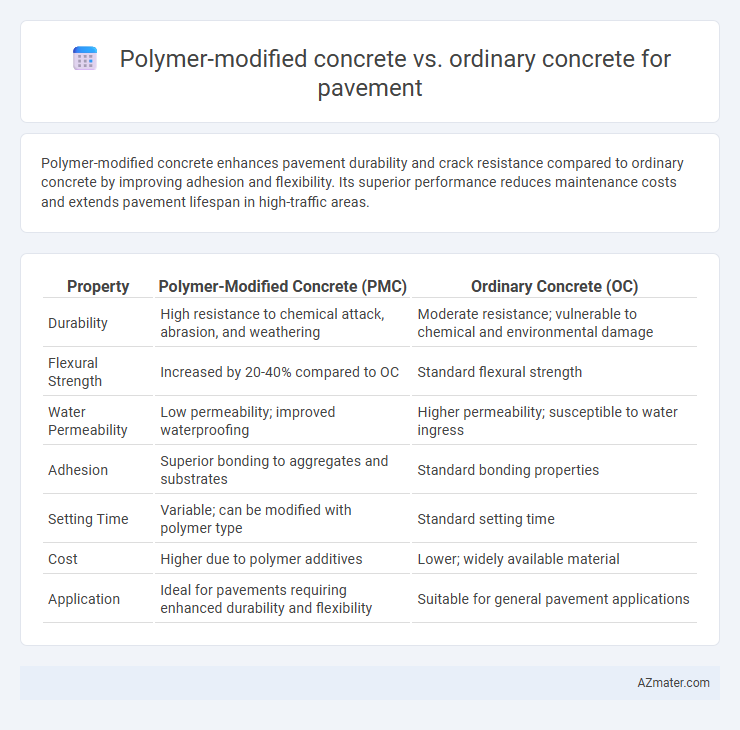
Polymer-modified concrete enhances pavement durability and crack resistance compared to ordinary concrete by improving adhesion and flexibility. Its superior performance reduces maintenance costs and extends pavement lifespan in high-traffic areas.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymer-Modified Concrete (PMC) | Ordinary Concrete (OC) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to chemical attack, abrasion, and weathering | Moderate resistance; vulnerable to chemical and environmental damage |
| Flexural Strength | Increased by 20-40% compared to OC | Standard flexural strength |
| Water Permeability | Low permeability; improved waterproofing | Higher permeability; susceptible to water ingress |
| Adhesion | Superior bonding to aggregates and substrates | Standard bonding properties |
| Setting Time | Variable; can be modified with polymer type | Standard setting time |
| Cost | Higher due to polymer additives | Lower; widely available material |
| Application | Ideal for pavements requiring enhanced durability and flexibility | Suitable for general pavement applications |
Introduction to Pavement Concrete Types
Polymer-modified concrete (PMC) enhances ordinary concrete by incorporating polymers to improve durability, flexibility, and resistance to cracking, making it ideal for pavement applications subjected to heavy traffic and harsh weather. Ordinary concrete, composed mainly of cement, water, and aggregates, provides a rigid and cost-effective solution but may suffer from lower resistance to shrinking and thermal stresses. Pavement types utilizing PMC typically experience extended service life and reduced maintenance compared to those built with traditional ordinary concrete.
What is Ordinary Concrete?
Ordinary concrete is a mixture of cement, water, fine aggregates, and coarse aggregates commonly used in pavement construction for its strength and durability. It lacks any additives or polymers, leading to lower resistance against cracking, abrasion, and chemical attacks compared to polymer-modified concrete. Ordinary concrete typically exhibits higher permeability and reduced flexibility, which can result in faster deterioration under heavy traffic and adverse environmental conditions.
Understanding Polymer-Modified Concrete
Polymer-modified concrete (PMC) incorporates polymers to enhance durability, flexibility, and resistance to cracking compared to ordinary concrete, making it ideal for pavement applications. The addition of polymers improves adhesion between cement paste and aggregates, resulting in reduced permeability and increased resistance to chemical attacks, freeze-thaw cycles, and abrasion. These properties extend pavement lifespan and reduce maintenance costs, providing significant performance benefits over traditional concrete mixes.
Composition Differences: Polymer vs Ordinary Concrete
Polymer-modified concrete incorporates synthetic polymers such as styrene-butadiene rubber or acrylics that enhance bonding, flexibility, and water resistance, unlike ordinary concrete which relies primarily on cement, water, and aggregates. The polymer content reduces permeability and improves adhesion between the cement matrix and aggregates, resulting in higher tensile strength and durability. Ordinary concrete, without these polymers, exhibits lower resistance to cracking and environmental stresses commonly encountered in pavement applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polymer-modified concrete (PMC) exhibits significantly enhanced mechanical properties compared to ordinary concrete (OC) in pavement applications, including higher tensile strength, improved flexural strength, and increased impact resistance. The incorporation of polymers reduces porosity and microcracking in PMC, leading to superior durability and greater resistance to thermal and mechanical stresses. Studies indicate that PMC's elastic modulus and abrasion resistance outperform those of OC, resulting in extended pavement lifespan and reduced maintenance costs.
Durability and Longevity in Pavement Applications
Polymer-modified concrete (PMC) exhibits superior durability compared to ordinary concrete due to enhanced resistance to cracking, water infiltration, and chemical attacks, which are critical factors in pavement longevity. The inclusion of polymers in PMC significantly improves flexibility and adhesion, reducing freeze-thaw damage and abrasion from traffic loads. Long-term studies indicate that polymer-modified pavements maintain structural integrity and surface quality longer, leading to extended service life and lower maintenance costs compared to ordinary concrete pavements.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Polymer-modified concrete exhibits superior resistance to environmental factors compared to ordinary concrete, especially in pavement applications. It demonstrates enhanced durability against freeze-thaw cycles, chemical attacks, and moisture ingress due to the polymer matrix improving the concrete's impermeability and flexibility. This increased resistance results in longer pavement service life and reduced maintenance costs under harsh environmental conditions.
Cost Analysis: Polymer-Modified vs Ordinary Concrete
Polymer-modified concrete (PMC) typically incurs higher initial costs than ordinary concrete due to the price of polymers and specialized mixing processes, with costs increasing by 15-30%. Despite the higher upfront investment, PMC offers enhanced durability, reduced maintenance expenses, and longer service life, which can result in lower lifecycle costs compared to ordinary concrete. Cost-benefit analyses demonstrate that for high-traffic pavements, the reduced repair frequency and extended pavement lifespan make PMC a more economical choice over time.
Construction Practices and Workability
Polymer-modified concrete enhances pavement construction practices by improving workability through increased flexibility and reduced water-cement ratio, allowing easier placement and compaction compared to ordinary concrete. The polymers improve bonding, reduce segregation, and delay setting time, which facilitates better surface finishing and longer working periods. Ordinary concrete typically requires more curing time and is prone to cracking under traffic loads, while polymer-modified concrete offers superior durability and resistance to chemical and environmental stress during pavement applications.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Pavement Projects
Polymer-modified concrete offers enhanced durability, improved flexural strength, and superior resistance to cracking compared to ordinary concrete, making it ideal for high-traffic pavement projects. Ordinary concrete remains cost-effective and suitable for low-traffic or residential pavements where load and environmental stress are minimal. Selecting the right concrete depends on project-specific factors such as load requirements, environmental conditions, budget constraints, and desired longevity of the pavement.
Infographic: Polymer-modified concrete vs Ordinary concrete for Pavement
 azmater.com
azmater.com