3D-printed concrete offers superior acoustic insulation and customizable density for sound barriers compared to cellular concrete, which features inherent porosity but lower structural integrity. Optimizing 3D-printed concrete's microstructure enhances sound absorption while maintaining durability in noise mitigation applications.
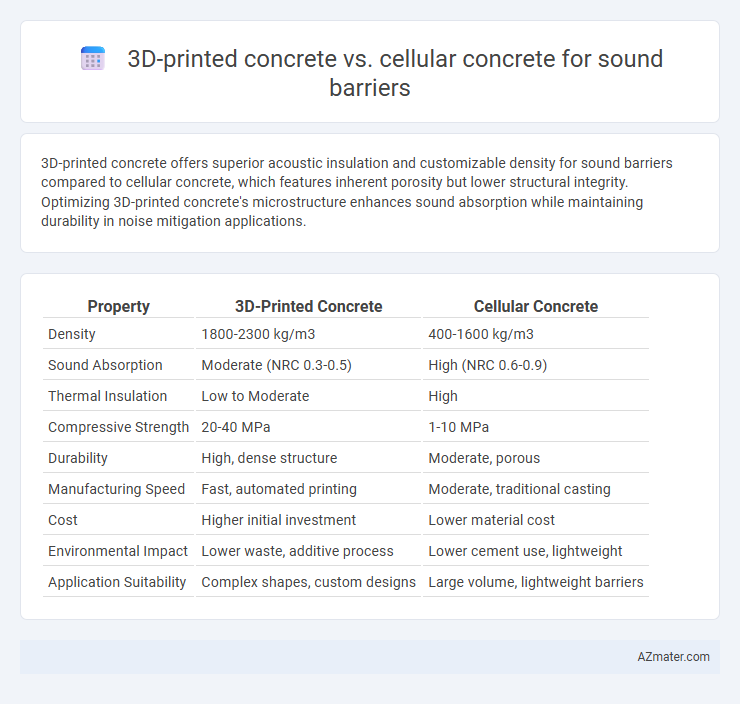
Table of Comparison
| Property | 3D-Printed Concrete | Cellular Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1800-2300 kg/m3 | 400-1600 kg/m3 |
| Sound Absorption | Moderate (NRC 0.3-0.5) | High (NRC 0.6-0.9) |
| Thermal Insulation | Low to Moderate | High |
| Compressive Strength | 20-40 MPa | 1-10 MPa |
| Durability | High, dense structure | Moderate, porous |
| Manufacturing Speed | Fast, automated printing | Moderate, traditional casting |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower material cost |
| Environmental Impact | Lower waste, additive process | Lower cement use, lightweight |
| Application Suitability | Complex shapes, custom designs | Large volume, lightweight barriers |
Introduction: Emerging Materials for Sound Barriers
3D-printed concrete offers precise customization and enhanced structural integrity, making it ideal for complex sound barrier designs that require durability and acoustic performance. Cellular concrete, characterized by its lightweight and porous structure, provides excellent sound absorption due to trapped air pockets that reduce noise transmission. Both materials represent innovative solutions in noise reduction technology, balancing strength and acoustic efficiency for urban infrastructure.
3D-Printed Concrete: An Overview
3D-printed concrete offers precise customization and complex geometries for sound barriers, enabling enhanced acoustic performance through tailored porosity and patterning. The material's high density and controlled layer composition improve sound insulation compared to cellular concrete's porous structure. Advanced 3D printing techniques also reduce material waste and construction time, making it an efficient choice for durable, high-performance noise mitigation.
Cellular Concrete: Composition and Properties
Cellular concrete, also known as foam concrete, consists of cement, water, fine aggregates, and pre-formed foam, creating a lightweight and porous material with excellent sound absorption properties. Its unique composition results in low density and high thermal insulation, making it highly effective for sound barrier applications by reducing noise transmission. Compared to 3D-printed concrete, cellular concrete offers superior acoustic performance due to its porous structure and ability to dissipate sound waves efficiently.
Acoustic Performance: Sound Insulation Comparison
3D-printed concrete offers superior acoustic performance due to its high density and minimal porosity, effectively reducing sound transmission compared to cellular concrete. Cellular concrete's porous structure provides moderate sound absorption but lower sound insulation, making it less effective in blocking airborne noise. Therefore, 3D-printed concrete is preferable for sound barriers requiring enhanced sound insulation and noise reduction in urban environments.
Structural Strength and Durability Considerations
3D-printed concrete offers superior structural strength and durability for sound barriers due to its dense, continuous material composition and customizable reinforcement integration. Cellular concrete, characterized by its lightweight and porous structure, provides effective sound absorption but generally exhibits lower compressive strength and reduced long-term durability under environmental stress. For applications demanding enhanced load-bearing capacity and longevity, 3D-printed concrete remains the preferred choice in sound barrier construction.
Design Flexibility and Architectural Possibilities
3D-printed concrete offers superior design flexibility compared to cellular concrete, enabling the creation of complex geometries and intricate patterns that enhance both acoustic performance and aesthetic appeal of sound barriers. The layer-by-layer additive manufacturing process allows for customization in density and porosity, optimizing sound absorption and diffusion properties. In contrast, cellular concrete, while lightweight and effective for sound insulation, has limited architectural possibilities due to its uniform structure and traditional casting methods.
Installation Speed and Construction Processes
3D-printed concrete offers significantly faster installation speed due to its automated layering process, reducing manual labor and onsite assembly time compared to cellular concrete, which requires conventional formwork and curing stages. The construction process of 3D-printed concrete is highly precise and customizable, allowing for complex geometries and minimal material waste, whereas cellular concrete relies on mixing and casting techniques that are more time-intensive and less adaptable. Overall, 3D-printed concrete's streamlined production enhances efficiency in sound barrier construction projects, leading to quicker completion timelines.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
3D-printed concrete offers precise material placement, reducing waste and energy consumption compared to traditional methods, enhancing sustainability in sound barrier construction. Cellular concrete, known for its lightweight and insulating properties, lowers the carbon footprint by using less raw material and improving thermal performance, which can reduce energy use over the barrier's lifecycle. Both materials contribute to environmental benefits, with 3D printing optimizing resource efficiency and cellular concrete promoting energy savings through improved insulation.
Cost Analysis: Material and Lifecycle Perspective
3D-printed concrete for sound barriers generally incurs higher initial material costs due to advanced printing technology and specialized cement mixtures compared to cellular concrete, which uses lightweight aggregates to reduce material expenses. From a lifecycle perspective, 3D-printed concrete offers enhanced durability and precision, potentially lowering long-term maintenance and repair costs relative to cellular concrete's susceptibility to cracking and weathering. Evaluating total cost of ownership highlights the trade-off between upfront investment in 3D printing and the frequent upkeep required for cellular concrete installations, influencing budget decisions for infrastructure projects.
Future Trends and Innovations in Concrete Sound Barriers
3D-printed concrete sound barriers are advancing with customizable geometries and enhanced acoustic performance through precise layering and material variations, enabling optimized sound absorption and structural strength. Cellular concrete offers innovations in lightweight, porous structures that improve sound insulation while reducing material usage and environmental impact, with ongoing research into nano-additives for enhanced durability and noise attenuation. Future trends include integrating smart sensors into 3D-printed barriers for real-time noise monitoring and adaptive sound control, alongside hybrid designs combining 3D-printed and cellular concrete to maximize acoustic efficiency and sustainability.
Infographic: 3D-printed concrete vs Cellular concrete for Sound barrier
 azmater.com
azmater.com