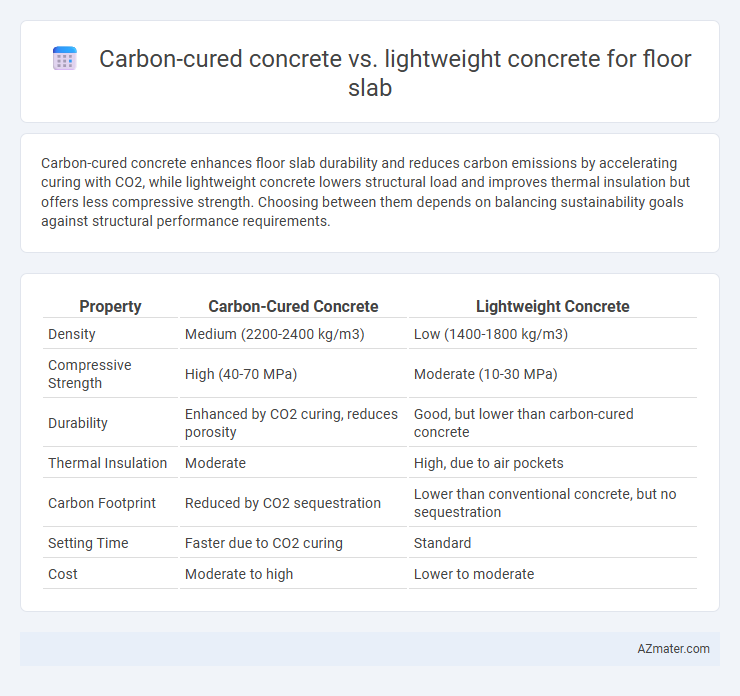
Carbon-cured concrete enhances floor slab durability and reduces carbon emissions by accelerating curing with CO2, while lightweight concrete lowers structural load and improves thermal insulation but offers less compressive strength. Choosing between them depends on balancing sustainability goals against structural performance requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon-Cured Concrete | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Medium (2200-2400 kg/m3) | Low (1400-1800 kg/m3) |
| Compressive Strength | High (40-70 MPa) | Moderate (10-30 MPa) |
| Durability | Enhanced by CO2 curing, reduces porosity | Good, but lower than carbon-cured concrete |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate | High, due to air pockets |
| Carbon Footprint | Reduced by CO2 sequestration | Lower than conventional concrete, but no sequestration |
| Setting Time | Faster due to CO2 curing | Standard |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Lower to moderate |
Introduction to Floor Slab Material Choices
Carbon-cured concrete enhances floor slab durability by utilizing accelerated curing processes that reduce carbon emissions and improve strength. Lightweight concrete offers benefits such as reduced structural load and improved thermal insulation, making it ideal for floor slabs in multi-story constructions. Selecting between carbon-cured and lightweight concrete depends on project priorities like environmental impact, load-bearing capacity, and insulation requirements.
Overview of Carbon-Cured Concrete
Carbon-cured concrete undergoes accelerated carbonation, converting CO2 into stable calcium carbonates, which enhances strength and durability compared to traditional curing methods. This process reduces curing time and improves resistance to chemical attack, making it a sustainable alternative for floor slabs. Carbon-cured concrete often exhibits higher compressive strength and lower permeability than lightweight concrete, which mainly focuses on reducing slab weight through porous aggregates.
Key Properties of Lightweight Concrete
Lightweight concrete for floor slabs offers reduced density ranging from 1200 to 1850 kg/m3, resulting in lower dead loads and improved structural efficiency compared to carbon-cured concrete. It exhibits enhanced thermal insulation with thermal conductivity values between 0.1 to 0.3 W/m*K, contributing to better energy efficiency in buildings. Key mechanical properties include compressive strength typically from 10 to 40 MPa and higher fire resistance, making lightweight concrete ideal for applications demanding both structural performance and energy conservation.
Strength Comparison: Carbon-Cured vs. Lightweight Concrete
Carbon-cured concrete exhibits higher compressive strength compared to lightweight concrete due to enhanced carbonation processes accelerating cement hydration. Lightweight concrete generally has lower density but reduced strength, making it less suitable for high-load floor slabs requiring durability and structural integrity. Engineers often select carbon-cured concrete for floor slabs where maximum strength and long-term performance are critical.
Durability and Longevity in Floor Slabs
Carbon-cured concrete incorporates CO2 during curing, enhancing compressive strength and reducing permeability, which significantly improves durability and resistance to environmental degradation in floor slabs. Lightweight concrete offers reduced load and improved thermal insulation but generally has lower compressive strength and higher porosity, potentially impacting long-term durability under heavy loading conditions. For floor slabs requiring extended longevity and resistance to cracking or chemical attack, carbon-cured concrete provides superior performance benefits compared to traditional lightweight alternatives.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Carbon-cured concrete reduces carbon emissions by utilizing captured CO2 in the curing process, enhancing strength while lowering the carbon footprint compared to traditional methods. Lightweight concrete offers benefits in thermal insulation and reduced material usage, leading to decreased transportation emissions and less resource extraction. Combining carbon curing with lightweight aggregates can maximize sustainability by lowering embodied carbon and improving energy efficiency in floor slab applications.
Installation Methods and Construction Efficiency
Carbon-cured concrete for floor slabs utilizes accelerated curing techniques involving carbon dioxide injection, reducing curing time and enhancing early strength gain. Lightweight concrete offers easier handling and faster placement due to its reduced density, improving on-site productivity and lowering labor intensity. Installation of carbon-cured slabs requires specialized equipment for CO2 injection, whereas lightweight concrete benefits from conventional placement methods, making it more flexible for diverse construction scenarios.
Cost Analysis: Material and Lifecycle Expenses
Carbon-cured concrete typically involves higher upfront material costs due to specialized carbon curing technology and equipment, whereas lightweight concrete offers reduced material expenses through the use of lightweight aggregates like expanded clay or shale. Lifecycle costs for carbon-cured concrete are often lower because of enhanced durability and faster curing times that reduce labor and maintenance expenses over time. Lightweight concrete may incur higher long-term maintenance costs due to potential lower strength and susceptibility to damage, impacting overall lifecycle affordability.
Performance in Residential and Commercial Applications
Carbon-cured concrete offers enhanced durability and faster curing times, making it ideal for floor slabs in both residential and commercial buildings where early strength is crucial. Lightweight concrete provides excellent thermal insulation and reduces structural load, benefiting multi-story residential complexes and commercial spaces requiring energy efficiency. Performance considerations include carbon-cured concrete's superior compressive strength versus lightweight concrete's advantages in flexibility and sustainability.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Your Floor Slab
Carbon-cured concrete offers enhanced durability and reduced carbon footprint, making it ideal for sustainable floor slabs with high compressive strength requirements. Lightweight concrete, with its reduced density, improves thermal insulation and reduces load on structural elements, benefiting slabs in multi-story or thermal-sensitive buildings. Selecting between carbon-cured and lightweight concrete depends on balancing sustainability goals, structural load demands, and desired thermal performance in floor slab applications.
Infographic: Carbon-cured concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Floor slab
 azmater.com
azmater.com