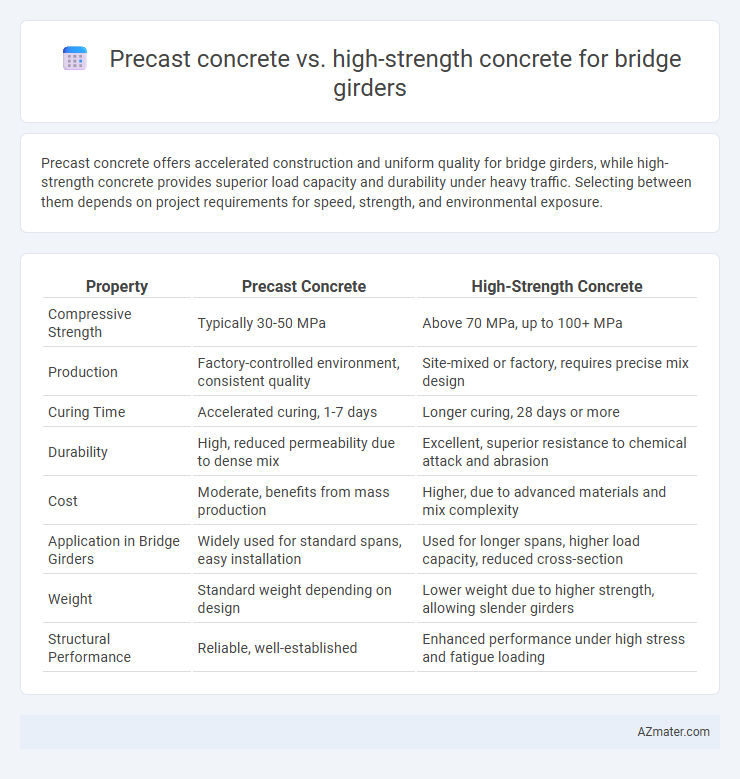
Precast concrete offers accelerated construction and uniform quality for bridge girders, while high-strength concrete provides superior load capacity and durability under heavy traffic. Selecting between them depends on project requirements for speed, strength, and environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Precast Concrete | High-Strength Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Compressive Strength | Typically 30-50 MPa | Above 70 MPa, up to 100+ MPa |
| Production | Factory-controlled environment, consistent quality | Site-mixed or factory, requires precise mix design |
| Curing Time | Accelerated curing, 1-7 days | Longer curing, 28 days or more |
| Durability | High, reduced permeability due to dense mix | Excellent, superior resistance to chemical attack and abrasion |
| Cost | Moderate, benefits from mass production | Higher, due to advanced materials and mix complexity |
| Application in Bridge Girders | Widely used for standard spans, easy installation | Used for longer spans, higher load capacity, reduced cross-section |
| Weight | Standard weight depending on design | Lower weight due to higher strength, allowing slender girders |
| Structural Performance | Reliable, well-established | Enhanced performance under high stress and fatigue loading |
Introduction to Bridge Girder Materials
Bridge girders rely on materials with high durability and load-bearing capacity; precast concrete offers controlled manufacturing conditions, ensuring uniform quality and accelerated construction timelines. High-strength concrete provides superior compressive strength, allowing for slimmer, lighter girders that enhance structural efficiency and reduce material use. Selecting between precast and high-strength concrete depends on project requirements, including span length, load demands, and environmental exposure.
Overview of Precast Concrete in Bridge Construction
Precast concrete offers enhanced quality control, faster installation, and improved durability for bridge girders due to factory-controlled manufacturing environments. This method reduces on-site labor and minimizes construction time while maintaining high structural performance. Precast elements are designed for precise specifications, enabling efficient load distribution and long-term resistance to environmental stressors in bridge applications.
Understanding High-Strength Concrete for Girders
High-strength concrete (HSC) used in bridge girders offers superior compressive strength, typically exceeding 6,000 psi, enabling longer spans and reduced girder sizes compared to conventional precast concrete. Enhanced durability and resistance to environmental stresses make HSC ideal for critical infrastructure requiring extended service life and reduced maintenance costs. Incorporating HSC in bridge girders improves load-carrying capacity and allows more slender designs, optimizing material usage without compromising structural integrity.
Structural Performance Comparison
Precast concrete bridge girders offer consistent quality and accelerated construction due to factory-controlled production, resulting in superior dimensional accuracy and reduced curing time compared to cast-in-place solutions. High-strength concrete, typically exceeding 6000 psi compressive strength, provides enhanced load-bearing capacity and improved durability under heavy traffic and environmental stressors. Structural performance evaluation shows precast girders optimize installation efficiency while high-strength concrete ensures greater resistance to cracking and long-term service performance under dynamic loads.
Durability and Longevity Factors
Precast concrete bridge girders offer enhanced durability due to controlled manufacturing conditions, ensuring uniform curing and reducing the risk of defects that can lead to premature deterioration. High-strength concrete girders provide superior compressive strength, which improves load capacity and resistance to mechanical wear but may exhibit increased brittleness affecting long-term performance under dynamic stresses. The choice between precast and high-strength concrete for bridge girders depends on balancing durability factors like freeze-thaw resistance, chloride ion penetration, and fatigue life to optimize longevity in specific environmental conditions.
Construction Speed and Installation
Precast concrete bridge girders significantly accelerate construction speed by enabling off-site fabrication and rapid on-site installation, reducing overall project timelines. High-strength concrete, while offering enhanced load capacity, often requires longer curing times, potentially delaying installation and extending construction schedules. Choosing precast concrete optimizes efficiency through modular assembly, whereas high-strength concrete may be better suited for customized, in-situ applications demanding exceptional performance.
Cost Analysis: Precast vs High-Strength Concrete
Precast concrete bridge girders typically offer lower labor costs due to factory-controlled production and faster on-site installation, reducing overall project timelines and associated expenses. High-strength concrete, while providing superior load-bearing capacity and durability, often incurs higher material costs and requires specialized on-site mixing and curing processes, increasing labor and quality control expenses. A detailed cost analysis shows precast concrete is more cost-effective for standardized designs, whereas high-strength concrete may justify its premium in projects demanding enhanced performance and longer span capabilities.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Precast concrete bridge girders significantly reduce onsite construction waste and energy consumption, promoting sustainability through factory-controlled production processes and minimized material usage. High-strength concrete requires fewer materials to achieve the same load-bearing capacity, lowering the carbon footprint associated with cement production and transportation. Both methods contribute to environmental conservation, with precast concrete enabling efficient resource management and high-strength concrete supporting durability and long-term structural performance.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifecycle Costs
Precast concrete bridge girders offer reduced maintenance requirements due to factory-controlled quality and uniform curing, leading to fewer cracks and surface defects compared to high-strength concrete girders which may require more frequent inspections and repairs to address potential brittleness and micro-cracking. Lifecycle costs for precast concrete are generally lower as rapid installation minimizes construction time and labor expenses, while high-strength concrete, despite its superior load-bearing capacity, can incur higher long-term maintenance costs due to specialized repair techniques and sensitivity to environmental factors. Selection between these materials depends on balancing initial production quality control against extended durability and maintenance budgets in bridge infrastructure projects.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Case studies in bridge construction reveal that precast concrete girders offer advantages in accelerated project timelines and quality control, as demonstrated by the California High-Speed Rail project where modular precast sections reduced onsite labor and improved durability. High-strength concrete girders, employed in the Millau Viaduct in France, showcase enhanced load-carrying capacity and slender design possibilities, significantly reducing material usage and structural weight. Comparative real-world applications highlight that combining precast techniques with high-strength concrete optimizes both construction efficiency and structural performance in bridge girder production.
Infographic: Precast concrete vs High-strength concrete for Bridge girder
 azmater.com
azmater.com