Green concrete reduces carbon emissions by incorporating recycled materials, enhancing sustainability in floor slabs. Lightweight concrete offers improved thermal insulation and reduced structural load, ideal for floor slab applications requiring weight efficiency.
Table of Comparison
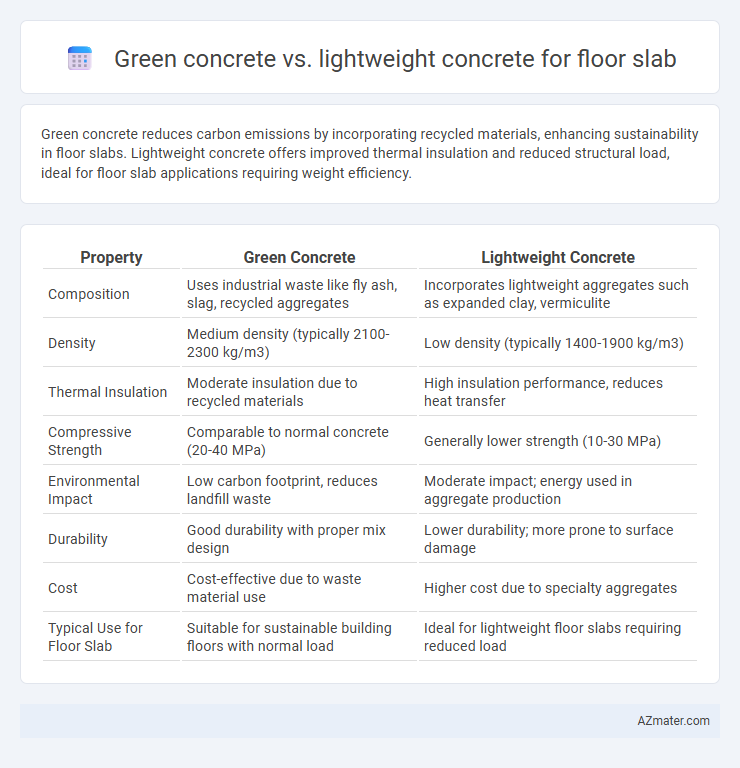
| Property | Green Concrete | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Uses industrial waste like fly ash, slag, recycled aggregates | Incorporates lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay, vermiculite |
| Density | Medium density (typically 2100-2300 kg/m3) | Low density (typically 1400-1900 kg/m3) |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate insulation due to recycled materials | High insulation performance, reduces heat transfer |
| Compressive Strength | Comparable to normal concrete (20-40 MPa) | Generally lower strength (10-30 MPa) |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, reduces landfill waste | Moderate impact; energy used in aggregate production |
| Durability | Good durability with proper mix design | Lower durability; more prone to surface damage |
| Cost | Cost-effective due to waste material use | Higher cost due to specialty aggregates |
| Typical Use for Floor Slab | Suitable for sustainable building floors with normal load | Ideal for lightweight floor slabs requiring reduced load |
Introduction to Green Concrete and Lightweight Concrete
Green concrete incorporates industrial by-products like fly ash, slag, or recycled aggregates to reduce environmental impact and enhance sustainability in construction. Lightweight concrete uses expanded aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or perlite to reduce density and improve thermal insulation while maintaining adequate strength for floor slab applications. Both materials offer eco-friendly alternatives with specific benefits in durability, weight reduction, and energy efficiency for modern building practices.
Composition Differences: Green vs Lightweight Concrete
Green concrete incorporates recycled materials such as fly ash, slag, and recycled aggregates, reducing the environmental impact while maintaining structural integrity. Lightweight concrete uses lightweight aggregates like expanded clay, shale, or pumice, significantly decreasing density to enhance thermal insulation and reduce load on the floor slab. The key composition difference lies in green concrete's emphasis on sustainability through material substitution, whereas lightweight concrete focuses on aggregate selection for weight reduction.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Green concrete significantly reduces carbon emissions by incorporating recycled materials and industrial by-products, lowering the demand for Portland cement and minimizing landfill waste. Lightweight concrete contributes to sustainability through enhanced thermal insulation properties, which reduce energy consumption for heating and cooling in buildings. Both materials offer environmental benefits, but green concrete excels in carbon footprint reduction, while lightweight concrete optimizes energy efficiency throughout the building lifecycle.
Strength and Structural Performance Comparison
Green concrete, incorporating recycled materials and industrial by-products, offers comparable compressive strength to traditional concrete but typically exhibits enhanced durability and sustainability benefits. Lightweight concrete, made with expanded aggregates such as perlite or pumice, provides reduced density which improves structural load efficiency but may have lower compressive strength than typical green concrete mixes. Structural performance of green concrete slabs often exceeds lightweight options in load-bearing capacity and crack resistance, making it preferable for floors requiring both strength and environmental considerations.
Insulation and Thermal Properties
Green concrete offers superior insulation and enhanced thermal mass, reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling in floor slabs. Lightweight concrete provides excellent thermal insulation due to its lower density and higher air void content, helping to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures. Both types improve energy efficiency, but lightweight concrete is often preferred for insulation-focused applications where weight reduction is critical.
Weight and Load Considerations for Floor Slabs
Green concrete typically incorporates recycled materials and industrial by-products, resulting in a heavier mix compared to lightweight concrete, which uses lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay or shale to reduce density. The weight of green concrete can increase the dead load on floor slabs, requiring stronger structural support, whereas lightweight concrete reduces the dead load, allowing for longer spans and less structural reinforcement. Load considerations for floor slabs must balance material strength with weight, where lightweight concrete offers advantages in seismic zones and multi-story buildings due to its lower mass and improved load distribution.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Factors
Green concrete, incorporating recycled materials and industrial by-products, typically offers superior cost efficiency by reducing raw material expenses and lowering energy consumption during production compared to traditional mixes. Lightweight concrete floor slabs provide economic benefits through reduced structural load, leading to smaller foundation requirements and decreased construction time, which lowers overall project costs. However, the choice between green concrete and lightweight concrete depends on the balance between material costs, performance requirements, and long-term sustainability objectives specific to the floor slab application.
Workability and Construction Techniques
Green concrete, incorporating recycled materials and industrial by-products, offers improved workability due to its balanced mix design, facilitating smoother pouring and compaction in floor slab applications. Lightweight concrete, made with expanded aggregates such as expanded clay or shale, presents enhanced workability through reduced density and easier handling, allowing faster placement and reduced labor effort. Construction techniques for green concrete require careful curing to ensure strength and durability, while lightweight concrete benefits from specialized formworks and reinforcement methods to accommodate its lower weight and thermal properties.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Green concrete, composed of recycled materials and industrial by-products, offers enhanced durability with lower permeability, reducing susceptibility to chemical attacks and increasing lifespan in floor slabs. Lightweight concrete, while providing excellent thermal insulation and reduced structural load, may require more frequent maintenance due to its porous nature and potential for surface wear. For floor slabs, green concrete minimizes maintenance needs through superior resistance to cracking and environmental degradation compared to lightweight concrete.
Best Applications and Suitability for Floor Slabs
Green concrete offers enhanced sustainability with recycled materials and reduces carbon footprint, making it ideal for eco-friendly floor slabs in residential and commercial buildings. Lightweight concrete provides superior thermal insulation and reduces dead load, suitable for multistory structures and roofs where weight reduction is critical. For floor slabs, green concrete suits projects prioritizing environmental impact, while lightweight concrete excels in applications requiring energy efficiency and structural load savings.
Infographic: Green concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Floor slab
 azmater.com
azmater.com