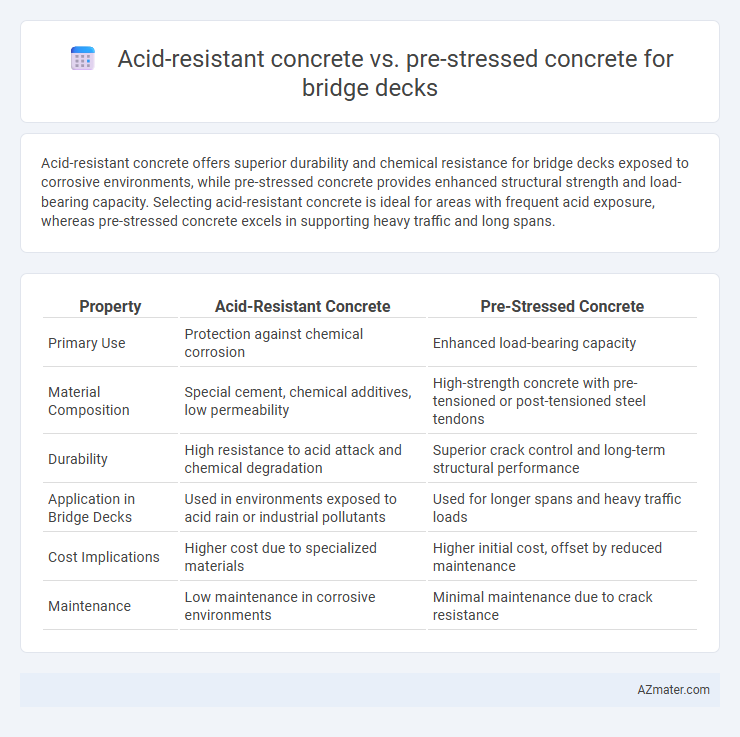
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior durability and chemical resistance for bridge decks exposed to corrosive environments, while pre-stressed concrete provides enhanced structural strength and load-bearing capacity. Selecting acid-resistant concrete is ideal for areas with frequent acid exposure, whereas pre-stressed concrete excels in supporting heavy traffic and long spans.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acid-Resistant Concrete | Pre-Stressed Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Protection against chemical corrosion | Enhanced load-bearing capacity |
| Material Composition | Special cement, chemical additives, low permeability | High-strength concrete with pre-tensioned or post-tensioned steel tendons |
| Durability | High resistance to acid attack and chemical degradation | Superior crack control and long-term structural performance |
| Application in Bridge Decks | Used in environments exposed to acid rain or industrial pollutants | Used for longer spans and heavy traffic loads |
| Cost Implications | Higher cost due to specialized materials | Higher initial cost, offset by reduced maintenance |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance in corrosive environments | Minimal maintenance due to crack resistance |
Introduction to Bridge Deck Concrete Types
Acid-resistant concrete is specifically formulated with chemical additives and specialized aggregates to withstand corrosive environments, enhancing durability in bridge decks exposed to industrial pollutants or acidic rain. Pre-stressed concrete utilizes high-tensile steel tendons tensioned before loading to improve load-bearing capacity and reduce cracking in bridge decks, making it ideal for spans requiring high strength and flexibility. Selecting between these types depends on environmental exposure and structural demands, with acid-resistant concrete prioritizing chemical protection and pre-stressed concrete emphasizing mechanical performance.
Overview of Acid-Resistant Concrete
Acid-resistant concrete for bridge decks is engineered to withstand harsh chemical environments, particularly aggressive acidic conditions caused by industrial pollutants or de-icing salts. It incorporates special cement types, such as sulfate-resisting Portland cement, and additives like silica fume or fly ash to enhance chemical durability and reduce permeability. This concrete type offers superior longevity in corrosive settings compared to traditional or pre-stressed concrete, making it ideal for infrastructure exposed to acidic agents.
Understanding Pre-Stressed Concrete
Pre-stressed concrete for bridge decks offers enhanced tensile strength by introducing internal compressive forces through tensioned steel tendons, reducing cracking and improving durability under dynamic loads. Unlike acid-resistant concrete, which primarily protects against chemical attacks from acidic environments, pre-stressed concrete focuses on structural performance and long span capability. Its optimized load distribution and minimized deflection make pre-stressed concrete ideal for highway and railway bridge decks requiring high strength-to-weight ratios and extended service life.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Acid-resistant concrete for bridge decks features enhanced chemical durability due to additives like silica fume and polymer modifiers, providing superior resistance to acidic environments and sulfate attack. Pre-stressed concrete offers high tensile strength and crack control by incorporating tensioned steel tendons, resulting in improved load-bearing capacity and reduced deflections under heavy traffic loads. While acid-resistant concrete focuses on chemical stability and longevity in corrosive conditions, pre-stressed concrete emphasizes structural performance and durability under mechanical stresses.
Durability in Aggressive Environments
Acid-resistant concrete offers enhanced durability in aggressive environments by incorporating specialized cementitious materials and chemical additives that protect against acid attack and corrosion, making it ideal for bridge decks exposed to industrial pollutants or acidic rain. Pre-stressed concrete provides high tensile strength and crack resistance, reducing permeability but may require additional protective coatings to withstand prolonged exposure to acidic conditions. Combining acid-resistant properties with pre-stressing techniques can significantly extend the service life of bridge decks in aggressive environments.
Structural Performance and Load-Bearing Capacity
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior durability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for bridge decks exposed to corrosive environments, thus maintaining structural integrity under aggressive conditions. Pre-stressed concrete provides enhanced load-bearing capacity and crack control through the application of pre-tensioned or post-tensioned reinforcement, enabling longer spans and reduced structural deflections. While pre-stressed concrete excels in managing tensile stresses and heavy traffic loads, acid-resistant concrete ensures longevity against chemical attack, with both materials significantly improving the safety and lifespan of bridge decks.
Installation and Construction Techniques
Acid-resistant concrete for bridge decks requires specialized mixing and curing processes to ensure durability against chemical exposure, often involving precise additive integration and protective coatings applied during installation. Pre-stressed concrete involves tensioning steel tendons before or after concrete pouring, demanding meticulous placement of formwork and post-tensioning equipment to achieve optimal load distribution and structural integrity. Both methods require skilled labor and rigorous quality control, but pre-stressed concrete generally allows for faster construction times due to modular precasting and streamlined tensioning procedures.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Costs
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior durability in environments exposed to chemical attacks, significantly reducing maintenance frequency and associated costs over the bridge deck's lifecycle. Pre-stressed concrete provides enhanced structural performance and crack control but may require more frequent inspections and repairs due to potential corrosion of prestressing tendons. Evaluating lifecycle costs, acid-resistant concrete can lead to lower long-term expenses in chemically aggressive settings, whereas pre-stressed concrete may optimize initial construction costs with moderate maintenance demands.
Suitability for Different Bridge Locations
Acid-resistant concrete is ideal for bridge decks in industrial or coastal areas where exposure to acidic rain, chemicals, or saltwater can cause corrosion and deterioration. Pre-stressed concrete suits locations requiring high load-bearing capacity and longer spans, such as urban highways or heavy traffic bridges. Selecting concrete type depends on environmental conditions and structural demands to ensure durability and performance.
Final Recommendations and Best Practices
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior durability against chemical attack, making it ideal for bridge decks exposed to industrial pollutants or acidic environments, while pre-stressed concrete provides enhanced load-bearing capacity and crack control suited for long-span bridges. Selecting acid-resistant concrete is recommended when bridges face aggressive chemical exposure to reduce maintenance costs and extend service life, whereas pre-stressed concrete is best for high-traffic or heavy-load conditions requiring structural efficiency and reduced deflections. Combining both methods through layered or composite designs can optimize performance, ensuring resistance to environmental degradation alongside structural robustness.
Infographic: Acid-resistant concrete vs Pre-stressed concrete for Bridge deck
 azmater.com
azmater.com