materials like fly ash or slag. Shotcrete provides rapid strength gain and superior bonding to irregular tunnel surfaces, making it ideal for initial support, yet green concrete's improved long-term mechanical properties contribute to sustainability without sacrificing performance. Analysis of modulus of elasticity and tensile strength shows green concrete's potential to reduce cracking, while shotcrete's flexibility ensures effective load distribution during tunnel excavation.
Application Techniques in Tunnel Linings
Green concrete for tunnel linings employs sustainable materials such as fly ash and slag to reduce carbon emissions while maintaining structural integrity, often applied using traditional formwork methods ensuring controlled curing and durability. Shotcrete offers a versatile application technique, where concrete is pneumatically projected onto tunnel surfaces, allowing rapid placement and adaptation to complex geometries without the need for extensive formwork. The choice between green concrete and shotcrete depends on project-specific factors like environmental goals, application speed, and tunnel design complexity.
Cost Analysis: Green Concrete vs Shotcrete
Green concrete offers cost advantages in tunnel lining through reduced material expenses by incorporating industrial byproducts such as fly ash and slag, lowering cement consumption and overall carbon footprint. Shotcrete, while providing rapid application and flexibility in irregular tunnel surfaces, tends to have higher labor and equipment costs due to specialized spraying machinery and skilled operators. Lifecycle cost assessments reveal green concrete's potential for long-term savings in maintenance and environmental compliance compared to shotcrete's upfront installation efficiency but higher initial expenditures.
Durability and Long-Term Performance
Green concrete for tunnel lining exhibits enhanced durability through reduced permeability, improved resistance to chemical attacks, and lower thermal cracking risk due to supplementary cementitious materials like fly ash and slag. Shotcrete offers rapid application and strong adhesion to irregular tunnel surfaces but can be susceptible to rebound and variable density, impacting its long-term performance under cyclic loading and moisture conditions. Choosing green concrete improves sustainability while maintaining superior long-term strength and durability, whereas shotcrete provides flexible, immediate support but may require additional quality control to ensure durability.
Choosing the Right Material for Tunnel Lining Projects
Green concrete offers enhanced sustainability by incorporating recycled materials and reducing carbon emissions, making it an ideal choice for environmentally-conscious tunnel lining projects. Shotcrete provides superior adaptability and faster application, excelling in complex geometries and immediate structural support within tunnel construction. Selecting between green concrete and shotcrete depends on project-specific requirements such as environmental impact goals, structural performance, application speed, and cost constraints.
Infographic: Green concrete vs Shotcrete for Tunnel lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com