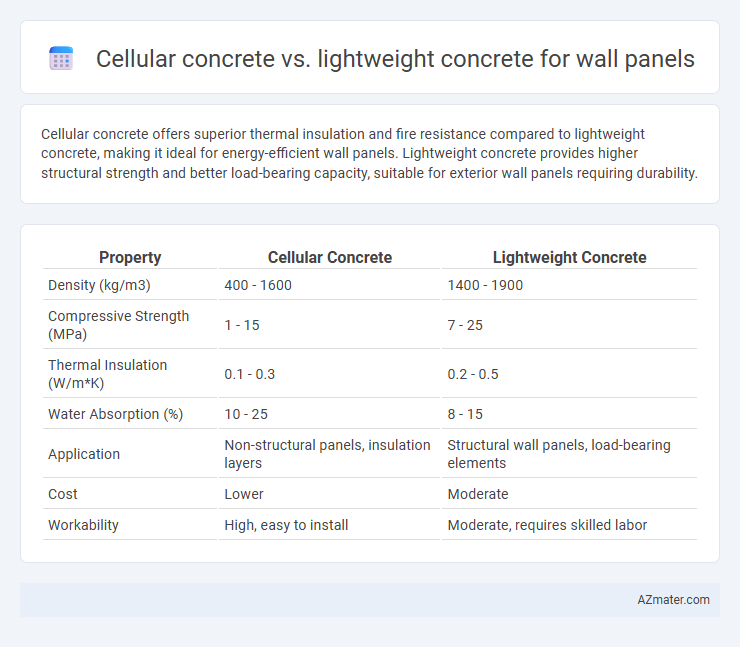
Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation and fire resistance compared to lightweight concrete, making it ideal for energy-efficient wall panels. Lightweight concrete provides higher structural strength and better load-bearing capacity, suitable for exterior wall panels requiring durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cellular Concrete | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density (kg/m3) | 400 - 1600 | 1400 - 1900 |
| Compressive Strength (MPa) | 1 - 15 | 7 - 25 |
| Thermal Insulation (W/m*K) | 0.1 - 0.3 | 0.2 - 0.5 |
| Water Absorption (%) | 10 - 25 | 8 - 15 |
| Application | Non-structural panels, insulation layers | Structural wall panels, load-bearing elements |
| Cost | Lower | Moderate |
| Workability | High, easy to install | Moderate, requires skilled labor |
Introduction to Cellular Concrete and Lightweight Concrete
Cellular concrete, also known as aerated concrete, is a lightweight material produced by incorporating air bubbles or gas into the cement mixture, resulting in enhanced thermal insulation and reduced density. Lightweight concrete is typically made by using lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or pumice, offering improved strength-to-weight ratios and better durability compared to traditional concrete. Both materials are favored for wall panels due to their insulation properties and reduced structural load, but cellular concrete excels in thermal performance while lightweight concrete provides superior mechanical strength.
Key Properties of Cellular Concrete
Cellular concrete is characterized by its low density, excellent thermal insulation, and high fire resistance, making it ideal for wall panels that require energy efficiency and safety. It also offers superior sound absorption and ease of handling due to its lightweight nature, which reduces structural load and installation time. In comparison, lightweight concrete primarily focuses on reduced weight and strength but may not match cellular concrete's insulation and fire-resistant properties.
Key Properties of Lightweight Concrete
Lightweight concrete for wall panels features a density typically ranging from 1400 to 1800 kg/m3, providing superior thermal insulation and reduced structural load compared to traditional concrete. Its high porosity and inclusion of lightweight aggregates enhance fire resistance and sound insulation, making it ideal for energy-efficient building envelopes. Cellular concrete, while also lightweight, generally offers lower compressive strength and higher water absorption, making lightweight concrete preferable for structural wall panel applications requiring durability and moisture control.
Raw Materials and Production Techniques
Cellular concrete for wall panels primarily uses cement, water, fine aggregates, and a foaming agent to create a lightweight, porous structure, while lightweight concrete relies on natural or synthetic lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or pumice to reduce density. The production of cellular concrete involves mixing a pre-formed foam with the cement slurry, ensuring uniform air bubble distribution, whereas lightweight concrete production entails substituting traditional aggregates with lightweight alternatives, requiring careful control of moisture content and mixing duration. Both materials aim to provide thermal insulation and reduced weight, but cellular concrete offers superior workability and insulation due to its uniform pore structure derived from specific foaming processes.
Structural Performance: Strength and Durability
Cellular concrete exhibits lower compressive strength compared to lightweight concrete, making the latter more suitable for load-bearing wall panels requiring higher structural performance. Lightweight concrete offers superior durability and resistance to environmental factors, ensuring long-term stability in wall applications. The enhanced density and material composition of lightweight concrete contribute to its better strength-to-weight ratio, optimizing wall panel structural integrity.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Capabilities
Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation due to its high air content, significantly reducing heat transfer in wall panels compared to traditional lightweight concrete. Lightweight concrete provides moderate acoustic insulation, but cellular concrete's porous structure enhances sound absorption, making it more effective for noise reduction. Both materials contribute to energy efficiency, yet cellular concrete excels in creating thermally and acoustically optimized wall solutions.
Cost Comparison and Economic Feasibility
Cellular concrete offers lower material costs due to its high air content and lightweight aggregates, reducing transportation expenses and easing installation for wall panels. Lightweight concrete, while denser, provides better structural performance but often incurs higher raw material and production costs. Economic feasibility depends on project requirements, with cellular concrete being more cost-effective for non-load-bearing panels and lightweight concrete preferred where structural integrity is critical.
Installation and Construction Methods
Cellular concrete offers superior ease of installation for wall panels due to its lightweight nature and excellent flowability, allowing for quick pouring and minimal formwork requirements compared to traditional lightweight concrete. Lightweight concrete requires more complex handling and compaction techniques during construction, often needing skilled labor and vibration equipment to achieve the desired density and strength. Both materials support efficient construction, but cellular concrete reduces labor time and equipment costs through simplified casting and faster curing rates.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cellular concrete offers superior environmental benefits compared to lightweight concrete due to its use of recycled materials and lower cement content, which reduce carbon emissions during production. Lightweight concrete typically relies on natural aggregates that involve more energy-intensive extraction processes, leading to higher environmental footprints. The enhanced thermal insulation properties of cellular concrete contribute to energy savings in buildings, promoting overall sustainability in wall panel applications.
Choosing the Right Material for Wall Panels
Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation and fire resistance, making it ideal for energy-efficient wall panels, whereas lightweight concrete provides higher compressive strength suitable for structural support. Selecting the right material depends on balancing load-bearing requirements with insulation needs to optimize wall panel performance. Cost-effectiveness and ease of installation also influence the choice, with cellular concrete reducing overall building weight and enhancing sustainability.
Infographic: Cellular concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Wall panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com