Sulfate-resistant concrete offers enhanced durability against chemical attacks in facade elements exposed to sulfate-rich environments, while ultra-high performance concrete provides superior compressive strength and durability with a dense microstructure, ideal for thin, load-bearing facade panels. Choosing between these materials depends on environmental exposure and structural requirements of the facade system.
Table of Comparison
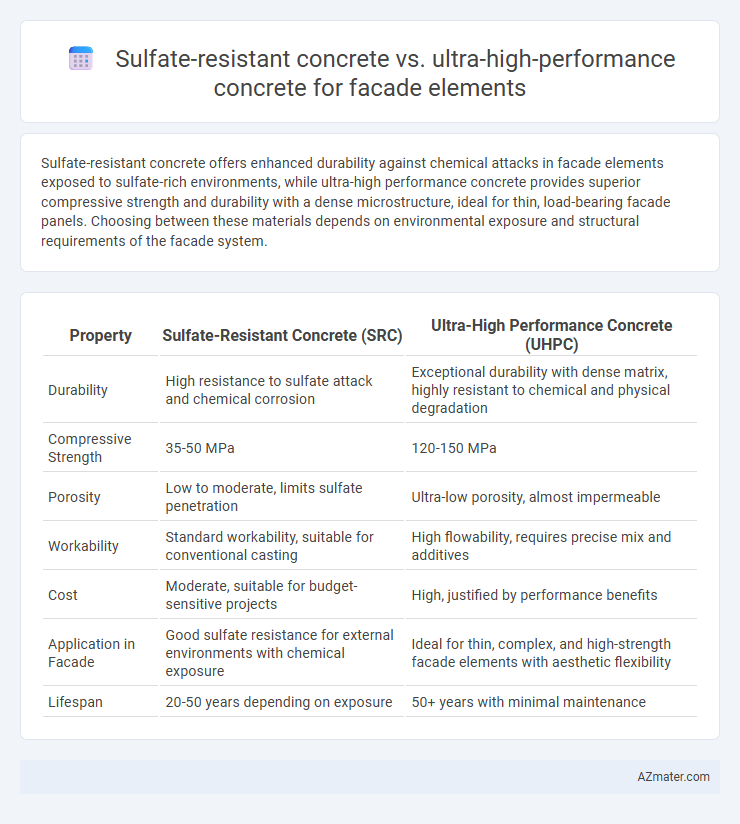
| Property | Sulfate-Resistant Concrete (SRC) | Ultra-High Performance Concrete (UHPC) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to sulfate attack and chemical corrosion | Exceptional durability with dense matrix, highly resistant to chemical and physical degradation |
| Compressive Strength | 35-50 MPa | 120-150 MPa |
| Porosity | Low to moderate, limits sulfate penetration | Ultra-low porosity, almost impermeable |
| Workability | Standard workability, suitable for conventional casting | High flowability, requires precise mix and additives |
| Cost | Moderate, suitable for budget-sensitive projects | High, justified by performance benefits |
| Application in Facade | Good sulfate resistance for external environments with chemical exposure | Ideal for thin, complex, and high-strength facade elements with aesthetic flexibility |
| Lifespan | 20-50 years depending on exposure | 50+ years with minimal maintenance |
Introduction to Façade Elements and Concrete Types
Facade elements serve as the protective and aesthetic outer layer of a building, requiring materials that withstand environmental stressors while maintaining structural integrity. Sulfate-resistant concrete is specifically designed to resist chemical attacks from sulfates in soil or groundwater, making it ideal for facade elements exposed to aggressive environments. Ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) offers superior strength, durability, and enhanced mechanical properties, providing slim, lightweight facade elements with exceptional resistance to impact and weathering.
Overview of Sulfate-Resistant Concrete
Sulfate-resistant concrete is specially formulated to withstand environments with high sulfate concentrations, utilizing low C3A cement to enhance durability against chemical attack. This type of concrete is ideal for facade elements exposed to aggressive soils or seawater, ensuring structural integrity and longevity. Its reduced permeability and increased resistance to sulfate-induced expansion make it a critical choice for maintaining facade aesthetics and performance in sulfate-rich conditions.
Key Properties of Ultra-High Performance Concrete (UHPC)
Ultra-High Performance Concrete (UHPC) exhibits exceptional compressive strength exceeding 150 MPa, ultra-low permeability, and superior durability, making it ideal for facade elements exposed to aggressive environments. Its dense microstructure enhances resistance to sulfate attack, freeze-thaw cycles, and chloride penetration, outperforming sulfate-resistant concrete in longevity and maintenance. The high tensile strength and ductility of UHPC enable slender, lightweight facade designs with increased architectural flexibility and reduced material usage.
Durability Considerations in Façade Applications
Sulfate-resistant concrete offers enhanced durability by mitigating damage from sulfate-rich environments, making it suitable for facade elements exposed to aggressive soils or groundwater. Ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) provides superior mechanical strength and exceptional resistance to environmental degradation, ensuring long-term facade integrity under severe climatic and load conditions. In facade applications, UHPC's low permeability and high tensile strength outperform sulfate-resistant concrete, although the latter is cost-effective for moderate exposure scenarios requiring chemical resistance.
Resistance to Environmental Factors: Sulfates, Moisture, and Extremes
Sulfate-resistant concrete (SRC) is specifically formulated with low C3A content and supplementary cementitious materials like fly ash or slag, enhancing its durability against sulfate attack and moisture penetration in aggressive environments. Ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) offers superior impermeability and exceptional mechanical strength due to its dense matrix and optimized particle packing, providing outstanding resistance to both moisture ingress and extreme temperature variations. For facade elements exposed to harsh sulfate-rich soils or marine environments, SRC ensures chemical stability, while UHPC delivers enhanced protection against physical degradation and freeze-thaw cycles.
Strength and Structural Capabilities Comparison
Sulfate-resistant concrete offers enhanced durability in aggressive environments by resisting chemical attacks, typically achieving compressive strengths ranging from 40 to 60 MPa, suitable for facade elements exposed to sulfate-rich soil or water. Ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) significantly surpasses sulfate-resistant concrete with compressive strengths exceeding 150 MPa, providing superior load-bearing capacity and exceptional tensile strength due to its dense microstructure and fiber reinforcement, ideal for slender, intricate facade designs requiring higher structural performance. While sulfate-resistant concrete prioritizes chemical durability, UHPC delivers unmatched strength and structural capability, making it the preferred choice for facades demanding advanced mechanical properties and long-span applications.
Aesthetic Flexibility and Design Possibilities
Sulfate-resistant concrete offers enhanced durability in aggressive environments, making it ideal for facade elements exposed to sulfate-rich soils or seawater, yet its aesthetic flexibility is somewhat limited compared to ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC). UHPC enables intricate architectural designs due to its superior tensile strength, thinner sections, and smooth finishes, allowing for complex shapes, dynamic textures, and vibrant surface treatments that elevate facade creativity. The choice between the two depends on balancing environmental resilience with innovative design potential to achieve both functional and visually striking exterior facades.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Sulfate-resistant concrete requires specialized handling and slower curing times to ensure durability against sulfate exposure, making installation more time-sensitive and demanding precise construction conditions. Ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) offers superior mechanical properties and self-consolidating behavior, allowing for faster and more flexible installation processes with reduced formwork requirements. Maintenance for sulfate-resistant concrete involves regular sulfate level checks and potential surface treatments, whereas UHPC's dense microstructure significantly minimizes permeability and reduces long-term maintenance needs for facade elements.
Long-Term Economic and Sustainability Impacts
Sulfate-resistant concrete offers enhanced durability against chemical attacks, reducing maintenance costs and extending the lifespan of facade elements in aggressive environments, which contributes to long-term economic savings. Ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) provides superior strength and durability with reduced material thickness, leading to lower material consumption and transportation emissions, thereby improving sustainability outcomes. The selection between sulfate-resistant concrete and UHPC directly influences lifecycle costs and environmental impact, with UHPC generally presenting higher initial costs but greater sustainability benefits over the service life.
Best Use Cases for Sulfate-Resistant vs UHPC in Façade Construction
Sulfate-resistant concrete is best suited for facade elements exposed to aggressive sulfate-rich environments, such as coastal or industrial areas, due to its enhanced durability against chemical attack. Ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) is ideal for facade construction requiring superior mechanical strength, durability, and aesthetic versatility, allowing for thin, lightweight panels with intricate designs and high load-bearing capacity. Selecting between sulfate-resistant concrete and UHPC depends on environmental exposure, structural demands, and architectural complexity of the facade system.
Infographic: Sulfate-resistant concrete vs Ultra-high performance concrete for Façade element
 azmater.com
azmater.com