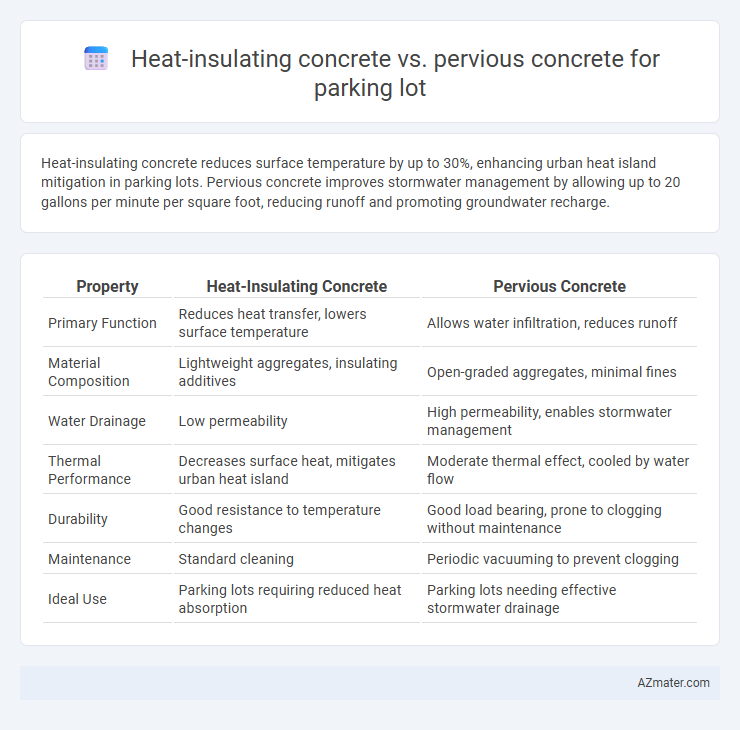
Heat-insulating concrete reduces surface temperature by up to 30%, enhancing urban heat island mitigation in parking lots. Pervious concrete improves stormwater management by allowing up to 20 gallons per minute per square foot, reducing runoff and promoting groundwater recharge.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Heat-Insulating Concrete | Pervious Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Reduces heat transfer, lowers surface temperature | Allows water infiltration, reduces runoff |
| Material Composition | Lightweight aggregates, insulating additives | Open-graded aggregates, minimal fines |
| Water Drainage | Low permeability | High permeability, enables stormwater management |
| Thermal Performance | Decreases surface heat, mitigates urban heat island | Moderate thermal effect, cooled by water flow |
| Durability | Good resistance to temperature changes | Good load bearing, prone to clogging without maintenance |
| Maintenance | Standard cleaning | Periodic vacuuming to prevent clogging |
| Ideal Use | Parking lots requiring reduced heat absorption | Parking lots needing effective stormwater drainage |
Introduction to Parking Lot Concrete Solutions
Heat-insulating concrete offers superior thermal regulation by reducing heat absorption, making it ideal for parking lots in hot climates to minimize urban heat islands. Pervious concrete enhances stormwater management through high permeability, allowing rainwater to infiltrate and reduce runoff, which is crucial for sustainable parking lot design. Choosing between these materials depends on prioritizing temperature control or environmental water management for optimized parking lot performance.
Overview of Heat-Insulating Concrete
Heat-insulating concrete for parking lots significantly reduces surface temperature by incorporating thermal insulation materials such as expanded polystyrene beads or aerogel, which lower heat absorption compared to traditional concrete. This type of concrete improves energy efficiency by maintaining cooler pavement surfaces, thereby mitigating urban heat island effects and enhancing comfort for pedestrians and vehicles. Its porous structure is carefully controlled to balance insulation capabilities with adequate load-bearing strength suitable for frequent vehicular traffic.
Overview of Pervious Concrete
Pervious concrete is a highly porous material designed to allow water to pass through, reducing runoff and promoting natural groundwater recharge in parking lots. It typically consists of a mixture of coarse aggregates, cement, water, and little to no fine aggregates, resulting in a high void content that enables permeability rates ranging from 500 to 2,000 gallons per minute per square foot. This permeable pavement solution helps mitigate urban flooding, improves stormwater management, and supports environmental sustainability compared to conventional heat-insulating concrete options.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Heat-insulating concrete offers superior thermal resistance with low thermal conductivity, reducing heat absorption and lowering surface temperatures in parking lots, which mitigates urban heat island effects. Pervious concrete, while promoting water infiltration and reducing runoff, exhibits higher thermal conductivity than heat-insulating concrete, resulting in less effective temperature regulation. Consequently, heat-insulating concrete provides enhanced thermal performance for parking lot surfaces, improving comfort and durability under high solar radiation.
Water Drainage and Permeability
Heat-insulating concrete offers moderate water drainage capabilities but primarily focuses on reducing heat absorption, making it less permeable compared to pervious concrete. Pervious concrete provides superior water permeability, allowing efficient stormwater infiltration and reducing runoff, which is crucial for parking lot drainage management. High permeability in pervious concrete prevents water pooling and enhances groundwater recharge, addressing urban flood risks more effectively than heat-insulating concrete.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Heat-insulating concrete for parking lots offers enhanced thermal resistance, reducing heat buildup and mitigating surface cracking caused by temperature fluctuations, which significantly improves long-term durability. Pervious concrete excels in stormwater management by allowing water infiltration, but it generally requires more frequent maintenance such as vacuuming to prevent pore clogging and maintain permeability, potentially impacting durability if neglected. When prioritizing durability and maintenance, heat-insulating concrete demands less upkeep and provides superior resistance to environmental stress, while pervious concrete necessitates consistent care to sustain its functional benefits.
Installation Process and Cost Analysis
Heat-insulating concrete requires specialized mixing of insulating aggregates, prolonging the installation process compared to pervious concrete, which uses conventional materials allowing for faster application and curing times. The cost analysis reveals that heat-insulating concrete has higher initial expenses due to premium materials and labor but offers long-term energy savings through temperature regulation. Pervious concrete presents lower upfront costs and efficient stormwater management benefits, reducing maintenance expenses in parking lot applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Heat-insulating concrete reduces urban heat island effects by lowering surface temperatures, enhancing energy efficiency, and decreasing cooling demands for nearby buildings. Pervious concrete facilitates stormwater infiltration, reducing runoff and improving groundwater recharge, which mitigates flooding and water pollution. Both materials contribute to sustainability by improving environmental performance, but pervious concrete offers superior benefits in water management, while heat-insulating concrete excels in thermal regulation.
Suitability for Different Climates
Heat-insulating concrete provides excellent thermal resistance, making it highly suitable for hot climates by reducing heat absorption and lowering surface temperatures in parking lots. Pervious concrete excels in managing stormwater through enhanced drainage, which is beneficial in wet or temperate climates prone to heavy rainfall. Climate-specific selection of these concrete types improves durability and environmental performance in parking lot applications.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Parking Lots
Heat-insulating concrete reduces surface temperature by reflecting and dissipating heat, enhancing vehicle comfort and reducing heat island effects in parking lots. Pervious concrete improves stormwater management through high permeability, preventing water pooling and promoting ground infiltration, which helps meet environmental regulations. Selecting the right concrete depends on priorities such as thermal comfort versus drainage needs, with heat-insulating concrete excelling in temperature control and pervious concrete optimizing water runoff and sustainability.
Infographic: Heat-insulating concrete vs Pervious concrete for Parking lot
 azmater.com
azmater.com