Nano-concrete incorporates nanoparticles to enhance strength and durability, making it ideal for high-performance block construction. Lightweight concrete uses lightweight aggregates to reduce density and improve thermal insulation, suitable for energy-efficient block applications.
Table of Comparison
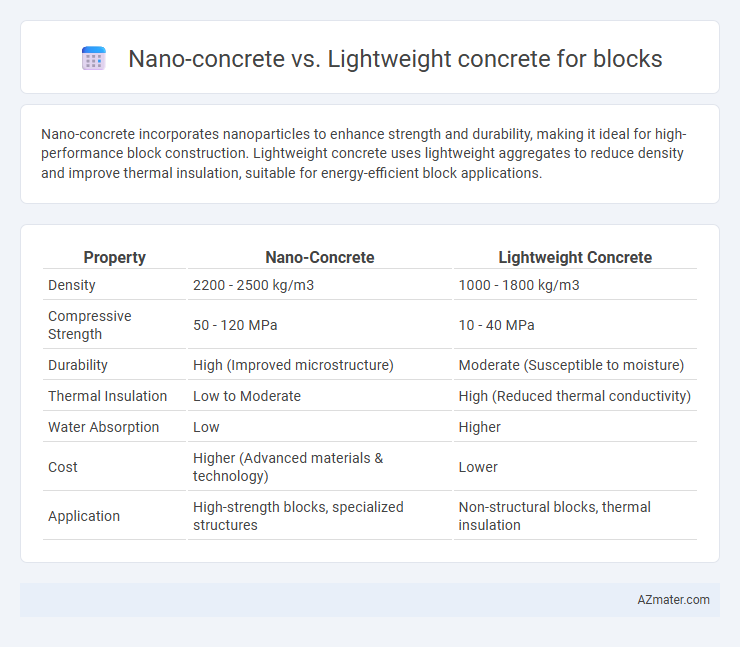
| Property | Nano-Concrete | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 2200 - 2500 kg/m3 | 1000 - 1800 kg/m3 |
| Compressive Strength | 50 - 120 MPa | 10 - 40 MPa |
| Durability | High (Improved microstructure) | Moderate (Susceptible to moisture) |
| Thermal Insulation | Low to Moderate | High (Reduced thermal conductivity) |
| Water Absorption | Low | Higher |
| Cost | Higher (Advanced materials & technology) | Lower |
| Application | High-strength blocks, specialized structures | Non-structural blocks, thermal insulation |
Introduction to Nano-concrete and Lightweight Concrete
Nano-concrete incorporates nanoparticles such as silica fume and nano-silica to enhance strength, durability, and microstructure compared to conventional concrete. Lightweight concrete utilizes lightweight aggregates like expanded clay, pumice, or vermiculite to reduce density and improve thermal insulation while maintaining adequate structural performance. Both materials address specific construction needs, with nano-concrete excelling in mechanical properties and lightweight concrete offering weight reduction and energy efficiency benefits.
Composition and Material Science
Nano-concrete incorporates nanoparticles like silica fume, titanium dioxide, and nano-silica to enhance microstructure, resulting in superior strength and durability compared to lightweight concrete, which primarily uses expanded clay, shale, or pumice aggregates to reduce density and improve insulation. The nano-scale additives in nano-concrete optimize hydration processes and reduce porosity, while lightweight concrete achieves low weight and thermal resistance by replacing conventional aggregates with low-density materials. Both materials exhibit distinct microstructural and compositional differences driven by their intended structural and thermal performance characteristics.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Nano-concrete exhibits significantly enhanced mechanical properties compared to lightweight concrete, with compressive strength improvements ranging from 15% to 30% due to the nano-scale reinforcement of cementitious materials. The incorporation of nanoparticles refines the microstructure, resulting in higher tensile strength and better durability under load. Lightweight concrete, while beneficial for reducing structural weight, typically demonstrates lower compressive strength and stiffness, making nano-concrete a superior choice for high-performance block applications requiring enhanced mechanical resilience.
Durability and Longevity
Nano-concrete incorporates nanoparticles that significantly enhance its microstructure, resulting in superior durability and resistance to cracking compared to lightweight concrete blocks. Lightweight concrete blocks, while offering reduced weight and improved thermal insulation, typically exhibit lower compressive strength and are more prone to moisture penetration, which can affect their longevity. The advanced nanoparticle integration in nano-concrete contributes to increased density and reduced porosity, making it a more durable and long-lasting option for structural and non-structural block applications.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation
Nano-concrete exhibits superior thermal insulation due to its enhanced density and reduced pore size, which significantly minimizes heat transfer compared to lightweight concrete. Its nanomaterial additives improve acoustic absorption, providing better soundproofing qualities in block construction. Lightweight concrete, while offering moderate thermal insulation through its air-entrained structure, generally falls short in acoustic performance when compared to the advanced nano-concrete composites.
Workability and Ease of Construction
Nano-concrete exhibits superior workability due to its enhanced particle packing and reduced water demand, facilitating easier mixing and application in block production. Lightweight concrete, while easier to handle because of its reduced density, may present challenges in workability and compaction compared to nano-concrete. The improved rheological properties of nano-concrete contribute to faster construction times and higher quality blocks with fewer defects.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Nano-concrete offers enhanced durability and reduced material usage due to its superior microstructure, leading to lower carbon emissions during production compared to traditional lightweight concrete blocks. Lightweight concrete blocks provide better thermal insulation, reducing energy consumption in buildings, but often require more cement, contributing to higher environmental footprints. Sustainable construction benefits from nano-concrete's potential to extend structural lifespan and decrease resource extraction, aligning with green building standards and carbon reduction goals.
Cost-effectiveness and Economic Analysis
Nano-concrete offers enhanced mechanical properties and durability, potentially reducing lifecycle costs despite higher initial material expenses compared to traditional lightweight concrete blocks. Lightweight concrete blocks remain popular for cost-effectiveness due to lower raw material and production costs, making them suitable for large-scale, budget-conscious projects. Economic analysis often favors lightweight concrete for upfront savings, while nano-concrete may deliver better long-term value through reduced maintenance and increased structural performance.
Typical Applications in Block Construction
Nano-concrete enhances block construction by providing superior strength and durability, making it ideal for load-bearing walls and seismic-resistant structures. Lightweight concrete blocks are preferred for non-load-bearing partitions and thermal insulation due to their reduced density and improved energy efficiency. Both materials are commonly utilized in residential and commercial buildings, with nano-concrete offering advanced performance in high-stress applications.
Future Trends and Innovations
Nano-concrete integrates nanoparticles to enhance durability, strength, and self-healing properties, positioning it as a forefront innovation in sustainable block construction. Lightweight concrete prioritizes thermal insulation and reduced dead load, with future trends focusing on bio-based aggregates and improved fire resistance. Emerging research explores hybrid composites combining nano-additives with lightweight matrices to maximize performance and environmental benefits in block applications.
Infographic: Nano-concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Block
 azmater.com
azmater.com