Precast concrete offers faster installation and consistent quality for structural beams, while high-strength concrete provides superior load-bearing capacity and durability. Selecting between them depends on project requirements for speed versus structural performance.
Table of Comparison
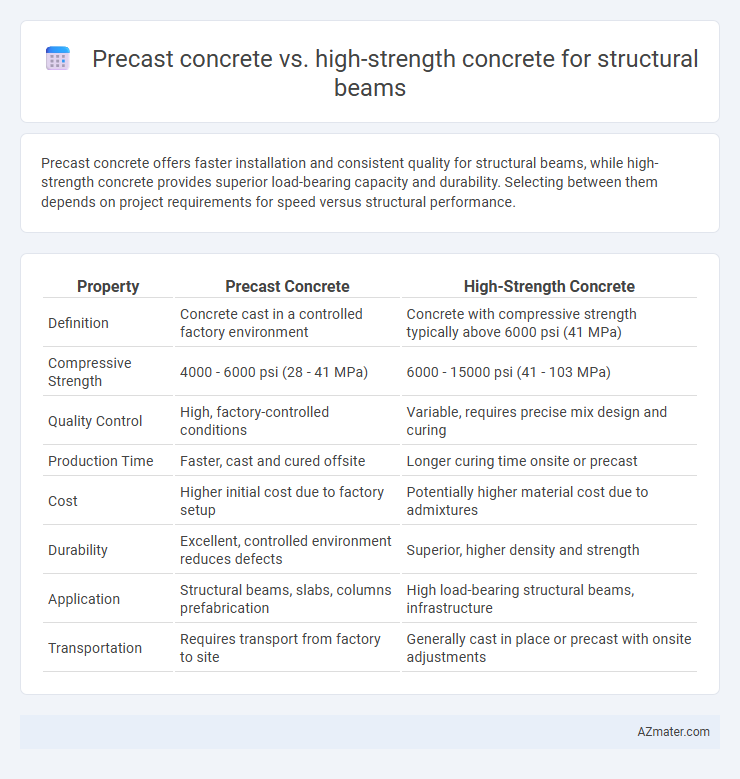
| Property | Precast Concrete | High-Strength Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete cast in a controlled factory environment | Concrete with compressive strength typically above 6000 psi (41 MPa) |
| Compressive Strength | 4000 - 6000 psi (28 - 41 MPa) | 6000 - 15000 psi (41 - 103 MPa) |
| Quality Control | High, factory-controlled conditions | Variable, requires precise mix design and curing |
| Production Time | Faster, cast and cured offsite | Longer curing time onsite or precast |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to factory setup | Potentially higher material cost due to admixtures |
| Durability | Excellent, controlled environment reduces defects | Superior, higher density and strength |
| Application | Structural beams, slabs, columns prefabrication | High load-bearing structural beams, infrastructure |
| Transportation | Requires transport from factory to site | Generally cast in place or precast with onsite adjustments |
Introduction to Structural Beams
Structural beams serve as critical load-bearing elements in construction, designed to support and transfer loads efficiently across spans. Precast concrete beams offer uniform quality and accelerated construction schedules due to factory fabrication, while high-strength concrete beams provide superior compressive strength, enabling slimmer profiles and longer spans. Selecting between precast and high-strength concrete depends on project requirements such as load capacity, construction speed, and design flexibility.
Understanding Precast Concrete
Precast concrete offers precise quality control and faster construction times due to factory fabrication, making it ideal for structural beams in complex projects. High-strength concrete beams provide superior load-bearing capacity but require careful on-site curing and formwork, increasing construction time and labor. Understanding precast concrete emphasizes its durability, reduced environmental impact, and versatility in repetitive structural beam elements.
Overview of High-Strength Concrete
High-strength concrete is characterized by a compressive strength exceeding 6,000 psi, making it ideal for structural beams requiring enhanced durability and load-bearing capacity. It offers superior tensile strength and reduced permeability compared to standard precast concrete, leading to improved longevity and resistance to environmental stressors. This concrete type allows for slimmer beam profiles and more efficient structural designs in high-rise buildings and infrastructure projects.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Precast concrete offers consistent quality control and faster construction times due to factory curing, with typical compressive strength ranging from 30 to 50 MPa. High-strength concrete surpasses standard mixes with compressive strengths exceeding 70 MPa, providing enhanced durability and load-bearing capacity for structural beams in demanding applications. The choice hinges on balancing the uniformity and efficiency of precasting against the superior compressive strength and reduced cross-sectional dimensions achievable with high-strength concrete.
Manufacturing and Installation Processes
Precast concrete beams offer streamlined manufacturing processes through controlled factory environments, ensuring consistent quality and faster production cycles. High-strength concrete beams require precise mixing and curing techniques on-site or in specialized facilities to achieve desired compressive strength, often demanding longer curing times and careful handling. Installation of precast beams benefits from pre-fabricated dimensions and embedded connection elements, reducing on-site labor and construction time compared to high-strength concrete beams, which may need additional formwork and reinforcement adjustments during casting.
Structural Performance and Load Capacity
Precast concrete beams offer uniform quality and faster installation, enhancing structural performance through controlled manufacturing processes that reduce shrinkage and cracking. High-strength concrete beams provide superior compressive strength, significantly increasing load capacity and allowing for slimmer beam designs in structural applications. Combining precast techniques with high-strength concrete can optimize structural efficiency by leveraging precise fabrication and enhanced material properties.
Durability and Longevity Considerations
Precast concrete structural beams exhibit enhanced durability through controlled factory conditions, ensuring consistent quality and reduced exposure to environmental stressors. High-strength concrete beams provide superior compressive strength and resistance to wear but may suffer from increased brittleness and potential microcracking affecting long-term longevity. Prioritizing durability, precast concrete offers improved resistance to freeze-thaw cycles and corrosion, which contributes to extended service life in structural applications.
Cost Analysis for Precast vs High-Strength Concrete
Precast concrete beams often reduce labor and formwork costs due to factory-controlled production, enabling faster installation and minimizing onsite delays compared to high-strength concrete beams that typically require longer curing times. High-strength concrete beams, although generally more expensive per cubic meter due to specialized materials and mix designs, can reduce beam size and overall structural weight, potentially lowering foundation costs. The cost-effectiveness of precast versus high-strength concrete beams depends on project scale, transportation logistics, and the balance between material costs and construction time savings.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Precast concrete offers enhanced sustainability by minimizing onsite waste and reducing construction time, which lowers overall carbon emissions. High-strength concrete reduces material usage due to its superior load-bearing capacity, leading to smaller cross-sections and less raw material extraction. Combining precast methods with high-strength concrete optimizes environmental impact through improved durability and efficient resource utilization in structural beams.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Project
Precast concrete offers uniform quality and faster installation times due to factory-controlled conditions, making it ideal for projects requiring efficient construction and consistent strength. High-strength concrete provides superior compressive strength and durability, suitable for structures subjected to heavy loads or harsh environmental conditions. Selecting the best option depends on project priorities such as timeline, structural demands, and long-term performance requirements.
Infographic: Precast concrete vs High-strength concrete for Structural beam
 azmater.com
azmater.com