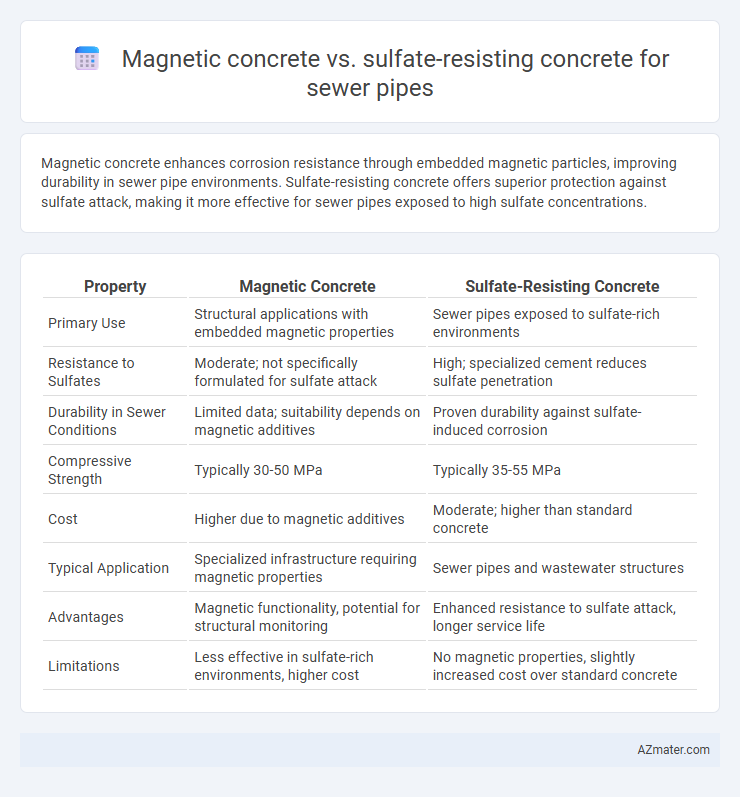
Magnetic concrete enhances corrosion resistance through embedded magnetic particles, improving durability in sewer pipe environments. Sulfate-resisting concrete offers superior protection against sulfate attack, making it more effective for sewer pipes exposed to high sulfate concentrations.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Magnetic Concrete | Sulfate-Resisting Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Structural applications with embedded magnetic properties | Sewer pipes exposed to sulfate-rich environments |
| Resistance to Sulfates | Moderate; not specifically formulated for sulfate attack | High; specialized cement reduces sulfate penetration |
| Durability in Sewer Conditions | Limited data; suitability depends on magnetic additives | Proven durability against sulfate-induced corrosion |
| Compressive Strength | Typically 30-50 MPa | Typically 35-55 MPa |
| Cost | Higher due to magnetic additives | Moderate; higher than standard concrete |
| Typical Application | Specialized infrastructure requiring magnetic properties | Sewer pipes and wastewater structures |
| Advantages | Magnetic functionality, potential for structural monitoring | Enhanced resistance to sulfate attack, longer service life |
| Limitations | Less effective in sulfate-rich environments, higher cost | No magnetic properties, slightly increased cost over standard concrete |
Introduction to Sewer Pipe Materials
Sewer pipe materials must withstand harsh environmental conditions, such as chemical exposure and mechanical stress. Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic particles that enhance structural integrity and provide electromagnetic properties, potentially improving durability in corrosive sewer environments. Sulfate-resisting concrete is specifically formulated with low tricalcium aluminate content to resist sulfate attack, making it highly effective in preventing degradation caused by sulfate-rich sewage and soils.
Overview of Magnetic Concrete
Magnetic concrete is an innovative material embedded with ferromagnetic particles that enhance structural integrity and provide electromagnetic properties beneficial for sewer pipe applications. Unlike sulfate-resisting concrete, which is specifically formulated to withstand chemical attacks from sulfates, magnetic concrete offers improved durability against mechanical stresses and potential real-time monitoring capabilities through magnetic field detection. This technology enables proactive maintenance and extends sewer pipe lifespan by detecting cracks or defects early without invasive inspection methods.
Overview of Sulfate-Resisting Concrete
Sulfate-resisting concrete is specifically designed to withstand the aggressive chemical attack from sulfate ions commonly found in sewer environments, offering enhanced durability compared to standard concrete. It incorporates low C3A cement and supplementary cementitious materials like fly ash or slag, reducing permeability and preventing sulfate penetration. Magnetic concrete, while innovative, lacks the targeted chemical resistance properties crucial for long-term sewer pipe performance under sulfate exposure.
Chemical Resistance in Sewer Environments
Magnetic concrete exhibits enhanced chemical resistance in sewer environments due to its ability to incorporate magnetic nanoparticles that improve its density and reduce permeability, effectively resisting sulfate and other aggressive chemical attacks. Sulfate-resisting concrete is specifically formulated with lower tricalcium aluminate (C3A) content, which provides superior resistance to sulfate ion penetration and subsequent deterioration caused by hydrogen sulfide corrosion in sewer pipes. Both types show improved durability, but magnetic concrete's novel composition offers advanced protection by minimizing microcrack formation and chemical ingress in harsh sewer conditions.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Magnetic concrete enhances durability in sewer pipes by improving microstructure density and resistance to chemical attacks, extending lifespan by reducing corrosion and degradation over time. Sulfate-resisting concrete specializes in mitigating sulfate ion penetration, preventing expansion and cracking caused by sulfate attack in aggressive sewer environments. While both types improve sewer pipe longevity, magnetic concrete offers broader chemical resistance, whereas sulfate-resisting concrete is optimized specifically for sulfate-rich conditions, typically resulting in a lifespan extension of 50-70% depending on environmental exposure.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Magnetic concrete offers enhanced self-sensing capabilities for crack detection, simplifying maintenance by enabling real-time monitoring of sewer pipe integrity, whereas sulfate-resisting concrete primarily focuses on chemical durability against sulfate attack, requiring routine inspections to prevent degradation. Installation of magnetic concrete may involve specialized equipment for embedding magnetic particles and sensors, potentially increasing initial costs, while sulfate-resisting concrete uses traditional casting methods but demands careful material selection to ensure sulfate resistance. Long-term maintenance favors magnetic concrete due to its proactive damage detection, reducing the risk of costly repairs compared to the reactive maintenance approach typical for sulfate-resisting concrete in aggressive sewer environments.
Cost Analysis: Magnetic vs Sulfate-Resisting Concrete
Magnetic concrete typically incurs higher initial costs due to the incorporation of magnetic materials and specialized manufacturing processes compared to sulfate-resisting concrete, which uses established additives like calcium aluminate cement to improve durability. Sulfate-resisting concrete offers cost efficiency in sewer pipe applications by reducing maintenance and repair expenses associated with sulfate-induced corrosion. When evaluating total lifecycle costs, sulfate-resisting concrete generally provides a more economically viable solution for sewer infrastructure, balancing material costs with enhanced longevity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Magnetic concrete incorporates iron-based additives that enhance durability and enable electromagnetic detection, reducing pipeline failures and minimizing environmental disruptions during maintenance in sewer systems. Sulfate-resisting concrete, formulated with low C3A content cement, prevents sulfate attack from aggressive sewage soil conditions, extending sewer pipe lifespan and reducing the frequency of replacements, thus lowering environmental waste. Both materials contribute to sustainability by improving sewer infrastructure longevity, but magnetic concrete's detectability offers additional environmental benefits through efficient maintenance and reduced excavation.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Magnetic concrete has demonstrated enhanced durability and corrosion resistance in sewer pipe case studies, reducing maintenance costs by mitigating microbial-induced corrosion, while sulfate-resisting concrete (SRC) has been extensively validated in real-world applications for its superior performance against sulfate attack commonly found in aggressive sewer environments. Field data from multiple municipal projects reveal that sulfate-resisting concrete maintains structural integrity over long-term exposure to sulfates, whereas magnetic concrete shows promising potential in extending pipe lifespan through its unique electromagnetic properties that inhibit corrosive agents. Comparative analyses emphasize SRC's proven reliability in harsh chemical conditions, with magnetic concrete emerging as an innovative alternative requiring further large-scale validation.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Concrete for Sewer Pipes
Magnetic concrete offers enhanced durability and corrosion resistance due to its unique magnetic properties, making it suitable for environments with heavy chemical exposure. Sulfate-resisting concrete specifically prevents sulfate attack, ensuring longevity in sewer pipes exposed to high sulfate concentrations. For sewer pipes in areas with aggressive sulfate-rich soils or waters, sulfate-resisting concrete is the optimal choice, while magnetic concrete is advantageous in settings demanding superior structural integrity and corrosion protection.
Infographic: Magnetic concrete vs Sulfate-resisting concrete for Sewer pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com