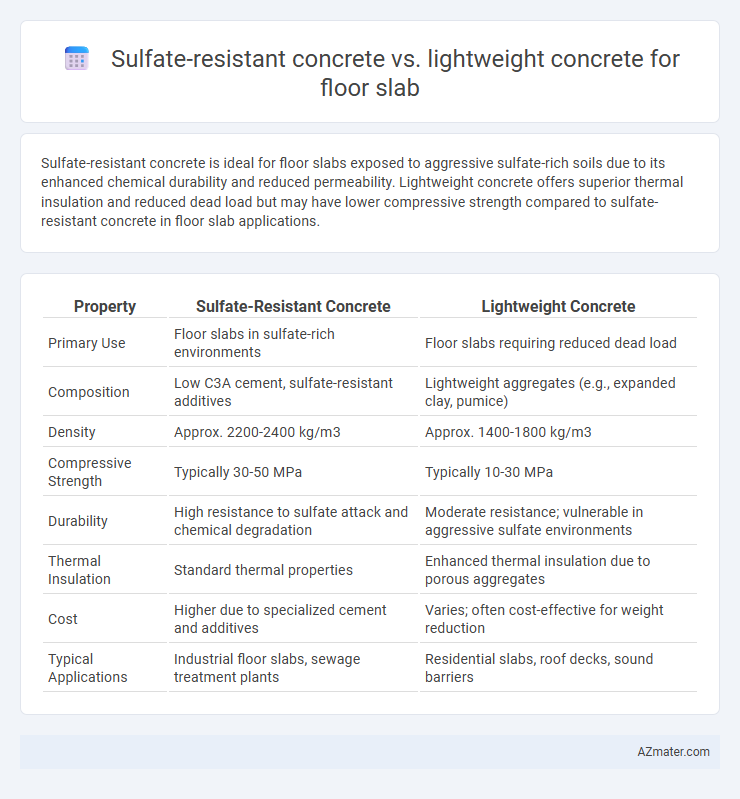
Sulfate-resistant concrete is ideal for floor slabs exposed to aggressive sulfate-rich soils due to its enhanced chemical durability and reduced permeability. Lightweight concrete offers superior thermal insulation and reduced dead load but may have lower compressive strength compared to sulfate-resistant concrete in floor slab applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sulfate-Resistant Concrete | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Floor slabs in sulfate-rich environments | Floor slabs requiring reduced dead load |
| Composition | Low C3A cement, sulfate-resistant additives | Lightweight aggregates (e.g., expanded clay, pumice) |
| Density | Approx. 2200-2400 kg/m3 | Approx. 1400-1800 kg/m3 |
| Compressive Strength | Typically 30-50 MPa | Typically 10-30 MPa |
| Durability | High resistance to sulfate attack and chemical degradation | Moderate resistance; vulnerable in aggressive sulfate environments |
| Thermal Insulation | Standard thermal properties | Enhanced thermal insulation due to porous aggregates |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized cement and additives | Varies; often cost-effective for weight reduction |
| Typical Applications | Industrial floor slabs, sewage treatment plants | Residential slabs, roof decks, sound barriers |
Introduction to Concrete Types for Floor Slabs
Sulfate-resistant concrete is designed to withstand sulfate-rich environments, preventing chemical deterioration and ensuring durability in aggressive soil and groundwater conditions commonly found in floor slab applications. Lightweight concrete, characterized by reduced density through the use of lightweight aggregates, offers enhanced thermal insulation, reduced dead load, and improved workability for floor slabs without compromising structural strength. Selecting between sulfate-resistant and lightweight concrete depends on site-specific factors such as exposure to sulfates, load requirements, and thermal performance needs, impacting the longevity and functionality of floor slabs.
Defining Sulfate-Resistant Concrete
Sulfate-resistant concrete is specially formulated to withstand chemical attacks from sulfate-rich environments, commonly using cement with low tricalcium aluminate content to enhance durability and prevent structural degradation. It offers superior resistance against sulfate-induced expansion and cracking compared to standard and lightweight concrete, making it ideal for floor slabs exposed to aggressive soil or groundwater conditions. Lightweight concrete, while beneficial for reducing structural load, typically lacks the chemical resilience required for sulfate environments and may require additional protective measures in such applications.
Understanding Lightweight Concrete
Lightweight concrete, characterized by its reduced density due to the use of lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay or shale, offers improved thermal insulation and reduced dead loads for floor slabs. Unlike sulfate-resistant concrete, which is specifically designed to withstand sulfate-rich environments through the use of low C3A cement, lightweight concrete emphasizes enhanced workability and energy efficiency while providing adequate compressive strength. Selecting lightweight concrete for floor slabs optimizes structural performance in applications where load reduction and thermal comfort are critical factors.
Key Properties: Durability and Strength
Sulfate-resistant concrete is specifically designed to withstand aggressive sulfate environments, offering exceptional durability by preventing sulfate attack that typically leads to expansion and cracking, while maintaining high compressive strength suitable for floor slabs in harsh conditions. Lightweight concrete, characterized by reduced density and improved thermal insulation, provides moderate strength but may exhibit lower durability in sulfate-rich soils due to its porous structure and higher permeability. For floor slab applications requiring resistance to chemical exposure and structural integrity, sulfate-resistant concrete delivers superior performance compared to lightweight concrete.
Performance in Aggressive Environments
Sulfate-resistant concrete provides superior durability and chemical stability when exposed to aggressive sulfate-rich soils or groundwater, preventing deterioration and maintaining structural integrity in harsh environments. Lightweight concrete, while offering reduced load and improved thermal insulation, generally exhibits lower resistance to sulfate attack due to its higher porosity and cement content variance. For floor slabs in aggressive environments, sulfate-resistant concrete ensures longer service life and minimizes maintenance costs by effectively mitigating sulfate-induced damage.
Weight Reduction and Structural Benefits
Sulfate-resistant concrete offers enhanced durability in aggressive sulfate environments, preserving the structural integrity of floor slabs by preventing chemical degradation, while maintaining standard weight and compressive strength. Lightweight concrete significantly reduces slab dead load by utilizing aggregates like expanded shale or clay, resulting in improved seismic performance and reduced foundation costs without compromising structural capacity. Combining sulfate resistance with lightweight concrete technology can optimize floor slabs for both chemical durability and weight reduction, enhancing overall structural efficiency.
Suitability for Floor Slab Applications
Sulfate-resistant concrete exhibits superior durability in aggressive soil and groundwater environments, making it highly suitable for floor slabs exposed to sulfate-rich conditions. Lightweight concrete, characterized by reduced density and thermal insulation properties, is ideal for floor slabs requiring load reduction without compromising structural integrity. For floor slab applications in corrosive environments, sulfate-resistant concrete ensures long-term performance, while lightweight concrete offers benefits in seismic zones and structures needing minimized dead loads.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Sulfate-resistant concrete typically incurs higher material costs due to specialized cement and additives designed to withstand sulfate attack, making it more expensive upfront than lightweight concrete. Lightweight concrete offers cost savings in terms of reduced dead load, which can lower structural support requirements and foundation expenses, translating into overall construction savings. Economic considerations should balance initial material costs with long-term durability and maintenance implications, where sulfate-resistant concrete may reduce repair needs in sulfate-rich environments, offsetting its higher initial price.
Installation and Maintenance Differences
Sulfate-resistant concrete requires more precise mixing and curing processes to ensure durability against sulfate attacks, making installation more labor-intensive than lightweight concrete. Lightweight concrete simplifies handling due to its reduced weight and improves thermal insulation but may demand more frequent surface maintenance to prevent wear. Maintenance of sulfate-resistant concrete involves regular inspection for chemical stability, while lightweight concrete flooring often requires routine sealing to maintain structural integrity.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Concrete for Your Floor Slab
Sulfate-resistant concrete is ideal for floor slabs exposed to aggressive sulfate-rich soils or groundwater, ensuring durability and preventing structural damage. Lightweight concrete offers advantages in reducing slab weight and improving thermal insulation but may lack the chemical resistance required in harsh environments. Selecting the right concrete depends on site conditions, load requirements, and environmental exposure to balance longevity and performance.
Infographic: Sulfate-resistant concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Floor slab
 azmater.com
azmater.com