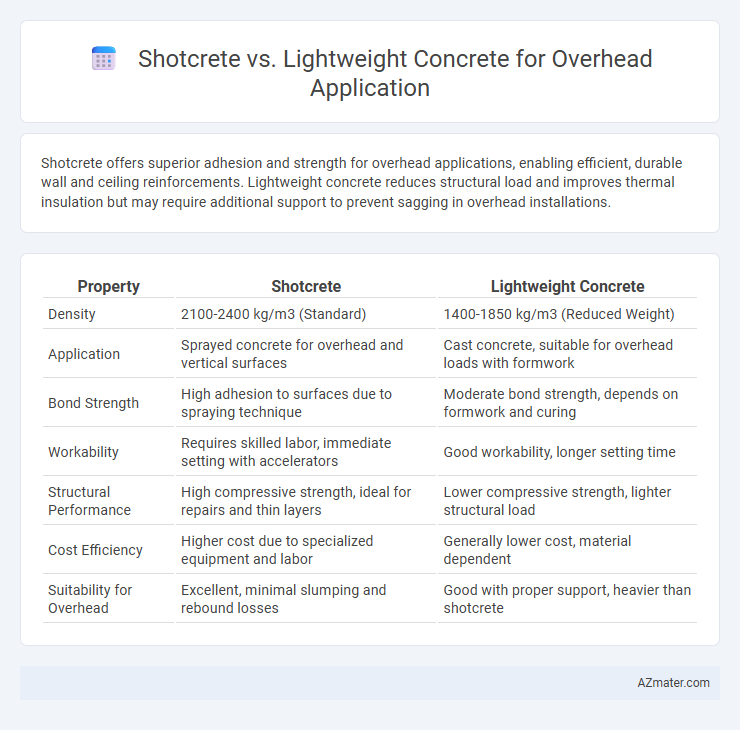
Shotcrete offers superior adhesion and strength for overhead applications, enabling efficient, durable wall and ceiling reinforcements. Lightweight concrete reduces structural load and improves thermal insulation but may require additional support to prevent sagging in overhead installations.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Shotcrete | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 2100-2400 kg/m3 (Standard) | 1400-1850 kg/m3 (Reduced Weight) |
| Application | Sprayed concrete for overhead and vertical surfaces | Cast concrete, suitable for overhead loads with formwork |
| Bond Strength | High adhesion to surfaces due to spraying technique | Moderate bond strength, depends on formwork and curing |
| Workability | Requires skilled labor, immediate setting with accelerators | Good workability, longer setting time |
| Structural Performance | High compressive strength, ideal for repairs and thin layers | Lower compressive strength, lighter structural load |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher cost due to specialized equipment and labor | Generally lower cost, material dependent |
| Suitability for Overhead | Excellent, minimal slumping and rebound losses | Good with proper support, heavier than shotcrete |
Introduction to Overhead Concrete Applications
Overhead concrete applications demand materials with superior adhesion, lightweight properties, and high structural integrity to ensure safety and durability. Shotcrete offers excellent bonding and rapid setting, making it ideal for complex overhead structures, while lightweight concrete reduces dead load but may require additional reinforcement for overhead use. Selecting the appropriate concrete type depends on factors such as load-bearing capacity, ease of application, and long-term performance in overhead environments.
What is Shotcrete?
Shotcrete is a method of applying concrete pneumatically at high velocity onto surfaces, creating dense, durable layers ideal for overhead applications where traditional concrete may sag or fall. This technique ensures superior adhesion and compaction without the need for extensive formwork, making it effective in tunnels, ceilings, and repair works. Its ability to quickly set and resist gravity-driven deformation distinguishes it from lightweight concrete, which relies more on material density than application method.
What is Lightweight Concrete?
Lightweight concrete is a specialized form of concrete that incorporates lightweight aggregates such as expanded shale, clay, or pumice to reduce the overall density and weight. This reduction in weight makes it ideal for overhead applications where minimizing structural load is critical. Compared to shotcrete, lightweight concrete offers improved thermal insulation and ease of handling, while maintaining adequate compressive strength for construction projects.
Key Material Properties Compared
Shotcrete exhibits superior adhesion and higher compressive strength, typically ranging between 20 to 40 MPa, compared to lightweight concrete's 10 to 25 MPa, making it more suitable for overhead applications where structural integrity is critical. Lightweight concrete offers significantly reduced density, often between 1600 to 1900 kg/m3, compared to regular concrete's 2200 to 2400 kg/m3, enhancing ease of handling and reducing load on supporting frameworks. Both materials demonstrate distinct water retention and curing characteristics, where shotcrete's rapid setting requires controlled moisture application, and lightweight concrete demands extended curing periods to achieve optimal strength and durability.
Installation Techniques for Overhead Work
Shotcrete installation for overhead applications utilizes pneumatic or robotic spraying methods that enable quick, uniform application and excellent adhesion on vertical and overhead surfaces. Lightweight concrete requires meticulous formwork and support systems to prevent sagging or slumping during curing, often demanding skilled labor for proper mixing and placement to achieve the desired strength-to-weight ratio. Shotcrete offers better control in overhead work due to its spray application, reducing labor intensity and enhancing structural integrity compared to the slower, more form-dependent lightweight concrete installations.
Structural Performance: Shotcrete vs Lightweight Concrete
Shotcrete exhibits superior structural performance in overhead applications due to its excellent adhesion, high compressive strength, and ability to conform to complex shapes without formwork. Lightweight concrete, while reducing dead load and enhancing thermal insulation, typically shows lower compressive strength and bond strength compared to shotcrete, limiting its use in high-stress overhead scenarios. The choice between shotcrete and lightweight concrete depends on specific project requirements, with shotcrete preferred for durability and load-bearing capacity in overhead structures.
Durability and Longevity
Shotcrete offers superior durability and longevity for overhead applications due to its dense, high-strength matrix and excellent adhesion properties that resist cracking and spalling under stress. Lightweight concrete provides ease of handling and reduced structural load but may exhibit lower resistance to impact and environmental degradation compared to shotcrete. For long-term performance in overhead structures, shotcrete's enhanced bonding and resilience make it a preferred choice, especially in demanding environments requiring sustained durability.
Cost and Efficiency Considerations
Shotcrete offers rapid application and superior adhesion for overhead projects, reducing labor time and overall installation costs compared to traditional methods. Lightweight concrete, while less costly in material terms, may require additional reinforcement and longer curing times, impacting project schedules and efficiency. Evaluating shotcrete's higher upfront cost against its efficiency gains is crucial for optimizing budget and performance in overhead construction applications.
Safety and Labor Requirements
Shotcrete offers superior adhesion and strength for overhead applications, minimizing rebound and reducing the risk of falling debris, which enhances job site safety. Lightweight concrete, while easier to handle due to reduced weight, requires careful mixing and curing to maintain structural integrity and prevent sagging, increasing labor intensity. Workers benefit from reduced physical strain with lightweight concrete, but shotcrete's quicker application process often leads to lower overall labor costs and improved safety through faster curing times.
Best Practices for Choosing the Right Material
Shotcrete offers superior adhesion and strength for overhead applications, making it ideal for structural repairs and complex shapes, while lightweight concrete reduces load on supporting structures and provides better thermal insulation. Best practices for choosing the right material include evaluating the project's load requirements, surface preparation, and environmental exposure to ensure optimal performance and durability. Selecting shotcrete is advantageous for applications demanding high bond strength and minimal rebound, whereas lightweight concrete is preferred for reducing dead load and enhancing energy efficiency.
Infographic: Shotcrete vs Lightweight Concrete for Overhead Application
 azmater.com
azmater.com