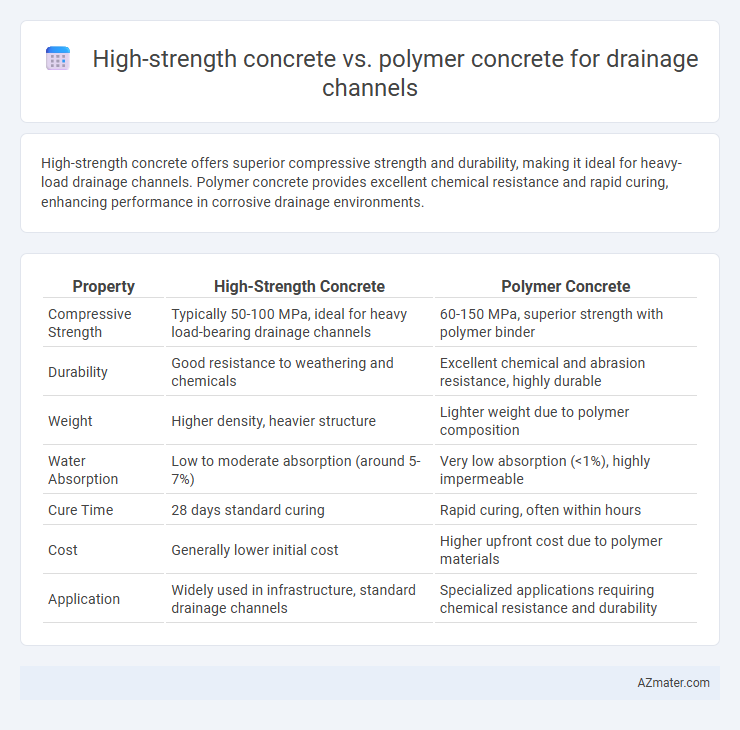
High-strength concrete offers superior compressive strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy-load drainage channels. Polymer concrete provides excellent chemical resistance and rapid curing, enhancing performance in corrosive drainage environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | High-Strength Concrete | Polymer Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Compressive Strength | Typically 50-100 MPa, ideal for heavy load-bearing drainage channels | 60-150 MPa, superior strength with polymer binder |
| Durability | Good resistance to weathering and chemicals | Excellent chemical and abrasion resistance, highly durable |
| Weight | Higher density, heavier structure | Lighter weight due to polymer composition |
| Water Absorption | Low to moderate absorption (around 5-7%) | Very low absorption (<1%), highly impermeable |
| Cure Time | 28 days standard curing | Rapid curing, often within hours |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher upfront cost due to polymer materials |
| Application | Widely used in infrastructure, standard drainage channels | Specialized applications requiring chemical resistance and durability |
Overview of Drainage Channel Materials
High-strength concrete offers superior compressive strength and durability, making it suitable for heavy-load drainage channels exposed to significant traffic and environmental stress. Polymer concrete incorporates resin binders that enhance chemical resistance and reduce permeability, ideal for corrosive or industrial drainage applications. Both materials provide tailored solutions for drainage channels, with high-strength concrete excelling in structural integrity while polymer concrete optimizes longevity against chemical exposure.
Defining High-Strength Concrete
High-strength concrete for drainage channels is defined by its compressive strength exceeding 6,000 psi (approximately 41 MPa), achieved through low water-cement ratio and advanced admixtures that enhance durability and load-bearing capacity. This concrete type provides superior resistance to heavy traffic loads, freeze-thaw cycles, and chemical attacks commonly encountered in drainage environments. Compared to polymer concrete, which uses polymer binders for improved chemical resistance and faster curing, high-strength concrete offers greater structural integrity and cost efficiency for large-scale drainage channel installations.
Understanding Polymer Concrete
Polymer concrete, composed of polymer binders instead of traditional cement, offers superior chemical resistance and rapid curing times compared to high-strength concrete, making it ideal for drainage channels exposed to aggressive environments. Its low permeability and high bonding strength enhance durability and reduce maintenance in wastewater and stormwater systems. Understanding polymer concrete's composition and performance benefits ensures optimal selection for infrastructure requiring long-lasting, corrosion-resistant drainage solutions.
Material Composition Differences
High-strength concrete for drainage channels primarily consists of cement, aggregates, water, and chemical admixtures designed to enhance compressive strength and durability under load. Polymer concrete replaces traditional cement with polymer binders such as epoxy or polyester resin, integrating aggregates to improve chemical resistance and reduce permeability. These material composition differences result in polymer concrete offering superior corrosion resistance and flexibility, while high-strength concrete provides greater structural load-bearing capacity.
Mechanical and Structural Properties
High-strength concrete offers superior compressive strength typically above 50 MPa, making it highly resistant to heavy loads and structural stress in drainage channels. Polymer concrete exhibits enhanced tensile strength and chemical resistance due to its polymer matrix, providing excellent durability against aggressive environmental agents and reducing microcracking. The choice depends on specific mechanical demands; high-strength concrete excels in load-bearing capacity, while polymer concrete outperforms in flexibility and chemical stability.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
High-strength concrete offers excellent compressive strength and durability for drainage channels but is vulnerable to chemical attack and corrosion from aggressive wastewater environments. Polymer concrete provides superior corrosion resistance and enhanced durability due to its chemically inert resin matrix, making it ideal for channels exposed to acidic or saline conditions. Selecting polymer concrete extends the service life and reduces maintenance costs in corrosive drainage applications compared to traditional high-strength concrete.
Installation and Handling Considerations
High-strength concrete offers robust durability and compressive strength ideal for drainage channels but requires careful curing and vibration during installation to avoid cracking and ensure longevity. Polymer concrete, while lighter and more chemically resistant, allows for quicker handling and faster installation with minimal curing time, reducing labor costs and potential installation errors. Both materials demand proper surface preparation and skilled handling, but polymer concrete's superior bonding properties can simplify complex drainage channel geometries.
Cost Comparison: Initial and Lifecycle
High-strength concrete offers lower initial costs due to widely available materials and established manufacturing processes, making it a budget-friendly option for drainage channels. Polymer concrete, although featuring higher upfront expenses because of specialized resins and additives, provides superior durability and chemical resistance that significantly reduce maintenance and repair costs over the lifecycle. Lifecycle cost analysis reveals polymer concrete's long-term savings through extended service life and decreased operational disruptions, despite its premium initial investment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
High-strength concrete, composed primarily of cement, aggregates, and water, has a higher carbon footprint due to cement production, which significantly contributes to CO2 emissions, whereas polymer concrete utilizes resins and recycled materials, reducing environmental impact and enhancing sustainability. Polymer concrete offers superior chemical resistance and durability, lowering maintenance frequency and associated environmental costs over the drainage channel's lifecycle. The use of recycled aggregates and energy-efficient manufacturing processes in polymer concrete supports sustainable construction practices, making it a preferable option for eco-friendly infrastructure projects.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Material
High-strength concrete offers superior compressive strength and durability, making it ideal for drainage channels exposed to heavy traffic loads and harsh environmental conditions. Polymer concrete excels in chemical resistance and rapid curing, suitable for drainage systems in industrial areas with highly corrosive fluids or where quick installation is critical. Selecting between high-strength and polymer concrete depends on load requirements, chemical exposure, and installation timelines to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: High-strength concrete vs Polymer concrete for Drainage channel
 azmater.com
azmater.com