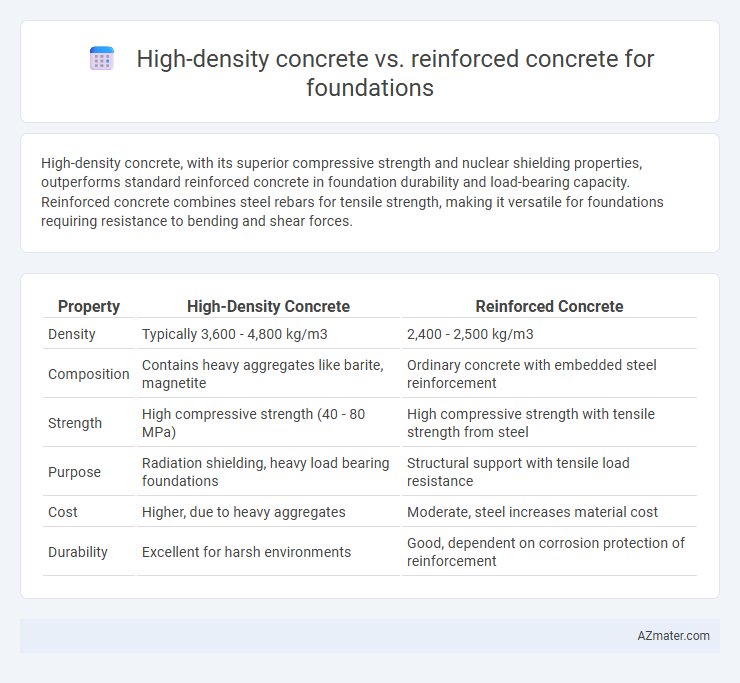
High-density concrete, with its superior compressive strength and nuclear shielding properties, outperforms standard reinforced concrete in foundation durability and load-bearing capacity. Reinforced concrete combines steel rebars for tensile strength, making it versatile for foundations requiring resistance to bending and shear forces.
Table of Comparison
| Property | High-Density Concrete | Reinforced Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Typically 3,600 - 4,800 kg/m3 | 2,400 - 2,500 kg/m3 |
| Composition | Contains heavy aggregates like barite, magnetite | Ordinary concrete with embedded steel reinforcement |
| Strength | High compressive strength (40 - 80 MPa) | High compressive strength with tensile strength from steel |
| Purpose | Radiation shielding, heavy load bearing foundations | Structural support with tensile load resistance |
| Cost | Higher, due to heavy aggregates | Moderate, steel increases material cost |
| Durability | Excellent for harsh environments | Good, dependent on corrosion protection of reinforcement |
Introduction to Foundation Materials
High-density concrete, composed of heavyweight aggregates like barite or magnetite, offers enhanced radiation shielding and increased compressive strength, making it suitable for specialized foundation applications. Reinforced concrete integrates steel rebar to improve tensile strength and resistance to cracking, providing structural stability for most conventional foundations. Choosing between high-density and reinforced concrete depends on load requirements, environmental conditions, and specific project needs in foundation construction.
What is High-Density Concrete?
High-density concrete is a specialized concrete material that incorporates heavy aggregates such as barite, magnetite, or hematite, resulting in increased density typically ranging from 3000 to 4500 kg/m3, compared to conventional concrete. It is primarily used for foundations requiring enhanced radiation shielding, ballast, or increased mass to reduce vibration and sound transmission. Reinforced concrete, while widely used for foundations due to its tensile strength from steel reinforcement, does not provide the same density-related benefits as high-density concrete in specialized construction applications.
What is Reinforced Concrete?
Reinforced concrete is a composite material composed of concrete embedded with steel bars or mesh, designed to improve tensile strength and durability in foundation structures. Unlike high-density concrete, which primarily enhances radiation shielding and weight-bearing capacity, reinforced concrete focuses on resisting tension and bending forces in foundations. This combination of materials provides a balanced solution for structural stability and long-term performance in various load conditions.
Key Properties Comparison
High-density concrete offers superior compressive strength and radiation shielding due to its increased weight and density, making it ideal for specialized foundation requirements in nuclear or heavy industrial facilities. Reinforced concrete integrates steel reinforcement to enhance tensile strength and ductility, providing improved resistance to bending and cracking under structural loads. Key properties comparison highlights that high-density concrete excels in load-bearing and protection applications, while reinforced concrete delivers balanced strength and flexibility for typical foundation designs.
Strength and Durability Factors
High-density concrete, characterized by its increased weight and compressive strength due to the use of heavyweight aggregates like barite or magnetite, offers superior resistance to high-stress loads and radiation shielding compared to conventional reinforced concrete. Reinforced concrete enhances structural integrity by embedding steel bars, improving tensile strength and flexibility, but generally has lower density and may be more susceptible to corrosion over time. For foundation applications demanding exceptional durability and load-bearing capacity, high-density concrete provides enhanced strength and longevity, while reinforced concrete remains versatile for seismic performance and crack resistance.
Load-Bearing Performance
High-density concrete offers superior load-bearing performance for foundations due to its increased density and mass, enabling it to withstand higher compressive forces and impact loads compared to standard reinforced concrete. Reinforced concrete incorporates steel reinforcement bars that improve tensile strength and crack resistance, but its load capacity is generally lower than that of high-density concrete, which is often used in structures requiring exceptional structural mass and radiation shielding. Optimal foundation design often balances high-density concrete's compressive strength with reinforced concrete's tensile capacity to meet specific load-bearing and structural stability requirements.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
High-density concrete offers enhanced resistance to environmental factors such as radiation, chemical attack, and moisture infiltration due to its dense aggregate composition and low permeability. Reinforced concrete, while strong structurally, is more susceptible to corrosion of steel reinforcement when exposed to aggressive environments like chlorides or sulfates. Selecting high-density concrete for foundations in harsh conditions ensures increased durability and longevity by minimizing degradation from environmental stressors.
Cost Implications
High-density concrete incurs higher material costs due to its heavy aggregates like barite or magnetite, impacting foundation budgets significantly. Reinforced concrete, utilizing standard aggregates combined with steel rebar, offers a more cost-effective option while providing enhanced structural strength. Project-specific requirements and environmental conditions ultimately dictate the most economical choice between these foundation materials.
Suitability for Different Foundation Types
High-density concrete offers superior radiation shielding and heavy load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for foundations in nuclear facilities or heavy industrial plants. Reinforced concrete provides enhanced tensile strength and flexibility, suited for shallow foundations such as slabs and footings in residential and commercial buildings. Selection depends on specific foundation requirements, with high-density concrete favored for specialized heavy-duty applications while reinforced concrete covers a broader range of conventional foundation types.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Concrete for Foundations
High-density concrete offers superior radiation shielding and enhanced durability for specialized foundation needs, while reinforced concrete provides exceptional tensile strength and flexibility under dynamic loads. Selecting the right concrete type depends on project-specific factors such as load-bearing requirements, environmental exposure, and structural design criteria. For most standard foundations, reinforced concrete remains the cost-effective and versatile choice, whereas high-density concrete suits applications requiring enhanced mass and resistance properties.
Infographic: High-density concrete vs Reinforced concrete for Foundation
 azmater.com
azmater.com