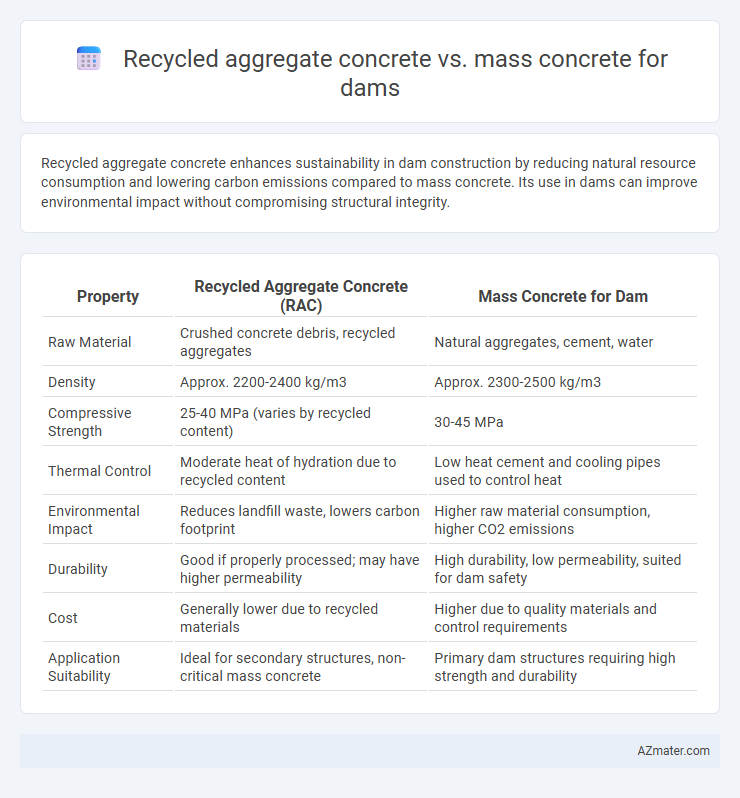
Recycled aggregate concrete enhances sustainability in dam construction by reducing natural resource consumption and lowering carbon emissions compared to mass concrete. Its use in dams can improve environmental impact without compromising structural integrity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Recycled Aggregate Concrete (RAC) | Mass Concrete for Dam |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Crushed concrete debris, recycled aggregates | Natural aggregates, cement, water |
| Density | Approx. 2200-2400 kg/m3 | Approx. 2300-2500 kg/m3 |
| Compressive Strength | 25-40 MPa (varies by recycled content) | 30-45 MPa |
| Thermal Control | Moderate heat of hydration due to recycled content | Low heat cement and cooling pipes used to control heat |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces landfill waste, lowers carbon footprint | Higher raw material consumption, higher CO2 emissions |
| Durability | Good if properly processed; may have higher permeability | High durability, low permeability, suited for dam safety |
| Cost | Generally lower due to recycled materials | Higher due to quality materials and control requirements |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for secondary structures, non-critical mass concrete | Primary dam structures requiring high strength and durability |
Introduction to Dam Construction Materials
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) offers an eco-friendly alternative to traditional mass concrete by utilizing crushed concrete debris, reducing natural aggregate consumption in dam construction. Mass concrete, typically comprising large volumes of conventional aggregates and cement, provides high strength and durability essential for structural integrity and water retention in dams. The choice between RAC and mass concrete depends on environmental impact, cost-efficiency, mechanical properties, and long-term performance in dam infrastructure.
Understanding Recycled Aggregate Concrete (RAC)
Recycled Aggregate Concrete (RAC) incorporates reclaimed aggregates from demolished structures, offering enhanced sustainability and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional mass concrete used in dam construction. RAC demonstrates comparable strength and durability characteristics when properly processed, making it a viable alternative for large-scale infrastructure projects like dams. Utilizing RAC helps conserve natural resources and minimizes construction waste while maintaining structural integrity in demanding applications.
Overview of Mass Concrete in Dam Applications
Mass concrete in dam applications involves large volumes of concrete characterized by low heat of hydration and controlled temperature to prevent thermal cracking. It typically uses conventional coarse and fine aggregates, with mix designs optimized for durability, strength, and impermeability to withstand hydrostatic pressure and environmental conditions. The thermal management strategies in mass concrete include cooling pipes and staged pouring to manage internal temperature gradients critical for structural integrity in dam construction.
Material Properties: RAC vs Mass Concrete
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) typically exhibits higher porosity and lower compressive strength compared to conventional mass concrete due to the presence of old mortar and adhered contaminants in recycled aggregates. RAC's increased water absorption and reduced density can affect durability and long-term performance, making mix design adjustments crucial for dam applications. Mass concrete benefits from homogeneity and consistent aggregate quality, resulting in better thermal control and structural integrity essential for large-scale dam construction.
Environmental Benefits and Sustainability
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) significantly reduces demand for natural aggregates, conserving natural resources and minimizing quarrying impacts in dam construction. Its use lowers carbon emissions by repurposing construction and demolition waste, promoting circular economy principles and reducing landfill burden. Mass concrete made from conventional materials typically involves higher environmental costs due to extensive raw material extraction and greater embodied energy, making RAC a more sustainable choice for eco-friendly dam projects.
Structural Performance and Durability
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) for dams demonstrates comparable structural performance to mass concrete, with adequate compressive strength and modulus of elasticity suitable for large-scale applications. RAC's durability is influenced by the quality of recycled aggregates, showing potential resistance to freeze-thaw cycles, sulfate attack, and alkali-silica reaction when properly processed. Mass concrete, traditionally made with natural aggregates, offers established long-term durability and thermal stability, critical for dam structures subjected to extensive loading and environmental exposure.
Cost Analysis and Economic Impact
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) offers significant cost advantages over traditional mass concrete in dam construction, primarily due to reduced raw material expenses and lower landfill fees. Mass concrete demands high volumes of virgin aggregates and cement, leading to increased procurement and transportation costs that escalate the overall project budget. Incorporating RAC not only lowers material costs but also minimizes environmental impact charges, enhancing the economic feasibility and sustainability of dam projects.
Construction Techniques and Challenges
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) for dam construction leverages crushed concrete waste, reducing environmental impact but requiring careful mix design to address variability in aggregate quality and potential strength reduction. Mass concrete involves placing large volumes of conventional concrete, demanding rigorous temperature control techniques such as cooling pipes and thermal monitoring to prevent thermal cracking. Both methods present challenges: RAC demands thorough characterization to ensure durability and structural integrity, while mass concrete requires meticulous thermal management to maintain stability during curing.
Case Studies: Dams Using RAC vs Mass Concrete
Case studies reveal that dams constructed with Recycled Aggregate Concrete (RAC) demonstrate comparable structural integrity and durability to traditional mass concrete dams while offering significant environmental benefits, including reduced carbon footprint and material waste. Notable examples include the Queensbury Dam project, where RAC achieved high compressive strength and enhanced sustainability, and the Jiangyin Dam, which validated RAC's freeze-thaw resistance and long-term performance. Mass concrete dams like the Hoover Dam remain benchmarks for robustness, but ongoing research and case studies increasingly support RAC as a feasible, eco-friendly alternative for large-scale dam construction.
Future Prospects and Recommendations
Recycled aggregate concrete offers sustainable advantages for dam construction by reducing environmental impact and conserving natural resources, while mass concrete remains favored for its proven durability and high compressive strength. Future prospects emphasize integrating recycled materials with advanced mix designs to enhance performance and longevity under hydraulic pressures. Recommendations include rigorous testing for permeability and freeze-thaw resistance, alongside developing guidelines for the proportion and treatment of recycled aggregates to ensure structural integrity in large-scale dam projects.
Infographic: Recycled aggregate concrete vs Mass concrete for Dam
 azmater.com
azmater.com