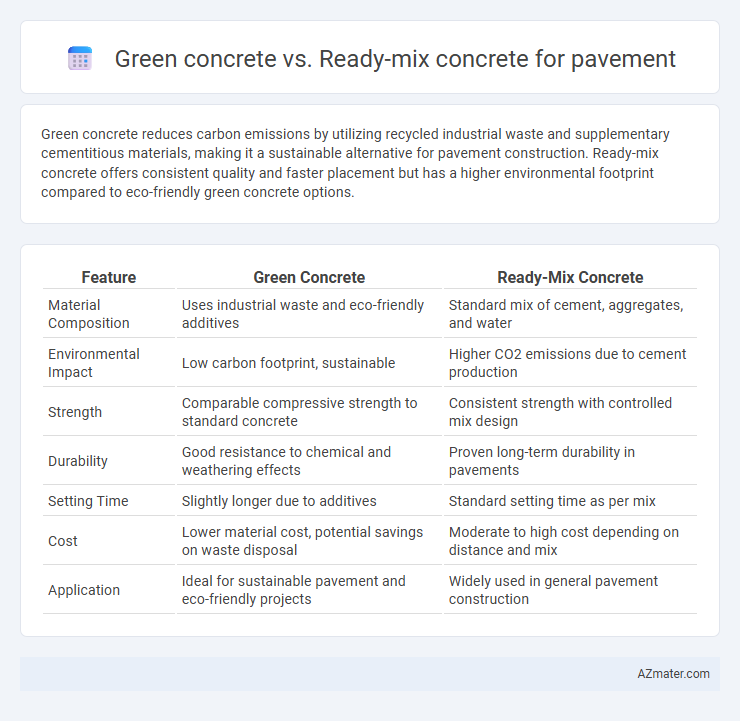
Green concrete reduces carbon emissions by utilizing recycled industrial waste and supplementary cementitious materials, making it a sustainable alternative for pavement construction. Ready-mix concrete offers consistent quality and faster placement but has a higher environmental footprint compared to eco-friendly green concrete options.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Green Concrete | Ready-Mix Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Uses industrial waste and eco-friendly additives | Standard mix of cement, aggregates, and water |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, sustainable | Higher CO2 emissions due to cement production |
| Strength | Comparable compressive strength to standard concrete | Consistent strength with controlled mix design |
| Durability | Good resistance to chemical and weathering effects | Proven long-term durability in pavements |
| Setting Time | Slightly longer due to additives | Standard setting time as per mix |
| Cost | Lower material cost, potential savings on waste disposal | Moderate to high cost depending on distance and mix |
| Application | Ideal for sustainable pavement and eco-friendly projects | Widely used in general pavement construction |
Introduction to Green Concrete and Ready-Mix Concrete
Green concrete incorporates recycled materials and industrial by-products such as fly ash, slag, and silica fume, reducing carbon emissions and environmental impact during pavement construction. Ready-mix concrete is a pre-mixed, factory-produced concrete delivered to the site, ensuring consistent quality, precise mix proportions, and reduced material waste for efficient pavement projects. Both types enhance pavement durability, but green concrete contributes significantly to sustainability in modern infrastructure development.
Composition and Raw Materials
Green concrete for pavement incorporates industrial byproducts like fly ash, slag, and silica fume as partial cement replacements, reducing carbon footprint and enhancing sustainability. Ready-mix concrete primarily uses traditional Portland cement, aggregates, sand, and water, mixed in controlled factory environments for consistent quality and workability. The raw materials of green concrete emphasize recycled and eco-friendly components, whereas ready-mix concrete relies on conventional raw materials for standardized pavement performance.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Green concrete significantly reduces carbon emissions by incorporating industrial waste such as fly ash and slag, lowering the demand for Portland cement, a major CO2 emitter. Ready-mix concrete, while convenient for large-scale pavement projects, typically involves higher energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions due to its traditional cement composition and transportation requirements. Using green concrete for pavement enhances sustainability by minimizing resource depletion and reducing the ecological footprint associated with conventional ready-mix concrete production and application.
Strength and Durability Factors
Green concrete exhibits enhanced durability due to the incorporation of industrial waste materials like fly ash and slag, which improve long-term strength and resistance to environmental degradation compared to traditional ready-mix concrete. Ready-mix concrete offers consistent compressive strength and rapid curing, making it suitable for immediate load-bearing requirements in pavement construction. While green concrete may have slightly lower early-age strength, its superior resistance to sulfate attack, corrosion, and freeze-thaw cycles often results in longer-lasting pavement performance.
Performance in Pavement Applications
Green concrete exhibits improved durability and reduced permeability, enhancing pavement lifespan under heavy traffic loads and environmental stressors. Ready-mix concrete offers consistent quality control and high compressive strength, ensuring uniform pavement performance and ease of application. In pavement applications, green concrete's sustainable additives contribute to crack resistance, while ready-mix concrete provides predictable strength and rapid setting times crucial for timely project completion.
Cost Analysis and Economic Feasibility
Green concrete for pavement offers significant cost savings through the use of recycled materials such as fly ash, slag, and other industrial byproducts, reducing raw material expenses compared to traditional ready-mix concrete. Although ready-mix concrete provides consistent quality and faster construction times, the initial material and transportation costs tend to be higher, impacting overall project budgets. Economic feasibility studies reveal that green concrete's lower lifecycle costs and reduced environmental impact make it a financially viable option for sustainable pavement projects in the long term.
Workability and Construction Process
Green concrete offers enhanced workability due to the use of supplementary cementitious materials like fly ash and slag, improving flow and reducing water demand compared to traditional ready-mix concrete. The construction process with green concrete benefits from lower heat generation during curing, minimizing thermal cracking risk and promoting sustainability in pavement projects. Ready-mix concrete provides consistent quality and faster setting times, but its higher cement content may reduce workability and increase environmental impact relative to green concrete.
Maintenance and Longevity
Green concrete, formulated with recycled materials and industrial by-products, offers enhanced durability and reduced environmental impact for pavement applications. Ready-mix concrete provides consistent quality and faster installation but may require more frequent maintenance due to potential shrinkage and cracking over time. Pavements constructed with green concrete typically exhibit longer service life and lower maintenance costs, making them a sustainable and cost-effective choice.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Green concrete for pavement must comply with stringent environmental regulations such as LEED certification and ASTM standards for recycled content to ensure sustainability and reduced carbon footprint. Ready-mix concrete adheres to established standards like AASHTO M 157 and ASTM C94, focusing on consistent quality, durability, and performance under load-bearing conditions. Both materials require compliance with local transportation and infrastructure codes, but green concrete emphasizes eco-friendly certifications while ready-mix concrete prioritizes structural and safety benchmarks.
Future Trends in Sustainable Pavement Solutions
Green concrete, incorporating recycled materials and industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, offers enhanced durability and reduced carbon footprint compared to traditional ready-mix concrete in pavement applications. Trends indicate growing adoption of green concrete due to stricter environmental regulations and increasing demand for low-carbon infrastructure solutions. Advances in nano-additives and carbon capture technologies further push the development of sustainable pavement systems, positioning green concrete as a key material for future urban and highway projects.
Infographic: Green concrete vs Ready-mix concrete for Pavement
 azmater.com
azmater.com