Sulfate-resistant concrete enhances foundation durability by resisting chemical attack from sulfates in soil or groundwater, unlike Ordinary Portland Cement concrete which is prone to sulfate-induced deterioration. Using sulfate-resistant concrete improves structural longevity in sulfate-rich environments.
Table of Comparison
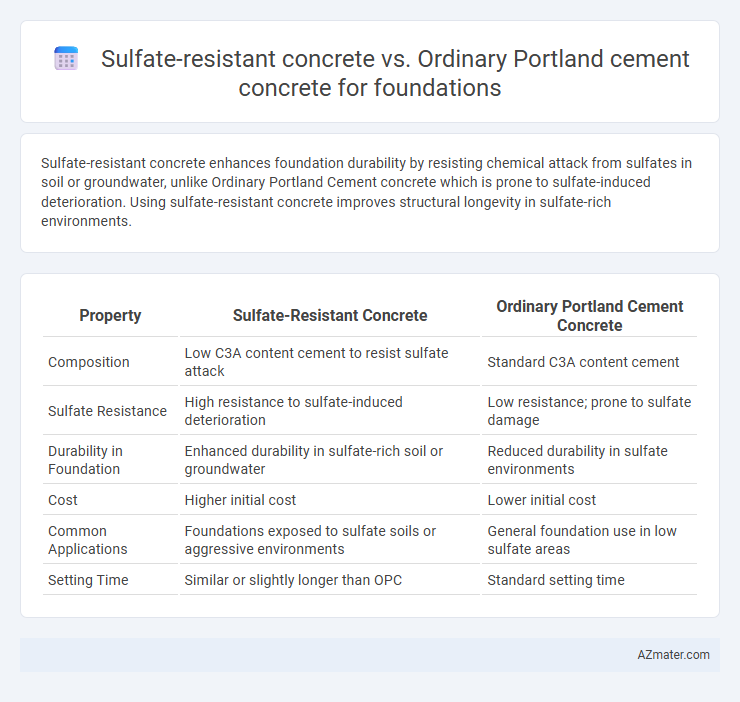
| Property | Sulfate-Resistant Concrete | Ordinary Portland Cement Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Low C3A content cement to resist sulfate attack | Standard C3A content cement |
| Sulfate Resistance | High resistance to sulfate-induced deterioration | Low resistance; prone to sulfate damage |
| Durability in Foundation | Enhanced durability in sulfate-rich soil or groundwater | Reduced durability in sulfate environments |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Common Applications | Foundations exposed to sulfate soils or aggressive environments | General foundation use in low sulfate areas |
| Setting Time | Similar or slightly longer than OPC | Standard setting time |
Introduction to Concrete Types for Foundations
Sulfate-resistant concrete is specifically designed to withstand aggressive sulfate environments, making it ideal for foundations exposed to sulfate-rich soils or groundwater, whereas Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) concrete is commonly used for general foundation applications without such exposure. Sulfate-resistant concrete typically contains Type V cement or supplementary cementitious materials like fly ash or slag to enhance durability and prevent sulfate attack. Choosing the appropriate concrete type is crucial for foundation longevity and structural integrity in varying environmental conditions.
Understanding Sulfate Attack in Concrete
Sulfate-resistant concrete is specifically designed to withstand sulfate attack, a chemical reaction between sulfate ions and the hydrated compounds in ordinary Portland cement (OPC) concrete that causes expansion and cracking, leading to structural damage. Ordinary Portland cement concrete is vulnerable to sulfate attack when exposed to high sulfate environments, such as soils or groundwater containing sulfates, resulting in compromised durability and reduced lifespan of foundations. The use of sulfate-resistant cement, typically containing lower tricalcium aluminate (C3A) content, helps mitigate the formation of expansive ettringite and thaumasite, ensuring enhanced foundation stability in sulfate-rich conditions.
Composition of Sulfate-Resistant Concrete
Sulfate-resistant concrete is specifically formulated with low tricalcium aluminate (C3A) content, typically less than 5%, to withstand aggressive sulfate environments, contrasting with Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) which contains higher C3A levels making it vulnerable to sulfate attack. The composition includes supplementary cementitious materials like fly ash, slag, or silica fume that enhance durability by reducing permeability and chemical reactivity. This optimized mix design significantly improves resistance to sulfate-induced expansion and cracking, making it ideal for foundations exposed to sulfate-rich soils or groundwater.
Ordinary Portland Cement Concrete: Properties and Uses
Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) concrete is widely used in foundation construction due to its strong compressive strength, good workability, and cost-effectiveness. It exhibits moderate resistance to weathering and chemical attacks but is vulnerable to sulfate-induced deterioration in aggressive soils, leading to cracking and loss of durability. Commonly applied in residential and commercial building foundations, OPC concrete is preferred for environments with low sulfate exposure and when economic constraints outweigh the need for specialized sulfate resistance.
Performance in Sulfate-Rich Environments
Sulfate-resistant concrete demonstrates superior durability and structural integrity in sulfate-rich environments compared to Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) concrete, significantly reducing the risk of sulfate attack-induced expansion, cracking, and deterioration. The use of calcium aluminate cement or low C3A content in sulfate-resistant concrete limits the formation of expansive ettringite and gypsum, ensuring better performance and longevity of foundations exposed to aggressive sulfate concentrations above 1500 ppm. In contrast, OPC concrete frequently suffers from sulfate-induced chemical degradation, compromising foundation stability and increasing maintenance costs in high sulfate soils and groundwater conditions.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Sulfate-resistant concrete enhances foundation durability by minimizing sulfate attack, which causes expansion and cracking in Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) concrete exposed to aggressive soils or groundwater. The reduced tricalcium aluminate content in sulfate-resistant cement significantly improves resistance to chemical degradation, extending the structural lifespan in sulfate-rich environments. Studies show sulfate-resistant concrete can maintain strength and stability over decades, outperforming OPC concrete in longevity under sulfate exposure conditions.
Cost Implications and Economic Considerations
Sulfate-resistant concrete incurs higher initial costs due to the specialized cement and additives required, but it significantly reduces long-term maintenance and repair expenses in sulfate-rich soil environments. Ordinary Portland cement concrete is cheaper upfront but may lead to costly structural damage and foundation failures when exposed to sulfates, increasing overall lifecycle costs. Investing in sulfate-resistant concrete enhances durability and economic sustainability for foundations subjected to aggressive sulfate conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sulfate-resistant concrete significantly reduces environmental impact by minimizing the deterioration caused by sulfate attack, which extends the lifespan of foundations and decreases the need for frequent repairs or rebuilds, leading to lower resource consumption. Its composition, typically involving low C3A clinker content, can reduce carbon emissions compared to Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) concrete, which generally has higher clinker ratios and CO2 footprints. Utilizing sulfate-resistant concrete promotes sustainability by enhancing durability and reducing maintenance-related waste, making it a more eco-friendly choice for foundation applications in sulfate-rich soils.
Best Applications for Each Concrete Type
Sulfate-resistant concrete is best suited for foundations exposed to aggressive sulfate-rich soils or groundwater, as it minimizes chemical attacks and prolongs structural durability. Ordinary Portland cement concrete performs well for standard foundation applications where sulfate exposure is minimal or absent, offering cost-efficient and high-strength properties. Selecting the appropriate concrete type depends on environmental sulfate concentration, soil conditions, and project-specific durability requirements.
Key Factors in Choosing the Right Concrete for Foundations
Sulfate-resistant concrete is designed to withstand high sulfate concentrations in soil or groundwater, preventing chemical attacks that degrade Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) concrete. Its lower permeability and use of supplementary cementitious materials like fly ash enhance durability and reduce expansion risks in sulfate-rich environments. Choosing the right concrete depends on factors such as sulfate exposure level, soil chemistry, structural load requirements, and long-term performance expectations for foundation integrity.
Infographic: Sulfate-resistant concrete vs Ordinary Portland cement concrete for Foundation
 azmater.com
azmater.com