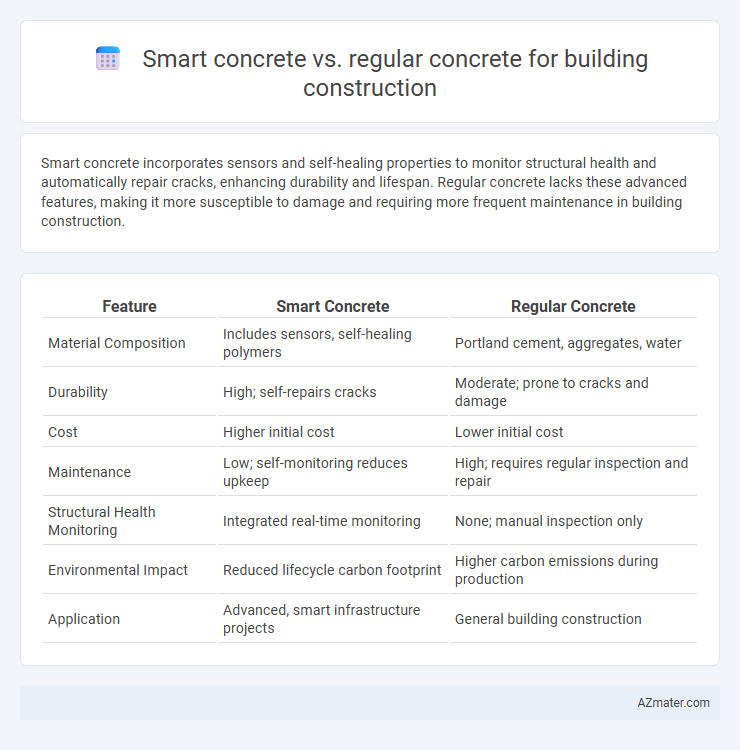
Smart concrete incorporates sensors and self-healing properties to monitor structural health and automatically repair cracks, enhancing durability and lifespan. Regular concrete lacks these advanced features, making it more susceptible to damage and requiring more frequent maintenance in building construction.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Smart Concrete | Regular Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Includes sensors, self-healing polymers | Portland cement, aggregates, water |
| Durability | High; self-repairs cracks | Moderate; prone to cracks and damage |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Maintenance | Low; self-monitoring reduces upkeep | High; requires regular inspection and repair |
| Structural Health Monitoring | Integrated real-time monitoring | None; manual inspection only |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced lifecycle carbon footprint | Higher carbon emissions during production |
| Application | Advanced, smart infrastructure projects | General building construction |
Introduction to Smart Concrete and Regular Concrete
Smart concrete incorporates advanced materials like carbon nanotubes and sensors to enhance durability, self-sensing, and crack detection, offering significant improvements over traditional construction materials. Regular concrete, composed primarily of cement, water, and aggregates, provides structural strength but lacks the intelligent properties for real-time monitoring or self-repair capabilities. The integration of smart technologies in concrete transforms building construction by enabling proactive maintenance and extending structural lifespan.
Composition Differences: Smart vs Regular Concrete
Smart concrete incorporates advanced materials such as carbon fibers, piezoelectric sensors, or nanoparticles, enhancing its self-sensing, self-healing, and durability properties compared to regular concrete. Regular concrete primarily consists of cement, aggregates, water, and chemical admixtures designed to meet basic structural requirements without embedded functional materials. The integration of conductive or responsive components in smart concrete significantly improves its performance monitoring and maintenance capabilities.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Smart concrete exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength than regular concrete due to the incorporation of nanomaterials and advanced additives that enhance compressive and tensile properties. Its durability surpasses that of traditional concrete by offering improved resistance to cracking, environmental degradation, and chemical attacks, resulting in longer service life and reduced maintenance costs. Smart concrete's self-sensing capabilities further enable early damage detection, ensuring structural integrity throughout the building's lifespan.
Self-Monitoring Capabilities of Smart Concrete
Smart concrete incorporates embedded sensors or conductive materials that enable real-time self-monitoring of structural health by detecting cracks, stress, and deformation. Unlike regular concrete, which requires external inspections for damage assessment, smart concrete provides continuous data, enhancing safety and maintenance efficiency in building construction. This proactive monitoring helps reduce repair costs and extends the lifespan of structures through timely interventions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Smart concrete integrates sensors and self-healing properties, significantly reducing maintenance needs and extending the lifespan of structures, which lowers overall resource consumption and waste. Its ability to monitor structural health in real time enables proactive repairs, minimizing environmental degradation compared to regular concrete that often requires frequent repairs or replacement. Reduced carbon emissions and waste generation from extended durability make smart concrete a more sustainable option in building construction.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Lifecycle
Smart concrete, embedded with sensors and self-healing properties, demands a higher initial investment compared to regular concrete, typically increasing upfront costs by 20-40%. Lifecycle analysis reveals that smart concrete can reduce maintenance expenses by up to 30%, extending structural lifespan through early damage detection and autonomous repair. Despite elevated initial costs, smart concrete offers superior long-term economic benefits by lowering repair frequency and improving durability in building construction.
Applications in Modern Building Construction
Smart concrete integrates sensors and self-healing properties to monitor structural health and enhance durability in modern building construction, enabling real-time data on stress, cracks, and temperature changes. Regular concrete, while cost-effective and widely used for foundational elements, lacks adaptive features and requires frequent maintenance to address wear and damage over time. Employing smart concrete in critical infrastructure like bridges, high-rise buildings, and seismic zones improves safety, reduces maintenance costs, and extends the service life of structures.
Maintenance and Long-Term Performance
Smart concrete incorporates self-healing properties and embedded sensors that enable real-time monitoring of structural health, reducing the need for frequent maintenance compared to regular concrete. Enhanced durability and crack resistance in smart concrete contribute to a longer lifespan and lower repair costs over time. Regular concrete lacks these advanced features, often leading to higher maintenance requirements and increased risk of premature deterioration in building construction.
Safety and Structural Health Monitoring Benefits
Smart concrete integrates embedded sensors that enable real-time structural health monitoring by detecting stress, cracks, and temperature changes, significantly enhancing building safety. This technology allows for early identification of potential failures, reducing the risk of catastrophic collapse compared to regular concrete. The continuous data collection supports proactive maintenance and extends the lifespan of structures, providing superior safety advantages over traditional concrete construction.
Future Trends in Concrete Technology
Smart concrete integrates sensors and self-healing properties to enhance structural health monitoring and longevity, outperforming regular concrete in durability and maintenance. Future trends emphasize the development of multifunctional smart concrete with embedded nanomaterials for improved strength, energy efficiency, and real-time data analytics. Advanced AI-driven predictive maintenance and 3D printing technologies are set to revolutionize the deployment of smart concrete in sustainable urban infrastructure.
Infographic: Smart concrete vs Regular concrete for Building construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com