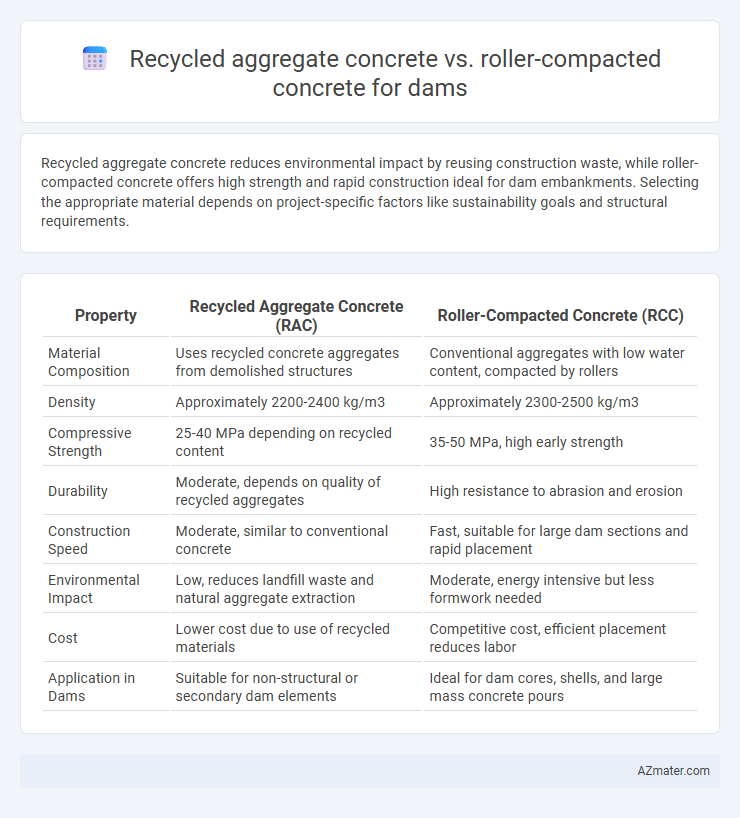
Recycled aggregate concrete reduces environmental impact by reusing construction waste, while roller-compacted concrete offers high strength and rapid construction ideal for dam embankments. Selecting the appropriate material depends on project-specific factors like sustainability goals and structural requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Recycled Aggregate Concrete (RAC) | Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Uses recycled concrete aggregates from demolished structures | Conventional aggregates with low water content, compacted by rollers |
| Density | Approximately 2200-2400 kg/m3 | Approximately 2300-2500 kg/m3 |
| Compressive Strength | 25-40 MPa depending on recycled content | 35-50 MPa, high early strength |
| Durability | Moderate, depends on quality of recycled aggregates | High resistance to abrasion and erosion |
| Construction Speed | Moderate, similar to conventional concrete | Fast, suitable for large dam sections and rapid placement |
| Environmental Impact | Low, reduces landfill waste and natural aggregate extraction | Moderate, energy intensive but less formwork needed |
| Cost | Lower cost due to use of recycled materials | Competitive cost, efficient placement reduces labor |
| Application in Dams | Suitable for non-structural or secondary dam elements | Ideal for dam cores, shells, and large mass concrete pours |
Introduction to Recycled Aggregate Concrete and Roller-Compacted Concrete
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) incorporates crushed construction waste as a sustainable alternative, reducing environmental impact while maintaining structural integrity for dam construction. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) is a dry mix concrete placed with heavy rollers, offering rapid placement, high durability, and cost-efficiency for large-scale dam projects. Both materials prioritize sustainability and strength but differ in composition, placement methods, and performance characteristics specific to dam engineering applications.
Material Composition and Source Sustainability
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) incorporates crushed concrete and masonry waste, reducing the demand for virgin aggregates and promoting circular economy practices in dam construction. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) primarily uses virgin aggregates but offers enhanced compaction and density, improving structural strength and durability. RAC emphasizes sustainability by minimizing landfill use and conserving natural resources, whereas RCC focuses on efficient placement and mechanical performance, making both materials pivotal for sustainable dam engineering depending on project priorities.
Structural Properties and Performance Comparison
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) for dams exhibits comparable compressive strength to roller-compacted concrete (RCC) but often shows reduced durability due to higher porosity and water absorption rates. RCC offers superior structural performance with enhanced density, lower permeability, and faster setting times, making it highly suitable for large-scale dam construction. Both materials require tailored mix designs to optimize mechanical properties, though RCC generally maintains better resistance to freeze-thaw cycles and chemical attacks.
Environmental Impact and Carbon Footprint
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) significantly reduces environmental impact by utilizing construction and demolition waste, lowering natural resource extraction and landfill use, which in turn decreases its carbon footprint compared to conventional materials. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) is valued for its rapid placement and durability in dam construction but typically relies on virgin aggregates and cement, resulting in higher embodied carbon emissions. Incorporating recycled aggregates into RCC can enhance sustainability by combining the low carbon benefits of RAC with the structural advantages of RCC in dam projects.
Workability and Construction Methods
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) offers reduced workability compared to roller-compacted concrete (RCC) due to the angularity and absorption of recycled aggregates, requiring careful mix design adjustments to maintain flow and compaction. RCC's low slump and zero-slump consistency facilitate rapid placement using heavy vibratory rollers, making it ideal for large-scale dam embankments with high construction speed and reduced labor. Construction methods for RAC demand prolonged curing and potential admixture use to ensure strength development, while RCC relies on staged layering and immediate compaction to achieve the dense, durable structure essential for dam safety.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) offers significant cost savings in dam construction by utilizing waste materials, reducing raw material expenses compared to roller-compacted concrete (RCC), which requires more energy-intensive production processes. RCC provides faster placement and reduced labor costs due to its dry mix and compacting method but often incurs higher initial material costs than RAC. Economic considerations favor RAC when prioritizing sustainability and landfill diversion, while RCC is preferred for projects demanding rapid construction and high early strength, impacting overall budget allocation.
Durability and Long-Term Maintenance
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) offers enhanced sustainability but may present challenges in durability due to variable aggregate quality and potential for increased porosity, affecting long-term maintenance costs in dam structures. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) exhibits superior durability with high density and low permeability, leading to reduced maintenance frequency and improved resistance to environmental stressors such as freeze-thaw cycles and erosion. Selecting RCC for dam construction typically results in longer service life and lower lifecycle maintenance expenses compared to RAC, ensuring structural integrity under hydraulic and climatic conditions.
Case Studies: Dams Utilizing Each Concrete Type
Dams such as the Yacyreta Dam in Argentina demonstrate the effective use of recycled aggregate concrete (RAC), emphasizing sustainability by incorporating construction waste materials without compromising structural integrity. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) has been extensively utilized in projects like the Hoover Dam Bypass in the USA, offering rapid construction and high durability under heavy loads. Comparative case studies reveal RAC's environmental benefits and RCC's efficiency in large-scale dam construction, guiding material selection based on project priorities.
Challenges and Limitations in Dam Applications
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) faces challenges in dam applications due to variability in aggregate quality, leading to inconsistent strength and durability, while moisture absorption can compromise concrete integrity under hydraulic pressure. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) presents limitations such as potential cold joint formation and difficulties in achieving uniform compaction on large dam faces, impacting long-term impermeability and structural performance. Both materials require rigorous quality control and tailored mix designs to meet the stringent demands of dam construction environments.
Future Trends in Concrete Technology for Dams
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) and roller-compacted concrete (RCC) are pivotal in advancing sustainable dam construction, with RAC promoting eco-friendly resource utilization by incorporating demolished concrete waste, thus reducing environmental impact while maintaining structural integrity. Future trends emphasize enhancing the durability and mechanical properties of RAC using innovative additives and nanomaterials, whereas RCC innovations target improved workability and accelerated curing processes to enable faster construction cycles and reduced costs. Integration of smart monitoring systems and digital twin technology in both concretes aims to optimize performance, predict maintenance needs, and extend dam service life, aligning with global sustainability and resilience goals in infrastructure development.
Infographic: Recycled aggregate concrete vs Roller-compacted concrete for Dam
 azmater.com
azmater.com