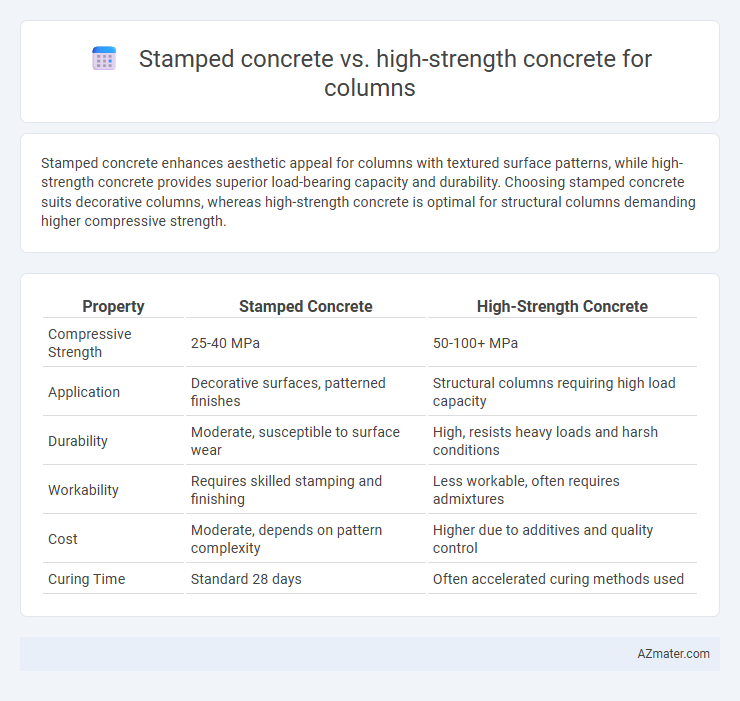
Stamped concrete enhances aesthetic appeal for columns with textured surface patterns, while high-strength concrete provides superior load-bearing capacity and durability. Choosing stamped concrete suits decorative columns, whereas high-strength concrete is optimal for structural columns demanding higher compressive strength.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Stamped Concrete | High-Strength Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Compressive Strength | 25-40 MPa | 50-100+ MPa |
| Application | Decorative surfaces, patterned finishes | Structural columns requiring high load capacity |
| Durability | Moderate, susceptible to surface wear | High, resists heavy loads and harsh conditions |
| Workability | Requires skilled stamping and finishing | Less workable, often requires admixtures |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on pattern complexity | Higher due to additives and quality control |
| Curing Time | Standard 28 days | Often accelerated curing methods used |
Introduction to Stamped Concrete and High-Strength Concrete
Stamped concrete offers a decorative finish that mimics natural materials like stone or brick while maintaining the durability of traditional concrete, making it ideal for aesthetic columns in architectural designs. High-strength concrete features enhanced compressive strength typically above 6,000 psi, providing superior load-bearing capacity essential for structural columns in high-rise buildings and infrastructure. Selecting between stamped and high-strength concrete depends on whether the priority lies in visual appeal or structural performance for column applications.
Key Differences Between Stamped Concrete and High-Strength Concrete
Stamped concrete features decorative patterns and textures that enhance aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for visually prominent columns. High-strength concrete, with compressive strengths often exceeding 6000 psi, prioritizes structural durability and load-bearing capacity crucial for supporting heavy loads. The key difference lies in stamped concrete's focus on surface design versus high-strength concrete's engineered performance for structural integrity.
Composition and Material Properties
Stamped concrete incorporates decorative aggregates and pigments within a standard concrete mix to enhance aesthetics, while high-strength concrete uses a lower water-cement ratio, higher cement content, and supplementary cementitious materials like silica fume to achieve compressive strengths exceeding 6,000 psi. The composition of stamped concrete prioritizes surface texture and visual appeal without significantly altering mechanical properties, whereas high-strength concrete emphasizes optimized particle packing, reduced porosity, and increased density to improve load-bearing capacity and durability. Material properties for stamped concrete typically include moderate compressive strength and enhanced surface hardness through sealants, whereas high-strength concrete exhibits superior modulus of elasticity, higher tensile strength, and improved resistance to environmental degradation critical for structural columns.
Structural Performance in Columns
Stamped concrete offers aesthetic appeal but typically lacks the high compressive strength required for load-bearing columns. High-strength concrete, with compressive strengths exceeding 6,000 psi, provides superior load-carrying capacity, enhanced durability, and improved resistance to structural stresses in column applications. The choice of concrete type significantly influences the structural performance, with high-strength concrete being optimal for ensuring column stability and long-term integrity.
Aesthetic and Design Considerations
Stamped concrete offers versatile aesthetic options for columns through customizable patterns and colors, enhancing architectural appeal and allowing imitation of natural materials like stone or brick. High-strength concrete prioritizes structural performance over visual design, typically featuring a smooth, uniform finish with limited decorative capabilities. For projects where column appearance is paramount, stamped concrete delivers superior design flexibility, while high-strength concrete suits applications focused on load-bearing and durability.
Installation Process and Techniques
Stamped concrete involves layering a concrete mix onto forms or molds with textured patterns, requiring precise timing to imprint designs before the concrete sets, which demands skilled labor and detailed surface finishing techniques. High-strength concrete for columns is poured using standard formwork but necessitates careful mixing, placement, and vibration to ensure density and minimize voids, followed by strict curing protocols to achieve the desired compressive strength. The installation of stamped concrete prioritizes aesthetic surface treatment and pattern accuracy, while high-strength concrete focuses on structural integrity and load-bearing capacity through controlled material properties and curing methods.
Cost Comparison and Budget Factors
Stamped concrete typically offers a lower initial cost due to simpler materials and installation methods, making it suitable for budget-conscious column projects seeking aesthetic appeal. High-strength concrete incurs higher expenses from advanced admixtures and stricter quality controls, but it provides superior load-bearing capacity critical for structural columns in high-stress environments. Budget factors must weigh immediate expenditure against long-term durability and maintenance costs, where high-strength concrete may prove more cost-effective over the lifespan of the column despite higher upfront investment.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Stamped concrete, often used for decorative surfaces, offers moderate durability but requires regular sealing to prevent wear and weather damage, making maintenance crucial for longevity. High-strength concrete, engineered with a compressive strength typically above 6,000 psi, provides superior durability and resistance to environmental stressors, significantly reducing the frequency and intensity of maintenance needed for structural columns. For columns, high-strength concrete ensures enhanced load-bearing capacity and long-term performance with minimal upkeep compared to stamped concrete.
Suitable Applications for Each Concrete Type
Stamped concrete is ideal for decorative columns in architectural projects where aesthetic appeal and surface texture mimicking natural materials are prioritized, such as in residential facades, garden columns, and commercial storefronts. High-strength concrete is suited for structural columns in high-rise buildings, bridges, and industrial facilities requiring superior load-bearing capacity, durability, and resistance to harsh environmental conditions. Choosing stamped concrete enhances visual design, while high-strength concrete ensures critical structural performance and safety.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Your Column Project
Stamped concrete offers aesthetic versatility with textured and colored surfaces that enhance the visual appeal of columns, making it ideal for decorative applications. High-strength concrete, characterized by compressive strengths exceeding 6,000 psi, provides superior load-bearing capacity and durability essential for structural columns in high-rise buildings and infrastructure projects. Selecting the right concrete depends on balancing design requirements with structural performance, where stamped concrete suits ornamental purposes while high-strength concrete ensures safety and longevity under significant loads.
Infographic: Stamped concrete vs High-strength concrete for Column
 azmater.com
azmater.com