Lightweight concrete offers reduced structural load and improved thermal insulation for industrial flooring, while fiber-reinforced concrete enhances tensile strength, crack resistance, and durability under heavy traffic. Choosing between them depends on balancing load requirements and long-term floor performance in industrial environments.
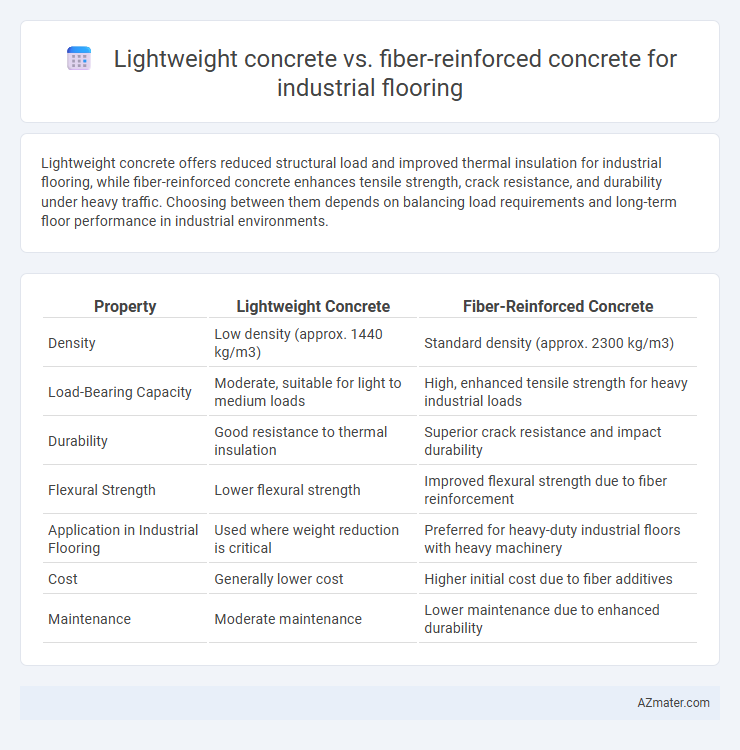
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lightweight Concrete | Fiber-Reinforced Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low density (approx. 1440 kg/m3) | Standard density (approx. 2300 kg/m3) |
| Load-Bearing Capacity | Moderate, suitable for light to medium loads | High, enhanced tensile strength for heavy industrial loads |
| Durability | Good resistance to thermal insulation | Superior crack resistance and impact durability |
| Flexural Strength | Lower flexural strength | Improved flexural strength due to fiber reinforcement |
| Application in Industrial Flooring | Used where weight reduction is critical | Preferred for heavy-duty industrial floors with heavy machinery |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher initial cost due to fiber additives |
| Maintenance | Moderate maintenance | Lower maintenance due to enhanced durability |
Introduction to Industrial Flooring Solutions
Lightweight concrete and fiber-reinforced concrete are essential materials in industrial flooring, offering unique benefits tailored to specific operational needs. Lightweight concrete provides reduced structural load and improved thermal insulation, making it ideal for facilities requiring energy efficiency and minimized foundation stress. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances durability and crack resistance, ensuring long-lasting performance in high-traffic industrial environments exposed to heavy machinery and dynamic loads.
Overview of Lightweight Concrete
Lightweight concrete for industrial flooring offers reduced density, improving load distribution and minimizing structural weight without compromising strength. It provides enhanced thermal insulation and fire resistance, which contributes to operational safety in industrial environments. Compared to fiber-reinforced concrete, it excels in minimizing dead loads but typically requires supplementary reinforcement to handle high tensile stresses.
Overview of Fiber-Reinforced Concrete
Fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) enhances industrial flooring by incorporating synthetic or steel fibers that improve tensile strength, crack resistance, and durability under heavy loads. Unlike lightweight concrete, FRC offers superior impact resistance and reduces shrinkage, making it ideal for environments with high mechanical stress and dynamic loads. Its enhanced structural integrity extends flooring lifespan and minimizes maintenance costs in industrial applications.
Key Material Properties Compared
Lightweight concrete for industrial flooring offers superior thermal insulation and reduced structural load due to its lower density, typically ranging between 1440 to 1840 kg/m3, while fiber-reinforced concrete provides enhanced tensile strength and crack resistance through the integration of synthetic or steel fibers, increasing flexural toughness by up to 50%. Compressive strength of lightweight concrete generally falls between 20 to 40 MPa, suitable for moderate load applications, whereas fiber-reinforced concrete achieves higher durability under dynamic stresses with compressive strengths often exceeding 50 MPa. Porosity and impact resistance differ significantly: lightweight concrete's higher porosity can reduce durability under harsh industrial conditions, while fiber reinforcement mitigates shrinkage and improves structural integrity against mechanical wear.
Load-Bearing Capacity Analysis
Lightweight concrete offers reduced dead load but typically exhibits lower compressive strength, making it less ideal for heavy-duty industrial flooring requiring high load-bearing capacity. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances tensile strength and crack resistance by incorporating steel, glass, or synthetic fibers, significantly improving durability under dynamic industrial loads. Analyzing load-bearing capacity shows fiber-reinforced concrete provides superior structural performance and longevity in industrial flooring applications compared to lightweight concrete.
Durability and Crack Resistance
Lightweight concrete offers improved thermal insulation and reduced structural load but typically has lower durability and higher susceptibility to shrinkage cracks compared to fiber-reinforced concrete, which incorporates synthetic or steel fibers to enhance toughness and resist crack propagation. Fiber-reinforced concrete significantly increases the flooring's resistance to tensile stresses and impact forces, reducing maintenance costs and extending service life in industrial environments. Studies show fiber addition can improve flexural strength by up to 50% and control crack widths below 0.3 mm, making it more effective for heavy-duty industrial flooring applications requiring high durability and crack resistance.
Installation and Construction Techniques
Lightweight concrete offers ease of installation due to its reduced weight, allowing faster placement and less labor-intensive handling in industrial flooring projects. Fiber-reinforced concrete requires specific mixing and careful placement to ensure even distribution of fibers, enhancing crack resistance and durability without the need for additional steel reinforcement. Both materials demand precise curing techniques to optimize performance, but fiber-reinforced concrete may involve more meticulous finishing procedures to maintain fiber exposure control.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Lightweight concrete typically offers lower initial material costs due to its reduced density and use of lightweight aggregates, making it economically attractive for industrial flooring projects with weight limitations. Fiber-reinforced concrete involves higher upfront expenses caused by the addition of synthetic or steel fibers, but it can reduce long-term maintenance and repair costs through enhanced durability and crack resistance. Evaluating total lifecycle costs reveals that fiber-reinforced concrete may provide better economic value over time by minimizing downtime and extending floor service life despite its higher initial investment.
Suitability for Industrial Flooring Applications
Lightweight concrete offers reduced density and improved thermal insulation, making it suitable for industrial flooring where load-bearing demands are moderate and weight reduction is crucial. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances tensile strength, crack resistance, and durability, which is ideal for high-traffic industrial flooring subjected to heavy machinery and dynamic loads. Choosing between lightweight and fiber-reinforced concrete depends on balancing structural performance requirements with insulation and weight constraints in industrial settings.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Concrete Type
Lightweight concrete offers excellent thermal insulation and reduces structural load, making it suitable for industrial flooring where weight constraints are critical. Fiber-reinforced concrete provides superior tensile strength, crack resistance, and durability under heavy machinery and high traffic conditions. Selecting the optimal concrete type depends on the specific industrial application, balancing factors such as load-bearing requirements, maintenance needs, and environmental performance.
Infographic: Lightweight concrete vs Fiber-reinforced concrete for Industrial flooring
 azmater.com
azmater.com