Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers high durability and fast installation for industrial flooring, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications; vacuum concrete, however, provides superior surface smoothness and reduced porosity, enhancing resistance to chemicals and wear. Choosing between RCC and vacuum concrete depends on specific load requirements and environmental exposure in industrial settings.
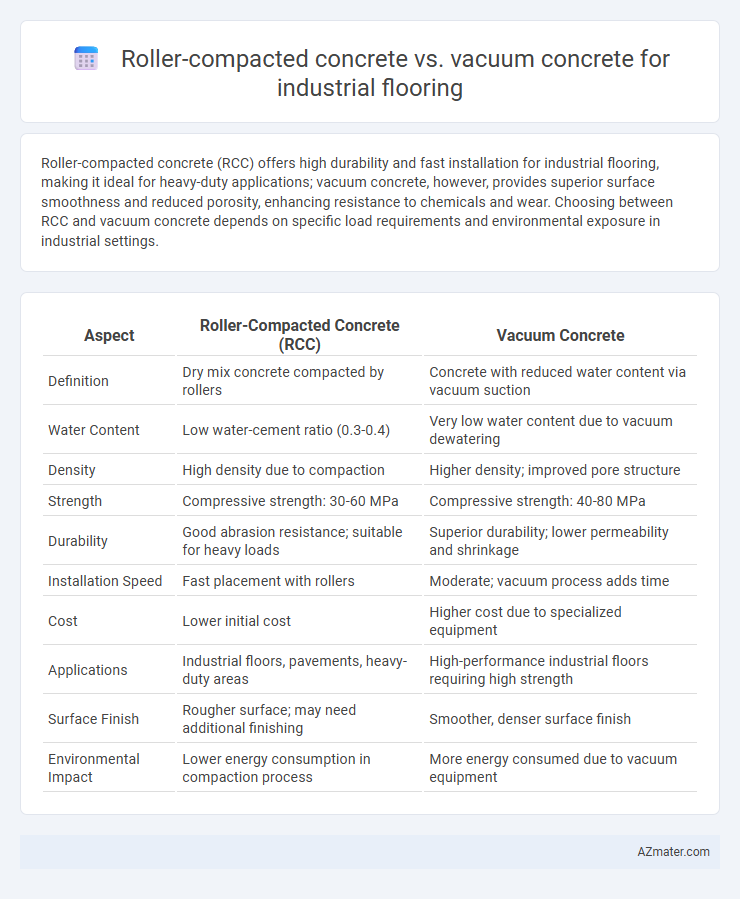
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC) | Vacuum Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dry mix concrete compacted by rollers | Concrete with reduced water content via vacuum suction |
| Water Content | Low water-cement ratio (0.3-0.4) | Very low water content due to vacuum dewatering |
| Density | High density due to compaction | Higher density; improved pore structure |
| Strength | Compressive strength: 30-60 MPa | Compressive strength: 40-80 MPa |
| Durability | Good abrasion resistance; suitable for heavy loads | Superior durability; lower permeability and shrinkage |
| Installation Speed | Fast placement with rollers | Moderate; vacuum process adds time |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher cost due to specialized equipment |
| Applications | Industrial floors, pavements, heavy-duty areas | High-performance industrial floors requiring high strength |
| Surface Finish | Rougher surface; may need additional finishing | Smoother, denser surface finish |
| Environmental Impact | Lower energy consumption in compaction process | More energy consumed due to vacuum equipment |
Introduction to Industrial Flooring Solutions
Industrial flooring solutions demand durable and high-performance materials, with Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offering rapid installation, exceptional compressive strength, and cost-efficiency for heavy-load environments. Vacuum concrete technology enhances floor density and surface quality by removing excess water, resulting in improved abrasion resistance and reduced permeability. Choosing between RCC and vacuum concrete depends on project-specific needs such as load capacity, curing time, and long-term maintenance requirements.
Overview of Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC)
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) is a robust, highly durable material commonly used for industrial flooring due to its low permeability and high compressive strength typically ranging from 25 to 40 MPa. This dry, stiff concrete mixture contains less water and is compacted with vibratory rollers, which accelerates construction time and reduces costs compared to traditional concrete methods. RCC's ability to withstand heavy loads and resist abrasion makes it ideal for warehouses, manufacturing plants, and heavy-traffic industrial environments.
What is Vacuum Concrete?
Vacuum concrete is a specialized type of concrete that undergoes a vacuum dewatering process to remove excess water from the mix immediately after placement, enhancing its density and strength. This method significantly improves the concrete's durability, reduces permeability, and accelerates the curing time, making it an excellent choice for industrial flooring that requires high load-bearing capacity and resistance to abrasion. Compared to roller-compacted concrete, vacuum concrete offers superior surface finish and durability, particularly in environments subjected to heavy machinery and chemical exposure.
Key Material Properties: RCC vs Vacuum Concrete
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) features lower water content and higher coarse aggregate volume, resulting in increased compressive strength and superior abrasion resistance for industrial flooring applications. Vacuum concrete, characterized by reduced air voids and enhanced density due to vacuum-induced dewatering, offers improved durability and lower permeability, making it ideal for environments requiring chemical resistance and minimal moisture penetration. RCC's rapid placement and compaction contrast with vacuum concrete's slower curing but higher quality surface finish and long-term performance under heavy loading conditions.
Installation Processes Compared
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) installation involves spreading and compacting a low-slump mix with heavy rollers, enabling rapid placement and reduced curing times ideal for large industrial floors. Vacuum concrete requires embedding a vacuum system beneath the slab to remove excess water during curing, enhancing strength and durability but extending installation complexity and time. RCC is favored for faster, cost-effective industrial flooring, while vacuum concrete suits applications demanding superior load-bearing capacity and minimal shrinkage.
Surface Finish and Durability
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) delivers a dense, durable surface finish suitable for heavy industrial flooring due to its low water content and compaction by heavy rollers, resulting in high compressive strength and resistance to abrasion. Vacuum concrete enhances surface finish quality by removing excess water through vacuum technology, producing a smoother, more uniform surface with improved durability against chemical spills and impact loads. RCC excels in large-scale, high-load industrial environments where rapid installation and cost-efficiency are priorities, whereas vacuum concrete provides superior surface integrity for environments requiring precision finishes and enhanced wear resistance.
Load-Bearing Capacity and Performance
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers superior load-bearing capacity due to its high density and compaction method, making it ideal for heavy industrial flooring subjected to intense traffic and machinery loads. Vacuum concrete enhances performance by reducing porosity and increasing strength through air removal, providing excellent durability and resistance to cracking under dynamic loads. Comparing both, RCC is preferred for large-scale industrial floors requiring rapid placement and strength, while vacuum concrete excels in applications demanding enhanced surface integrity and long-term performance.
Cost Efficiency Analysis
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers significant cost savings for industrial flooring due to its rapid placement and reduced need for formwork, lowering labor and equipment expenses compared to vacuum concrete. Vacuum concrete, while providing superior strength and durability through water removal, incurs higher upfront costs from specialized vacuum equipment and extended curing times. Evaluating project size and performance requirements is crucial; RCC is typically more cost-efficient for large-scale industrial floors, whereas vacuum concrete suits applications demanding enhanced structural integrity despite higher initial investments.
Maintenance and Long-Term Reliability
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers superior durability and low maintenance for industrial flooring due to its high compressive strength and resistance to heavy loads, chemicals, and abrasion. Vacuum concrete enhances long-term reliability by minimizing porosity and improving surface density, which reduces water penetration and prevents structural degradation. While RCC demands less frequent repairs, vacuum concrete ensures extended lifespan and consistent performance in environments with high moisture exposure.
Choosing the Best Concrete Type for Industrial Flooring
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers high durability and rapid installation, making it ideal for heavy-traffic industrial flooring requiring quick turnaround and load-bearing capacity. Vacuum concrete ensures superior compaction and reduced porosity, enhancing surface strength and resistance to chemical spills critical in industrial environments. Selecting between RCC and vacuum concrete depends on specific site requirements, with RCC favored for cost-efficiency and speed, while vacuum concrete excels in performance under extreme industrial conditions.
Infographic: Roller-compacted concrete vs Vacuum concrete for Industrial flooring
 azmater.com
azmater.com