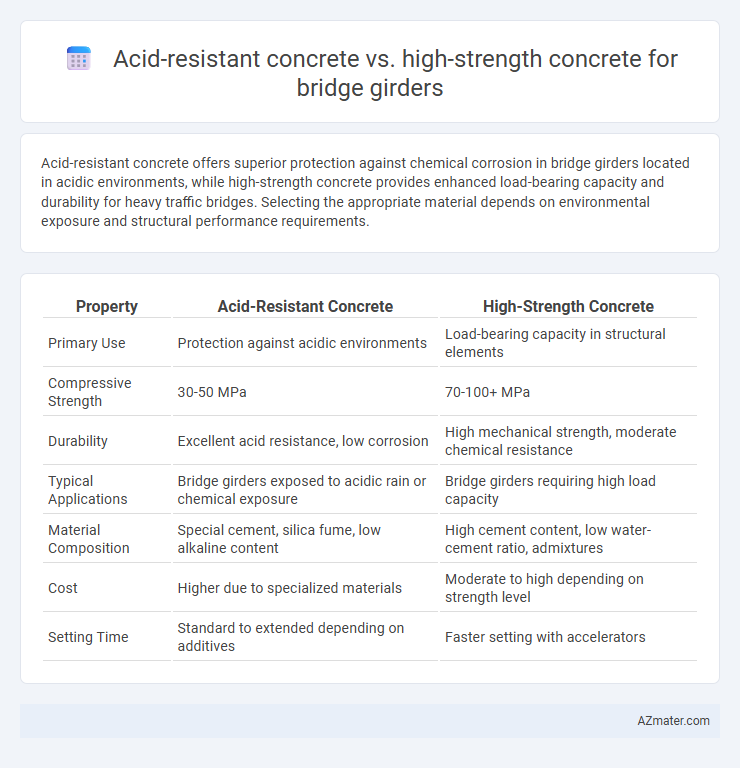
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior protection against chemical corrosion in bridge girders located in acidic environments, while high-strength concrete provides enhanced load-bearing capacity and durability for heavy traffic bridges. Selecting the appropriate material depends on environmental exposure and structural performance requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acid-Resistant Concrete | High-Strength Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Protection against acidic environments | Load-bearing capacity in structural elements |
| Compressive Strength | 30-50 MPa | 70-100+ MPa |
| Durability | Excellent acid resistance, low corrosion | High mechanical strength, moderate chemical resistance |
| Typical Applications | Bridge girders exposed to acidic rain or chemical exposure | Bridge girders requiring high load capacity |
| Material Composition | Special cement, silica fume, low alkaline content | High cement content, low water-cement ratio, admixtures |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized materials | Moderate to high depending on strength level |
| Setting Time | Standard to extended depending on additives | Faster setting with accelerators |
Introduction: Importance of Concrete Selection for Bridge Girders
Selecting the appropriate concrete for bridge girders is critical to ensure structural durability and longevity under specific environmental conditions. Acid-resistant concrete offers enhanced protection against chemical corrosion in industrial or polluted areas, extending lifespan where exposure to acidic agents is prevalent. High-strength concrete provides superior load-bearing capacity and durability for heavy traffic loads and long spans, optimizing structural performance in demanding bridge applications.
Overview of Acid-Resistant Concrete
Acid-resistant concrete is engineered to withstand aggressive chemical environments, particularly in bridge girders exposed to acidic water or industrial pollutants, providing superior durability by incorporating specialized aggregates and chemical admixtures that reduce permeability and enhance resistance to acid attack. This type of concrete typically contains additives such as silica fume, fly ash, or polymer modifiers that create a dense microstructure, preventing the ingress of harmful acids and extending the service life of critical infrastructure components. Compared to high-strength concrete, which prioritizes mechanical load-bearing capacity, acid-resistant concrete emphasizes chemical durability to maintain structural integrity in corrosive conditions.
Overview of High-Strength Concrete
High-strength concrete (HSC) for bridge girders typically exhibits compressive strengths above 6000 psi, enabling slimmer, lighter structures with enhanced load-bearing capacity and durability. Its optimized mix design, incorporating supplementary cementitious materials like silica fume and superplasticizers, improves workability and reduces permeability, resulting in superior resistance to environmental stresses. Compared to acid-resistant concrete, HSC prioritizes mechanical performance and structural efficiency while maintaining adequate durability in various service conditions.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Acid-resistant concrete for bridge girders features enhanced chemical durability and low permeability, resisting aggressive environmental agents such as sulfates and acids commonly found in industrial or coastal settings. High-strength concrete exhibits superior compressive strength, often exceeding 60 MPa, designed to support heavy structural loads and reduce girder cross-section size. The key material properties comparison highlights acid-resistant concrete's emphasis on chemical stability and longevity, while high-strength concrete prioritizes mechanical performance and load-bearing capacity.
Durability Against Environmental Challenges
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior durability against chemical attacks, making it ideal for bridge girders exposed to acidic environments or industrial pollutants. High-strength concrete provides enhanced load-bearing capacity but may require additional protective measures to resist environmental degradation such as carbonation or chloride ingress. Combining acid-resistant additives with high-strength formulations can optimize both mechanical performance and long-term durability in aggressive conditions.
Performance in Acidic and Aggressive Conditions
Acid-resistant concrete for bridge girders offers superior durability by incorporating specialized cement and additives that enhance resistance to acidic and aggressive chemical environments, preventing surface degradation and reinforcement corrosion. High-strength concrete provides exceptional load-bearing capacity but may be more vulnerable to acid attack due to its denser matrix potentially trapping aggressive agents, leading to micro-cracking and reduced lifespan in harsh conditions. Selecting acid-resistant concrete is essential for bridge girders exposed to industrial pollution, acid rain, or marine environments to ensure long-term structural integrity and lower maintenance costs.
Structural Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity
Acid-resistant concrete for bridge girders offers enhanced durability in corrosive environments but generally exhibits lower compressive strength compared to high-strength concrete. High-strength concrete provides superior structural strength and higher load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for heavy traffic and longer spans. Selecting between the two depends on the balance between chemical resistance requirements and maximum load performance.
Application Suitability: When to Use Each Type
Acid-resistant concrete is ideal for bridge girders exposed to aggressive chemical environments, such as industrial areas or regions with acidic rain, due to its enhanced durability against corrosion and chemical attack. High-strength concrete is preferable for girders requiring exceptional load-bearing capacity and structural performance in high-traffic or heavy-load bridges. Selecting the appropriate type depends on environmental exposure and structural demands, ensuring longevity and safety in bridge construction.
Cost, Maintenance, and Lifecycle Considerations
Acid-resistant concrete for bridge girders offers superior durability in corrosive environments, reducing maintenance frequency but often comes at higher initial costs due to specialized additives. High-strength concrete provides enhanced load-bearing capacity and faster construction times, potentially lowering labor costs, yet it may require more frequent inspections and repairs when exposed to aggressive chemicals. Considering lifecycle costs, acid-resistant concrete typically delivers longer service life with reduced overall maintenance expenses, while high-strength concrete may incur higher long-term costs if environmental resistance is compromised.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Concrete for Bridge Girders
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior durability in corrosive environments by incorporating specialized aggregates and chemical admixtures, making it ideal for bridge girders exposed to industrial pollutants or acidic runoff. High-strength concrete provides enhanced load-bearing capacity and structural performance, suited for bridges requiring increased span lengths or heavy traffic loads. Selecting the optimal concrete depends on environmental exposure and structural demands, with acid-resistant concrete prioritized for chemical resilience and high-strength concrete chosen for mechanical strength requirements.
Infographic: Acid-resistant concrete vs High-strength concrete for Bridge girder
 azmater.com
azmater.com