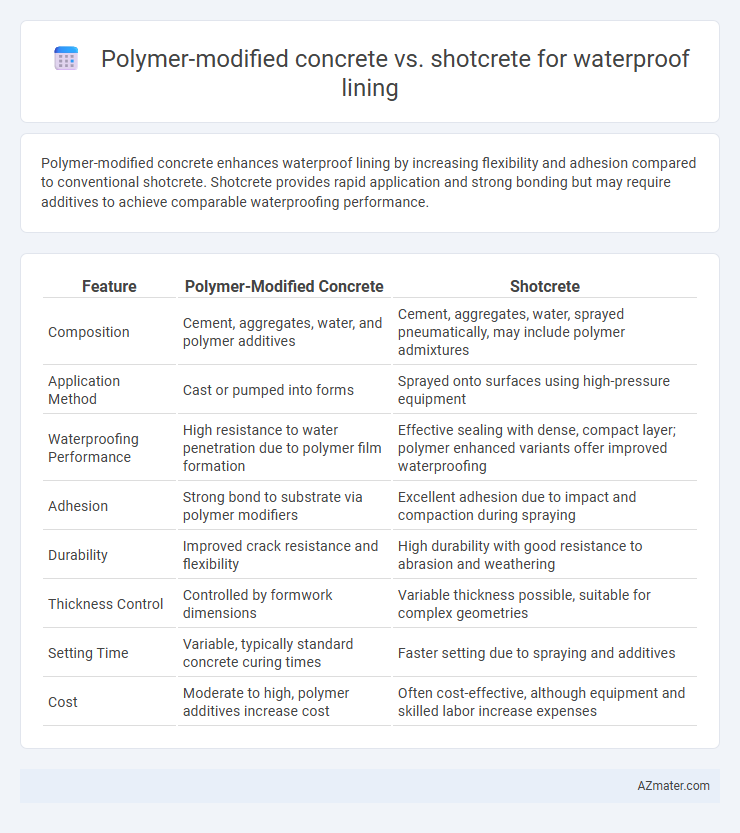
Polymer-modified concrete enhances waterproof lining by increasing flexibility and adhesion compared to conventional shotcrete. Shotcrete provides rapid application and strong bonding but may require additives to achieve comparable waterproofing performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polymer-Modified Concrete | Shotcrete |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Cement, aggregates, water, and polymer additives | Cement, aggregates, water, sprayed pneumatically, may include polymer admixtures |
| Application Method | Cast or pumped into forms | Sprayed onto surfaces using high-pressure equipment |
| Waterproofing Performance | High resistance to water penetration due to polymer film formation | Effective sealing with dense, compact layer; polymer enhanced variants offer improved waterproofing |
| Adhesion | Strong bond to substrate via polymer modifiers | Excellent adhesion due to impact and compaction during spraying |
| Durability | Improved crack resistance and flexibility | High durability with good resistance to abrasion and weathering |
| Thickness Control | Controlled by formwork dimensions | Variable thickness possible, suitable for complex geometries |
| Setting Time | Variable, typically standard concrete curing times | Faster setting due to spraying and additives |
| Cost | Moderate to high, polymer additives increase cost | Often cost-effective, although equipment and skilled labor increase expenses |
Introduction to Waterproof Lining Solutions
Polymer-modified concrete enhances waterproof lining solutions by providing superior adhesion, flexibility, and resistance to water penetration compared to traditional materials. Shotcrete offers efficient application through sprayed layers, ensuring uniform coverage and quick setting, ideal for complex surfaces and repairs. Both materials improve durability and waterproofing performance, with polymer-modified concrete excelling in chemical resistance and shotcrete favored for rapid installation.
Overview of Polymer-Modified Concrete
Polymer-modified concrete enhances traditional concrete by incorporating polymer additives, improving adhesion, flexibility, and impermeability essential for waterproof lining. These polymers reduce micro-cracking and increase resistance to chemical attacks, making it ideal for structures exposed to water and harsh environments. Compared to shotcrete, polymer-modified concrete offers superior durability and longer-lasting waterproof performance in critical infrastructure projects.
Understanding Shotcrete in Tunnel and Waterproof Applications
Shotcrete, a pneumatically applied concrete mixture, offers superior adhesion and rapid setting, making it ideal for tunnel waterproof lining where immediate structural support is critical. Unlike polymer-modified concrete, shotcrete incorporates fibers or additives directly into the spray process, enhancing water resistance and durability against groundwater infiltration. Its versatility in application thickness and ability to conform to complex tunnel geometries make shotcrete a preferred choice for effective waterproof lining in underground construction projects.
Material Composition and Properties Comparison
Polymer-modified concrete incorporates synthetic polymers enhancing adhesion, flexibility, and impermeability, making it highly effective for waterproof lining applications requiring durability and crack resistance. Shotcrete, a pneumatically applied concrete mix often reinforced with fibers or polymers, offers superior mechanical properties and rapid setting times, which improve its applicability in complex surface geometries and vertical or overhead structures. Comparing material composition, polymer-modified concrete emphasizes improved polymer matrix integration, while shotcrete's strength lies in its delivery method combined with tailored admixtures for optimized bonding and water resistance.
Installation Techniques and Application Methods
Polymer-modified concrete enhances waterproof lining through improved adhesion and flexibility, applied using conventional casting or troweling methods that ensure uniform coverage and crack resistance. Shotcrete, sprayed pneumatically at high velocity, enables rapid application on complex surfaces, providing dense compaction and strong bonding ideal for irregular or vertical structures. Installation of polymer-modified concrete often requires curing protocols for optimal durability, whereas shotcrete demands skilled nozzle control to prevent rebound and achieve consistent thickness.
Performance in Waterproofing and Durability
Polymer-modified concrete exhibits superior waterproofing performance due to its enhanced adhesion, reduced permeability, and resistance to chemical attack compared to traditional shotcrete formulations. Shotcrete provides quick application and high early strength but often requires additional waterproofing layers to achieve comparable durability in wet environments. The integration of polymers in concrete significantly improves its durability by minimizing micro-cracks, increasing flexibility, and extending the lifespan of waterproof linings under hydrostatic pressure.
Cost Analysis: Polymer-Modified Concrete vs Shotcrete
Polymer-modified concrete generally incurs higher upfront costs due to expensive polymer additives and specialized mixing requirements, yet offers enhanced durability and reduced permeability that can lower long-term maintenance expenses in waterproof linings. Shotcrete typically presents lower initial costs because of faster application and reduced formwork needs, making it cost-effective for large or complex surface areas. Evaluating overall project budgets requires balancing the higher material costs of polymer-modified concrete against the labor savings and application efficiency of shotcrete in waterproof lining applications.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Polymer-modified concrete offers enhanced durability and reduced permeability, significantly extending the lifespan of waterproof linings and minimizing resource consumption over time. Shotcrete, while providing rapid application and strong adhesion, may involve higher energy use and emissions due to its pneumatic application methods. Selecting polymer-modified concrete supports sustainability goals by lowering maintenance frequency and reducing environmental impact through improved material performance and longevity.
Common Challenges and Limitations
Polymer-modified concrete and shotcrete both enhance waterproof lining but face challenges such as shrinkage cracking and adhesion issues on damp or uneven surfaces. Polymer-modified concrete may suffer from limited workability and higher material costs, while shotcrete can experience rebound loss and inconsistency in thickness during application. Both methods require precise curing conditions to prevent permeability and ensure long-term durability in waterproofing applications.
Selecting the Right Solution: Key Factors to Consider
Polymer-modified concrete offers enhanced adhesion, flexibility, and chemical resistance, making it suitable for waterproof lining in aggressive environments, while shotcrete provides quick application and excellent bonding in complex geometries. Key factors for selecting between the two include substrate condition, project complexity, exposure to water pressure, and required curing time. Evaluating durability requirements, structural movement tolerance, and cost-effectiveness ensures optimal waterproof performance and longevity.
Infographic: Polymer-modified concrete vs Shotcrete for Waterproof lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com