Rapid-setting concrete achieves high early strength within hours, enabling fast pavement construction and minimal traffic disruption. Roller-compacted concrete features a dry, stiff mix placed with asphalt pavers and compacted by rollers, offering cost-effective, durable pavement ideal for heavy traffic loads.
Table of Comparison
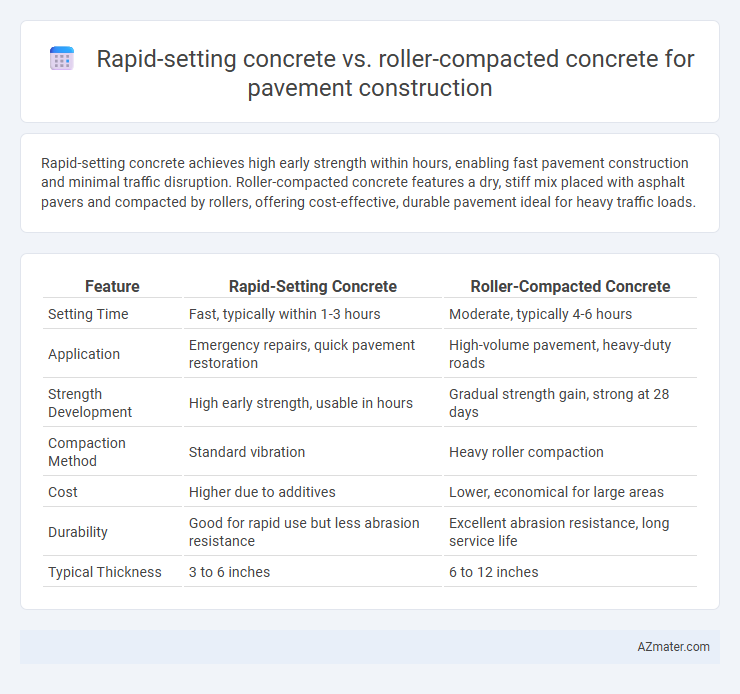
| Feature | Rapid-Setting Concrete | Roller-Compacted Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Setting Time | Fast, typically within 1-3 hours | Moderate, typically 4-6 hours |
| Application | Emergency repairs, quick pavement restoration | High-volume pavement, heavy-duty roads |
| Strength Development | High early strength, usable in hours | Gradual strength gain, strong at 28 days |
| Compaction Method | Standard vibration | Heavy roller compaction |
| Cost | Higher due to additives | Lower, economical for large areas |
| Durability | Good for rapid use but less abrasion resistance | Excellent abrasion resistance, long service life |
| Typical Thickness | 3 to 6 inches | 6 to 12 inches |
Introduction to Pavement Concrete Technologies
Rapid-setting concrete offers accelerated curing times, enabling faster project completion and early load application, ideal for high-traffic areas requiring minimal downtime. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) utilizes a drier mix compacted with heavy rollers, providing enhanced strength and durability at lower costs for large-scale pavement projects like highways and industrial floors. Both technologies optimize pavement construction by balancing performance, cost-efficiency, and construction speed tailored to specific infrastructure demands.
Overview of Rapid-Setting Concrete
Rapid-setting concrete offers accelerated curing times, enabling pavement construction to resume traffic within hours instead of days. It achieves high early strength through specialized cementitious materials and admixtures that promote quick hydration. This type of concrete is ideal for time-sensitive infrastructure repairs, reducing downtime and minimizing disruption in high-traffic areas.
Overview of Roller-Compacted Concrete
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) is a no-slump concrete mixture characterized by its dry consistency and high density, making it ideal for pavement construction. RCC is laid down using earthmoving equipment and compacted with vibratory rollers, providing rapid strength gain and enhanced durability for heavy traffic conditions. Its cost-effectiveness and ability to support large loads make RCC a preferred choice for highways, industrial yards, and airport pavements.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Rapid-setting concrete exhibits high early strength development, achieving significant load-bearing capacity within hours, making it ideal for fast-track pavement projects. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) features lower cement content with a zero-slump consistency, enabling efficient placement and compaction through heavy rollers, resulting in dense, durable pavement layers. While rapid-setting concrete prioritizes quick strength gain, RCC emphasizes workability and cost-effectiveness through reduced water content and optimized aggregate gradation, impacting long-term pavement performance and maintenance.
Strength and Durability Differences
Rapid-setting concrete achieves high early strength within hours, making it ideal for fast-track pavement repairs, while roller-compacted concrete (RCC) develops strength more gradually but provides superior long-term compressive strength and resistance to heavy traffic loads. RCC's dense, low-slump mix exhibits enhanced durability against rutting, freeze-thaw cycles, and chemical attacks compared to rapid-setting concrete, which may sacrifice some long-term durability for quick hardening. The choice between the two depends on project timelines and performance requirements, with RCC favored for new construction and rapid-setting concrete preferred for rapid maintenance.
Construction Methods and Equipment Requirements
Rapid-setting concrete requires specialized mixing equipment and expedited delivery systems to maintain low setting times, enabling quick pavement placement and early traffic opening. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) utilizes heavy rollers for compaction and is placed with standard paving equipment such as conveyors and vibratory rollers, eliminating the need for forms or finishing tools. The construction method for RCC emphasizes continuous layering and compaction, whereas rapid-setting concrete demands precise timing in batching, placement, and curing to optimize strength development.
Setting Time and Project Timeline Impacts
Rapid-setting concrete typically achieves initial set within 30 to 60 minutes, enabling faster pavement opening and significantly reducing project timelines in high-traffic areas. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) requires longer curing, often 24 to 48 hours before full load-bearing capacity, which may extend construction schedules but offers enhanced durability for heavy loads. Selecting rapid-setting concrete accelerates project turnover, whereas RCC balances longer setting times with structural benefits essential for pavement longevity.
Cost Analysis: Rapid-Setting vs Roller-Compacted
Rapid-setting concrete typically incurs higher material costs due to specialized admixtures and accelerated curing requirements, making it suitable for projects demanding quick turnaround. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers cost savings primarily through lower cement content and reduced labor intensity, as its placement method resembles asphalt paving and eliminates traditional finishing. The overall cost-effectiveness of RCC often depends on large-scale applications where bulk materials and rapid placement reduce expenses compared to the premium pricing of rapid-setting formulations.
Suitability for Various Pavement Applications
Rapid-setting concrete excels in applications requiring quick turnaround times, such as airport runways and emergency repairs, due to its accelerated curing and early strength gain. Roller-compacted concrete, characterized by its low slump and high density, is well-suited for heavy-duty pavements like highways, industrial yards, and dam infrastructure where durability and high load-bearing capacity are essential. Selection depends on factors like traffic load, project timeline, and structural requirements, with rapid-setting concrete favoring time-sensitive projects and roller-compacted concrete optimized for long-lasting, high-volume traffic pavements.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Rapid-setting concrete reduces construction time and limits environmental disruptions by enabling faster reopening of pavements, minimizing traffic congestion and emissions from idling vehicles. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) requires less cement and water, decreasing CO2 emissions and enhancing sustainability through reduced energy consumption in production. Both materials support sustainable pavement construction, but RCC offers better long-term durability and resource efficiency, making it preferable for eco-friendly infrastructure projects.
Infographic: Rapid-setting concrete vs Roller-compacted concrete for Pavement construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com