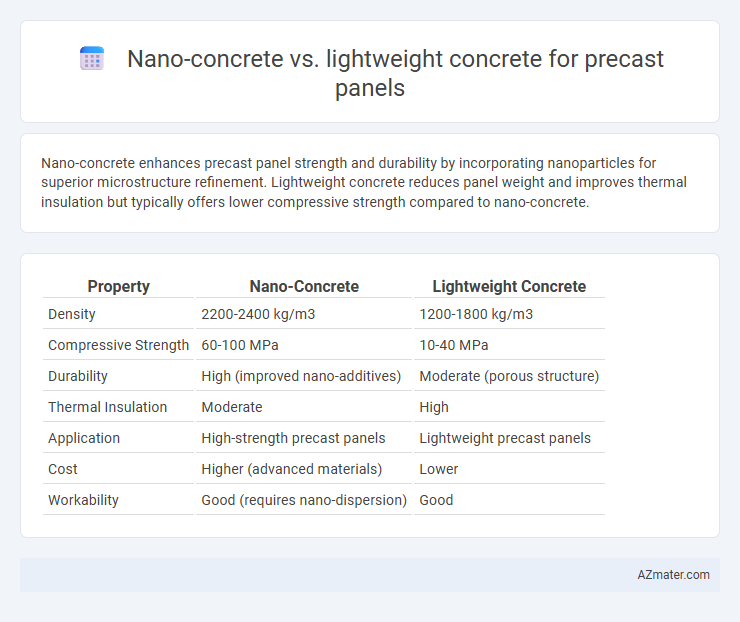
Nano-concrete enhances precast panel strength and durability by incorporating nanoparticles for superior microstructure refinement. Lightweight concrete reduces panel weight and improves thermal insulation but typically offers lower compressive strength compared to nano-concrete.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nano-Concrete | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 2200-2400 kg/m3 | 1200-1800 kg/m3 |
| Compressive Strength | 60-100 MPa | 10-40 MPa |
| Durability | High (improved nano-additives) | Moderate (porous structure) |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate | High |
| Application | High-strength precast panels | Lightweight precast panels |
| Cost | Higher (advanced materials) | Lower |
| Workability | Good (requires nano-dispersion) | Good |
Introduction to Nano-Concrete and Lightweight Concrete
Nano-concrete incorporates nanoparticles such as nano-silica and nano-titania to enhance the microstructure, resulting in superior strength, durability, and reduced permeability compared to conventional concrete. Lightweight concrete uses lightweight aggregates like expanded clay, shale, or pumice to reduce density and improve thermal insulation while maintaining adequate compressive strength for precast panels. Both materials present unique advantages in precast panel applications, with nano-concrete excelling in mechanical performance and durability, and lightweight concrete optimizing structural weight and energy efficiency.
Key Properties of Nano-Concrete
Nano-concrete exhibits superior compressive strength and enhanced durability compared to lightweight concrete, making it ideal for precast panels requiring high load-bearing capacity and resistance to environmental degradation. Its nano-scale additives improve microstructure density, resulting in reduced porosity and enhanced resistance to water penetration and freeze-thaw cycles. These key properties contribute to extended service life and improved structural performance in precast panel applications.
Key Properties of Lightweight Concrete
Lightweight concrete for precast panels offers key properties such as lower density ranging from 800 to 1900 kg/m3, enhanced thermal insulation with thermal conductivity values between 0.1 to 0.3 W/m*K, and improved fire resistance due to its porous structure. Its reduced weight facilitates easier handling and transportation while maintaining adequate compressive strength typically between 17 to 35 MPa. The material also exhibits good sound absorption and dimensional stability, making it a versatile choice compared to nano-concrete, which prioritizes ultra-high strength and durability but often requires specialized mixing processes.
Material Composition Comparison
Nano-concrete for precast panels incorporates nanoparticles such as nano-silica and nano-titania, enhancing microstructure density and mechanical strength, whereas lightweight concrete primarily uses lightweight aggregates like expanded clay or shale to reduce density. The nano-particles in nano-concrete improve hydration reaction and reduce porosity, resulting in superior durability and higher compressive strength compared to traditional lightweight concrete. Lightweight concrete sacrifices some strength for lower weight, making it suitable for non-structural elements, while nano-concrete maintains structural integrity with improved material performance.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Nano-concrete exhibits superior strength and enhanced durability compared to lightweight concrete in precast panels due to its refined particle size, which improves microstructure density and reduces porosity. The incorporation of nanoparticles such as nano-silica increases compressive strength by up to 25% and enhances resistance to environmental degradation, including freeze-thaw cycles and chloride penetration. Lightweight concrete, while beneficial for reducing structural weight, typically shows lower compressive strength and increased permeability, making nano-concrete a more robust choice for long-lasting precast panel applications.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Differences
Nano-concrete exhibits superior thermal insulation properties compared to lightweight concrete due to its denser microstructure, reducing heat transfer through precast panels. Acoustic insulation in nano-concrete is enhanced by its finely dispersed nanoparticles that absorb and scatter sound waves more effectively than the porous structure of lightweight concrete. Lightweight concrete, while offering decent thermal resistance thanks to its air voids, generally underperforms in sound insulation when compared to nano-concrete in precast panel applications.
Workability and Construction Efficiency
Nano-concrete enhances workability in precast panels through its ultra-fine particles, which improve particle packing density and reduce water demand, resulting in a smoother mix and faster setting times. Lightweight concrete offers improved handling due to its reduced density, facilitating easier transportation and installation, but may require admixtures to achieve comparable flow characteristics. In terms of construction efficiency, nano-concrete enables higher precision and faster curing, while lightweight concrete reduces structural load and accelerates onsite assembly, optimizing overall project timelines.
Cost Implications for Precast Panels
Nano-concrete offers improved strength and durability, which can reduce maintenance costs and enhance the lifespan of precast panels, although its initial material costs are higher than lightweight concrete. Lightweight concrete provides significant savings in transportation and handling due to its reduced density, lowering overall project expenses despite potentially lower mechanical performance. Choosing between nano-concrete and lightweight concrete for precast panels depends on balancing upfront material investment against long-term cost benefits related to durability and installation efficiency.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Nano-concrete exhibits enhanced durability and reduced permeability, leading to longer service life and fewer repairs in precast panels, significantly lowering lifecycle environmental impacts. Lightweight concrete offers reduced material consumption and lower transportation emissions due to decreased weight, but may have higher embodied energy from additives and manufacturing processes. Environmental Impact Assessment reveals that nano-concrete's extended lifespan and reduced maintenance typically outweigh the initial energy inputs, whereas lightweight concrete benefits primarily stem from operational phase savings in structural applications.
Conclusion: Which Concrete is Best for Precast Panels?
Nano-concrete offers superior strength, enhanced durability, and improved microstructure, making it ideal for high-performance precast panels requiring long-term resilience and minimal maintenance. Lightweight concrete provides benefits such as reduced self-weight, improved thermal insulation, and easier handling, which are advantageous for large-scale precast panel projects focusing on energy efficiency and cost savings. The best choice depends on project priorities: nano-concrete excels in structural performance and longevity, while lightweight concrete is preferred for weight reduction and insulation properties in precast panel applications.
Infographic: Nano-concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Precast panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com