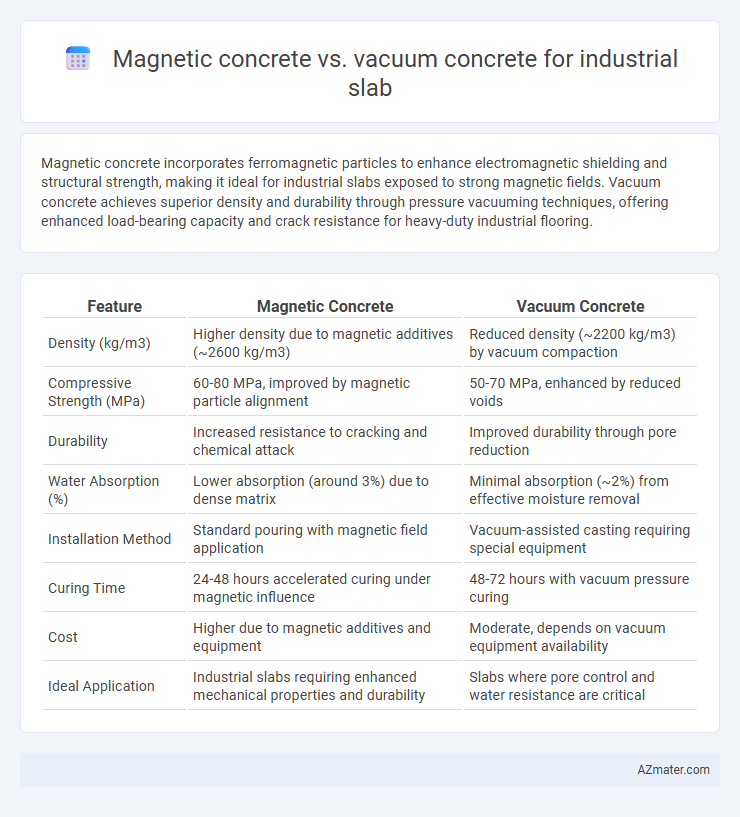
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic particles to enhance electromagnetic shielding and structural strength, making it ideal for industrial slabs exposed to strong magnetic fields. Vacuum concrete achieves superior density and durability through pressure vacuuming techniques, offering enhanced load-bearing capacity and crack resistance for heavy-duty industrial flooring.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Magnetic Concrete | Vacuum Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density (kg/m3) | Higher density due to magnetic additives (~2600 kg/m3) | Reduced density (~2200 kg/m3) by vacuum compaction |
| Compressive Strength (MPa) | 60-80 MPa, improved by magnetic particle alignment | 50-70 MPa, enhanced by reduced voids |
| Durability | Increased resistance to cracking and chemical attack | Improved durability through pore reduction |
| Water Absorption (%) | Lower absorption (around 3%) due to dense matrix | Minimal absorption (~2%) from effective moisture removal |
| Installation Method | Standard pouring with magnetic field application | Vacuum-assisted casting requiring special equipment |
| Curing Time | 24-48 hours accelerated curing under magnetic influence | 48-72 hours with vacuum pressure curing |
| Cost | Higher due to magnetic additives and equipment | Moderate, depends on vacuum equipment availability |
| Ideal Application | Industrial slabs requiring enhanced mechanical properties and durability | Slabs where pore control and water resistance are critical |
Introduction to Magnetic Concrete and Vacuum Concrete
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic materials that enhance electromagnetic properties, offering improved structural health monitoring and potential energy harvesting capabilities for industrial slabs. Vacuum concrete utilizes a vacuum dewatering process to increase density and strength while reducing water content, resulting in superior durability and early strength gain for industrial flooring. Both technologies address specific industrial demands by optimizing concrete performance through distinct material and processing innovations.
Key Differences Between Magnetic and Vacuum Concrete
Magnetic concrete incorporates magnetic particles to enhance strength and durability, while vacuum concrete utilizes vacuum techniques to remove air bubbles, resulting in higher density and reduced porosity. Magnetic concrete is primarily valued for its electromagnetic properties and increased wear resistance, whereas vacuum concrete excels in compressive strength and improved bond with reinforcement due to its compact microstructure. The choice between magnetic and vacuum concrete for industrial slabs depends on requirements for magnetic functionality versus mechanical integrity and longevity.
Material Composition of Magnetic vs. Vacuum Concrete
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic materials like iron filings or steel fibers within the cement matrix to enhance electromagnetic properties and improve structural integrity, while vacuum concrete relies on vacuum-assisted dewatering techniques to reduce water content and increase density for superior strength. The material composition of magnetic concrete is tailored for electromagnetic responsiveness and durability, whereas vacuum concrete's formulation emphasizes optimized particle packing and minimal voids. These compositional differences impact performance characteristics crucial for industrial slab applications, such as load-bearing capacity and lifespan.
Installation Process for Industrial Slabs
Magnetic concrete installation for industrial slabs involves embedding magnetic particles within the mix, allowing for enhanced alignment and compaction using magnetic vibrators, which reduces voids and improves structural integrity. Vacuum concrete requires a specialized vacuum system to extract entrapped air and excess water immediately after pouring, enhancing density and strength while accelerating curing times. Both methods demand precise equipment setup and skilled operators to ensure optimal slab durability but differ significantly in technique and equipment complexity.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Magnetic concrete enhances inter-particle bonding through electromagnetic fields, resulting in higher compressive strength and improved microstructure density compared to traditional vacuum concrete. Vacuum concrete achieves strength gains by removing entrapped air, reducing porosity, yet may fall short in long-term durability under cyclic industrial loads. In industrial slabs, magnetic concrete offers superior resistance to cracking and wear, making it more durable for heavy-duty applications.
Surface Finish and Quality Outcomes
Magnetic concrete offers superior surface finish due to its enhanced compaction and reduced porosity, resulting in a denser, smoother industrial slab ideal for heavy-duty applications. Vacuum concrete extraction removes trapped air and excess water, improving slab uniformity and minimizing shrinkage cracks, which enhances surface integrity and overall durability. Both methods significantly improve quality outcomes, but magnetic concrete is preferred when a high-gloss, imperfection-free finish is critical.
Cost Analysis: Magnetic Concrete vs. Vacuum Concrete
Magnetic concrete typically incurs higher initial costs due to the integration of magnetic materials and specialized mixing processes, whereas vacuum concrete involves additional equipment and labor for air removal, impacting overall expenses. Maintenance and long-term durability costs favor magnetic concrete as its enhanced material properties reduce repair frequency compared to vacuum concrete's susceptibility to micro-cracking. Cost analysis reveals magnetic concrete offers better lifecycle value despite upfront expenditure, while vacuum concrete presents lower initial investment but potentially higher ongoing maintenance costs for industrial slab applications.
Applications in Industrial Environments
Magnetic concrete enhances industrial slabs by improving electromagnetic interference shielding and supporting machinery that relies on magnetic properties, making it ideal for manufacturing plants with sensitive electronic equipment. Vacuum concrete offers superior density and reduced porosity, resulting in higher compressive strength and durability, which is critical for heavy-load industrial floors like warehouses or factories handling large machinery. Both materials address different industrial needs, with magnetic concrete favoring electromagnetic applications and vacuum concrete excellence in structural integrity and longevity.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic materials that enable recycling and reduce material waste, enhancing sustainability in industrial slabs by lowering the demand for virgin aggregates. Vacuum concrete significantly improves durability and minimizes permeability, which extends slab life and reduces maintenance frequency, thereby decreasing environmental impact over time. Both technologies contribute to eco-friendly construction by optimizing resource use and promoting long-term structural performance in industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Concrete Type for Your Project
Magnetic concrete enhances compaction through electromagnetic vibration, resulting in higher density and increased durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty industrial slabs requiring superior load-bearing capacity. Vacuum concrete utilizes a vacuum process to remove excess water, improving strength and reducing shrinkage, which is beneficial for projects needing rapid curing and minimal surface defects. Selecting between magnetic and vacuum concrete depends on project priorities such as load intensity, curing time, and surface quality to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Magnetic concrete vs Vacuum concrete for Industrial slab
 azmater.com
azmater.com