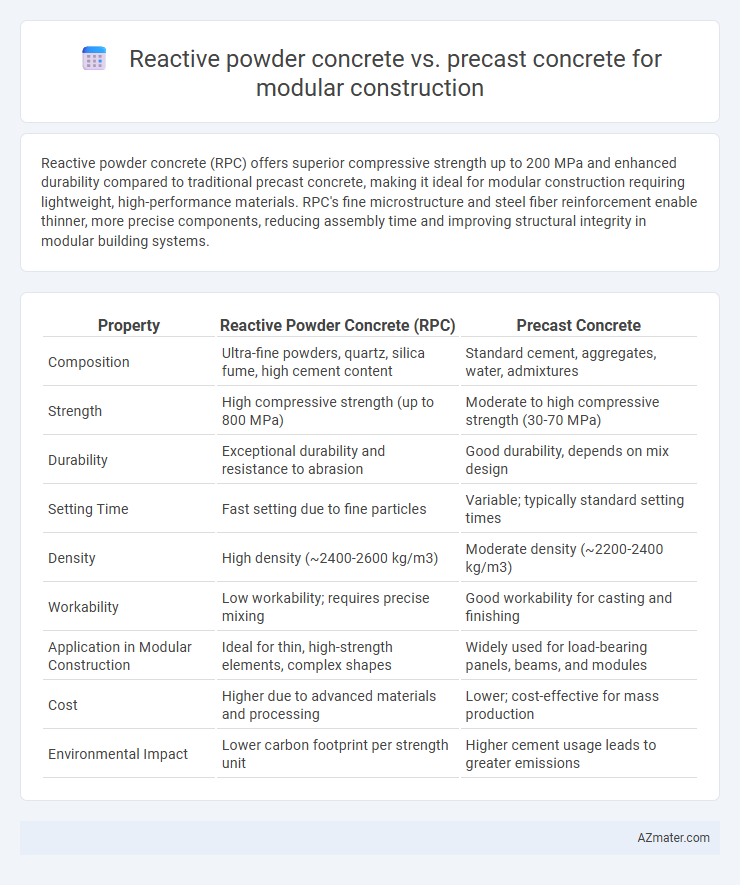
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) offers superior compressive strength up to 200 MPa and enhanced durability compared to traditional precast concrete, making it ideal for modular construction requiring lightweight, high-performance materials. RPC's fine microstructure and steel fiber reinforcement enable thinner, more precise components, reducing assembly time and improving structural integrity in modular building systems.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Reactive Powder Concrete (RPC) | Precast Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Ultra-fine powders, quartz, silica fume, high cement content | Standard cement, aggregates, water, admixtures |
| Strength | High compressive strength (up to 800 MPa) | Moderate to high compressive strength (30-70 MPa) |
| Durability | Exceptional durability and resistance to abrasion | Good durability, depends on mix design |
| Setting Time | Fast setting due to fine particles | Variable; typically standard setting times |
| Density | High density (~2400-2600 kg/m3) | Moderate density (~2200-2400 kg/m3) |
| Workability | Low workability; requires precise mixing | Good workability for casting and finishing |
| Application in Modular Construction | Ideal for thin, high-strength elements, complex shapes | Widely used for load-bearing panels, beams, and modules |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced materials and processing | Lower; cost-effective for mass production |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint per strength unit | Higher cement usage leads to greater emissions |
Introduction to Modular Construction Materials
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) offers superior compressive strength and enhanced durability compared to traditional precast concrete, making it ideal for modular construction that demands high-performance materials. Its ultra-fine powder composition and low water-to-cement ratio enable the creation of thin, lightweight, and highly resilient structural elements, accelerating assembly and reducing transportation costs. In contrast, precast concrete provides versatility and cost efficiency with established manufacturing processes, making it a widely used option for modular components requiring less extreme mechanical properties.
Overview of Reactive Powder Concrete (RPC)
Reactive Powder Concrete (RPC) is an advanced cementitious material characterized by its ultra-high strength, enhanced durability, and reduced porosity achieved through the use of fine powders, steel fibers, and optimized particle packing. This composite exhibits compressive strengths exceeding 200 MPa, making it suitable for structural applications in modular construction where high performance and slender profiles are required. Its exceptional mechanical properties and resistance to environmental degradation offer significant advantages over traditional precast concrete in modular building systems.
Understanding Precast Concrete
Precast concrete involves manufacturing concrete components in a controlled factory environment, ensuring consistent quality and rapid on-site assembly for modular construction projects. Its durability and high compressive strength make it ideal for structural elements and complex designs, reducing construction time and labor costs. Compared to reactive powder concrete, precast concrete offers easier customization and scalability, supporting efficient mass production in modular building systems.
Key Material Properties: RPC vs Precast Concrete
Reactive Powder Concrete (RPC) exhibits significantly higher compressive strength, often exceeding 200 MPa, compared to traditional Precast Concrete, which typically ranges between 30 to 80 MPa, enabling thinner, more durable structural elements. RPC's ultra-high density and low porosity enhance durability and resistance to chemical attack, while Precast Concrete offers versatility and faster production but with comparatively lower performance in extreme environments. The superior tensile strength and modulus of elasticity of RPC contribute to improved load-bearing capacity and reduced structural weight, making it advantageous for modular construction demanding high precision and longevity.
Structural Performance and Durability Comparison
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) exhibits superior structural performance compared to traditional precast concrete due to its ultra-high compressive strength, typically exceeding 200 MPa, and enhanced tensile properties from optimized particle packing and steel fiber reinforcement. Durability of RPC surpasses that of standard precast concrete by offering significantly improved resistance to chloride penetration, freeze-thaw cycles, and abrasion, resulting in extended service life and reduced maintenance for modular construction components. The dense microstructure and low porosity of RPC contribute to its exceptional durability, making it ideal for critical load-bearing elements in modular systems where longevity and structural integrity are paramount.
Speed and Efficiency in Modular Assembly
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) offers superior strength and durability, enabling thinner, lighter panels that accelerate modular assembly by reducing handling time and simplifying transportation logistics. Precast concrete, while robust and widely used, typically involves heavier components that can slow down installation and require more substantial lifting equipment. The advanced material properties of RPC facilitate faster curing and higher precision in prefabrication, directly enhancing speed and efficiency in modular construction workflows.
Cost Implications and Lifecycle Analysis
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) offers higher strength and durability compared to traditional precast concrete, resulting in longer service life and reduced maintenance costs for modular construction projects. Although RPC has higher initial material and production expenses due to its specialized composition and curing processes, these costs are offset by improved lifecycle performance and enhanced structural efficiency. Precast concrete, while more cost-effective upfront, may incur higher long-term costs associated with repairs and shorter lifespan, impacting the overall economic feasibility of modular building systems.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) offers superior durability and reduced material usage due to its ultra-high strength and dense microstructure, leading to lower carbon emissions over the lifecycle compared to traditional precast concrete. In modular construction, RPC components require less maintenance and have longer service lives, enhancing sustainability by minimizing resource consumption and waste generation. Precast concrete, while widely used for its ease of mass production, generally involves higher energy consumption and CO2 emissions during cement production, making RPC a more environmentally favorable option for eco-conscious modular building projects.
Design Flexibility and Customization Potential
Reactive powder concrete offers superior design flexibility and customization potential compared to precast concrete due to its ultra-high strength and improved workability, allowing for intricate shapes and thinner sections without compromising structural integrity. This material enables modular construction projects to achieve more complex geometries and tailored components, enhancing architectural expression and functional adaptability. Precast concrete, while beneficial for standardization and fast production, typically limits customization due to mold constraints and lower tensile capacity, making reactive powder concrete the preferred choice for innovative modular designs.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Modular Construction
Reactive powder concrete offers superior compressive strength and durability due to its ultra-fine particle composition, making it ideal for modular construction requiring thinner, lighter, and high-performance components. Precast concrete provides versatility and faster on-site assembly, benefiting projects focused on scalability and standardization with reliable quality control in factory conditions. Selecting between these concretes depends on project priorities such as structural demands, weight constraints, and speed of construction for optimal modular building efficiency.
Infographic: Reactive powder concrete vs Precast concrete for Modular construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com