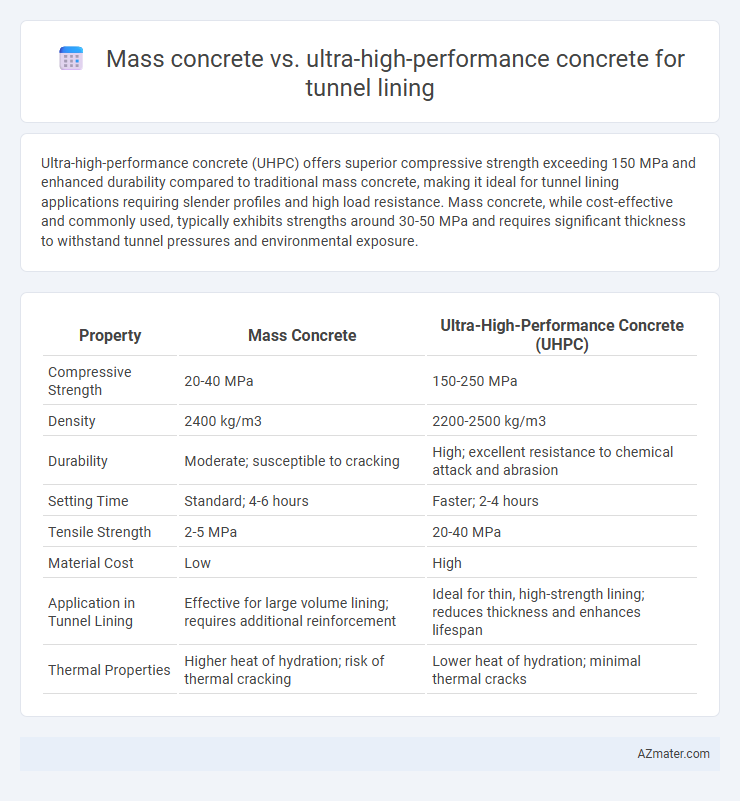
Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) offers superior compressive strength exceeding 150 MPa and enhanced durability compared to traditional mass concrete, making it ideal for tunnel lining applications requiring slender profiles and high load resistance. Mass concrete, while cost-effective and commonly used, typically exhibits strengths around 30-50 MPa and requires significant thickness to withstand tunnel pressures and environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Mass Concrete | Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC) |
|---|---|---|
| Compressive Strength | 20-40 MPa | 150-250 MPa |
| Density | 2400 kg/m3 | 2200-2500 kg/m3 |
| Durability | Moderate; susceptible to cracking | High; excellent resistance to chemical attack and abrasion |
| Setting Time | Standard; 4-6 hours | Faster; 2-4 hours |
| Tensile Strength | 2-5 MPa | 20-40 MPa |
| Material Cost | Low | High |
| Application in Tunnel Lining | Effective for large volume lining; requires additional reinforcement | Ideal for thin, high-strength lining; reduces thickness and enhances lifespan |
| Thermal Properties | Higher heat of hydration; risk of thermal cracking | Lower heat of hydration; minimal thermal cracks |
Introduction to Tunnel Lining Materials
Mass concrete offers robust compressive strength and thermal stability, making it suitable for large-scale tunnel lining applications where durability is critical. Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) exhibits exceptional mechanical properties, including superior tensile strength and enhanced durability, allowing for thinner, lighter tunnel linings with increased lifespan. Selection of tunnel lining materials depends on project requirements, emphasizing structural performance, environmental resistance, and long-term maintenance considerations.
Defining Mass Concrete and Ultra-High-Performance Concrete
Mass concrete for tunnel lining refers to large-volume concrete structures characterized by low heat generation and low permeability, designed to provide structural integrity and durability under underground conditions. Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) is a type of advanced concrete with superior compressive strength often exceeding 150 MPa, enhanced durability, and enhanced ductility, achieved through optimized mix designs including fine powders, fibers, and low water-to-cement ratios. The key distinctions between mass concrete and UHPC in tunnel lining applications lie in the material properties, such as UHPC's exceptional mechanical performance and durability compared to the traditional, cost-effective mass concrete used for extensive volume.
Structural Performance: Strength and Durability
Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) offers superior structural performance for tunnel lining, exhibiting compressive strengths exceeding 150 MPa and exceptional durability against chemical and environmental attacks. Mass concrete, while commonly used, typically has lower compressive strength around 20-40 MPa and is more susceptible to cracking and degradation over time. The enhanced fiber reinforcement and dense microstructure of UHPC significantly improve toughness, flexural capacity, and lifespan compared to traditional mass concrete in tunnel lining applications.
Crack Resistance and Shrinkage
Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) offers superior crack resistance and significantly reduced shrinkage compared to mass concrete, making it ideal for tunnel lining applications where durability and structural integrity are critical. UHPC's dense microstructure and enhanced tensile strength minimize microcrack formation, effectively mitigating potential damage caused by shrinkage stresses over time. In contrast, mass concrete exhibits higher shrinkage and increased susceptibility to cracking due to its coarser aggregate and lower tensile capacity, which may compromise tunnel lining longevity and safety.
Workability and Placement Considerations
Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) offers superior workability compared to traditional mass concrete due to its optimized particle packing and reduced water-cement ratio, allowing for easier placement and better flow in complex tunnel geometries. Mass concrete often requires careful management to prevent segregation and ensure uniform placement, especially in large-scale tunnel linings where thermal cracking risks are significant. UHPC's enhanced rheological properties reduce the need for vibration during placement, improving safety and efficiency in confined tunnel environments.
Cost Implications and Life Cycle Analysis
Mass concrete offers lower initial material and placement costs for tunnel lining, but Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC) provides superior durability, reducing maintenance and life cycle expenses significantly. UHPC's enhanced mechanical properties and resistance to environmental degradation extend tunnel service life, offsetting its higher upfront costs through reduced repair frequency and lifecycle interventions. Life cycle analysis confirms that despite higher initial investment, UHPC delivers greater long-term economic value and reduced total cost of ownership in tunnel infrastructure.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Mass concrete used in tunnel lining typically has a higher carbon footprint due to its large volume and lower cement efficiency, whereas ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) offers enhanced durability and reduced material content, leading to a smaller environmental impact over the tunnel's lifecycle. UHPC's superior strength and longevity minimize maintenance needs and associated emissions, promoting sustainability in subterranean infrastructure. Selecting UHPC contributes to resource conservation and reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional mass concrete applications in tunnel construction.
Maintenance Needs and Longevity
Mass concrete used in tunnel lining offers substantial structural strength but often requires more frequent maintenance due to its lower durability and susceptibility to cracking under environmental stress. Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) boasts superior durability, enhanced resistance to chemical attack, and significantly reduced permeability, resulting in extended service life and minimal maintenance demands. The advanced microstructure of UHPC contributes to its longevity, making it a preferred choice for tunnel lining applications where long-term performance and reduced maintenance costs are critical.
Case Studies: Tunnel Lining Applications
Mass concrete in tunnel lining offers durability and cost-effectiveness, demonstrated by the Gotthard Base Tunnel in Switzerland, where traditional mass concrete provided structural stability over extensive lengths. Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC), as utilized in the Lyon-Turin Base Tunnel project, delivers superior mechanical properties, enhanced durability, and reduced thickness, enabling faster installation and improved tunnel safety. Comparative case studies reveal UHPC's advantages in corrosive environments and complex geometries, while mass concrete remains a viable choice for large-scale projects with standard performance requirements.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Concrete for Tunnel Linings
Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) offers superior strength, durability, and reduced permeability compared to traditional mass concrete, making it highly suitable for critical tunnel lining applications exposed to aggressive environments. While mass concrete remains cost-effective for large-scale, standard tunnel projects, UHPC's enhanced mechanical properties and longevity justify its higher initial investment in tunnels requiring increased structural performance and extended service life. Selecting the optimal concrete depends on balancing project-specific demands for durability, load-bearing capacity, and maintenance considerations against upfront material and construction costs.
Infographic: Mass concrete vs Ultra-high-performance concrete for Tunnel lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com