Heat-insulating concrete reduces thermal stress and enhances pavement durability by minimizing heat transfer, while rolled compacted concrete offers high density and strength with faster placement, ideal for heavy traffic surfaces. Choosing heat-insulating concrete improves energy efficiency in extreme climates, whereas rolled compacted concrete provides cost-effective, rapid construction for durable pavements.
Table of Comparison
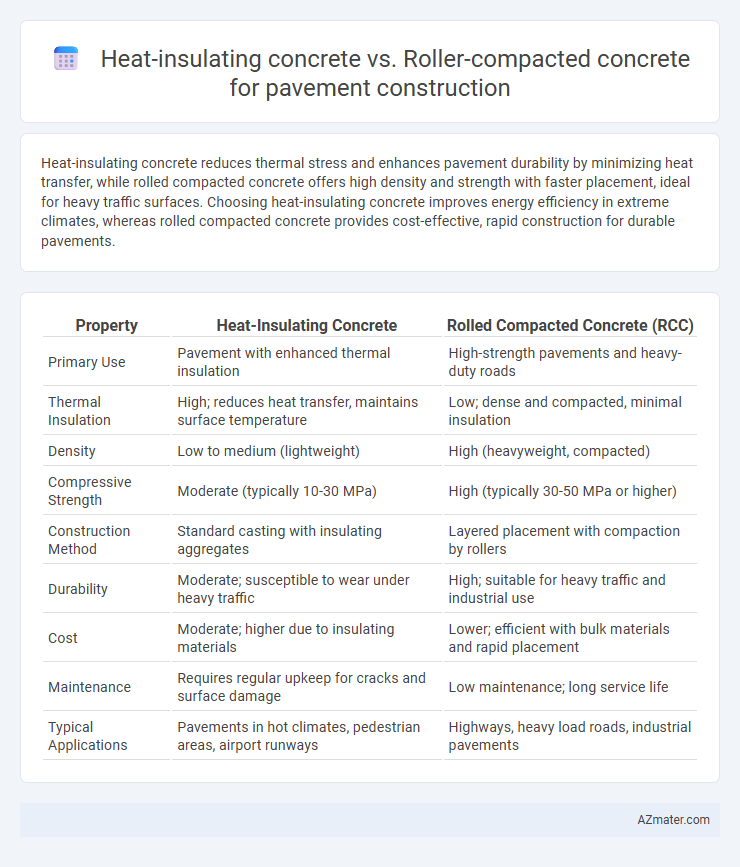
| Property | Heat-Insulating Concrete | Rolled Compacted Concrete (RCC) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Pavement with enhanced thermal insulation | High-strength pavements and heavy-duty roads |
| Thermal Insulation | High; reduces heat transfer, maintains surface temperature | Low; dense and compacted, minimal insulation |
| Density | Low to medium (lightweight) | High (heavyweight, compacted) |
| Compressive Strength | Moderate (typically 10-30 MPa) | High (typically 30-50 MPa or higher) |
| Construction Method | Standard casting with insulating aggregates | Layered placement with compaction by rollers |
| Durability | Moderate; susceptible to wear under heavy traffic | High; suitable for heavy traffic and industrial use |
| Cost | Moderate; higher due to insulating materials | Lower; efficient with bulk materials and rapid placement |
| Maintenance | Requires regular upkeep for cracks and surface damage | Low maintenance; long service life |
| Typical Applications | Pavements in hot climates, pedestrian areas, airport runways | Highways, heavy load roads, industrial pavements |
Introduction to Pavement Construction Materials
Heat-insulating concrete enhances pavement performance by reducing thermal conductivity and mitigating heat-related distress, making it ideal for extreme climate conditions. Rolled compacted concrete (RCC) offers superior strength and durability through its low-slump, high-density mixture compacted with rollers, providing a cost-effective solution for heavy-load pavements. Comparing these materials involves evaluating thermal insulation capacity, load-bearing requirements, and construction efficiency for optimal pavement design.
Overview of Heat-Insulating Concrete
Heat-insulating concrete enhances pavement performance by reducing thermal conductivity and mitigating temperature-related stresses, which helps prevent cracking and extends service life. This type of concrete incorporates lightweight aggregates and insulating additives, resulting in lower density and improved energy efficiency compared to traditional rolled compacted concrete (RCC). Its ability to maintain stable surface temperatures makes heat-insulating concrete especially suitable for regions with extreme thermal variations.
Overview of Roller Compacted Concrete (RCC)
Roller Compacted Concrete (RCC) is a dry mix concrete placed with heavy rollers, offering high strength and durability for pavement construction. Its low cement content, rapid setting time, and ability to withstand heavy traffic loads make RCC an efficient choice for highways, industrial yards, and airport runways. RCC's permeability and thermal conductivity are lower compared to traditional concrete, providing enhanced resistance to thermal cracking and deicing chemicals.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Heat-insulating concrete significantly reduces heat transfer due to its low thermal conductivity, enhancing pavement durability by minimizing temperature-induced stress and surface cracking. Rolled compacted concrete (RCC) offers higher density and strength but exhibits greater heat retention, which can lead to increased thermal expansion and potential pavement deformation. Choosing heat-insulating concrete improves thermal performance by maintaining cooler pavement temperatures, thereby extending service life and reducing maintenance costs.
Structural Strength and Load-bearing Capacity
Heat-insulating concrete offers enhanced thermal resistance, reducing heat transfer and protecting pavement layers from temperature-induced stresses, which can indirectly improve durability but generally exhibits lower structural strength compared to rolled compacted concrete (RCC). Rolled compacted concrete provides superior load-bearing capacity due to its dense, well-compacted matrix and high compressive strength, making it ideal for heavy traffic pavements requiring robust structural performance. The choice between heat-insulating concrete and RCC depends on balancing thermal performance requirements with the need for maximum structural strength and durability under load.
Installation and Construction Methods
Heat-insulating concrete for pavement construction requires precise layering techniques with embedded insulation materials to reduce thermal conductivity, ensuring effective temperature regulation beneath the pavement surface. Rolled compacted concrete (RCC) involves a high-density mix placed using standard asphalt pavers followed by heavy compaction with rollers, enabling rapid installation and high-strength pavement suitable for heavy traffic. Installation of heat-insulating concrete is more labor-intensive and time-consuming compared to RCC, which benefits from streamlined construction methods and faster curing times.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Heat-insulating concrete offers enhanced durability by reducing thermal cracking and mitigating temperature-induced stress, which extends pavement lifespan and lowers maintenance frequency. Rolled compacted concrete (RCC) provides high strength and resistance to heavy loads with minimal shrinkage but may require more frequent surface maintenance due to lower thermal insulation properties. Both materials deliver distinct advantages in pavement construction, with heat-insulating concrete excelling in thermal durability and RCC favoring structural load-bearing capacity.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Heat-insulating concrete offers improved thermal performance, reducing pavement maintenance costs by minimizing temperature-induced cracking, but generally incurs higher initial material costs compared to rolled compacted concrete (RCC), which is favored for its cost-effective rapid construction and lower material expenses. RCC, with its dense and durable composition, provides a more economical solution for large-scale pavement projects despite lacking the thermal benefits of insulating concrete. Life-cycle cost analysis often reveals that while RCC lowers upfront expenditure, heat-insulating concrete can deliver long-term savings through decreased repair frequency and extended pavement lifespan.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Heat-insulating concrete reduces urban heat island effects by incorporating materials with high thermal resistance, thereby lowering surface temperatures and energy consumption for cooling. Rolled compacted concrete (RCC) offers durability and requires less cement and water, resulting in reduced carbon emissions and resource usage during pavement construction. Both materials enhance sustainability, with heat-insulating concrete optimizing thermal performance and RCC promoting efficient resource management and long-term pavement resilience.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Pavement Applications
Heat-insulating concrete offers superior thermal resistance, reducing surface temperatures and mitigating urban heat island effects, making it ideal for pavements in hot climates. Rolled compacted concrete (RCC) provides high durability and rapid construction benefits due to its low water content and mechanical compaction, suitable for heavy-traffic pavements requiring strength and longevity. Selecting the right concrete depends on balancing thermal performance needs with load-bearing requirements and project timelines for optimized pavement functionality.
Infographic: Heat-insulating concrete vs Rolled compacted concrete for Pavement construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com