Cellular concrete offers lightweight, thermal insulation, and soundproofing advantages compared to precast concrete blocks, which provide higher structural strength and durability. Selecting between cellular and precast concrete blocks depends on project requirements such as load-bearing capacity and energy efficiency.
Table of Comparison
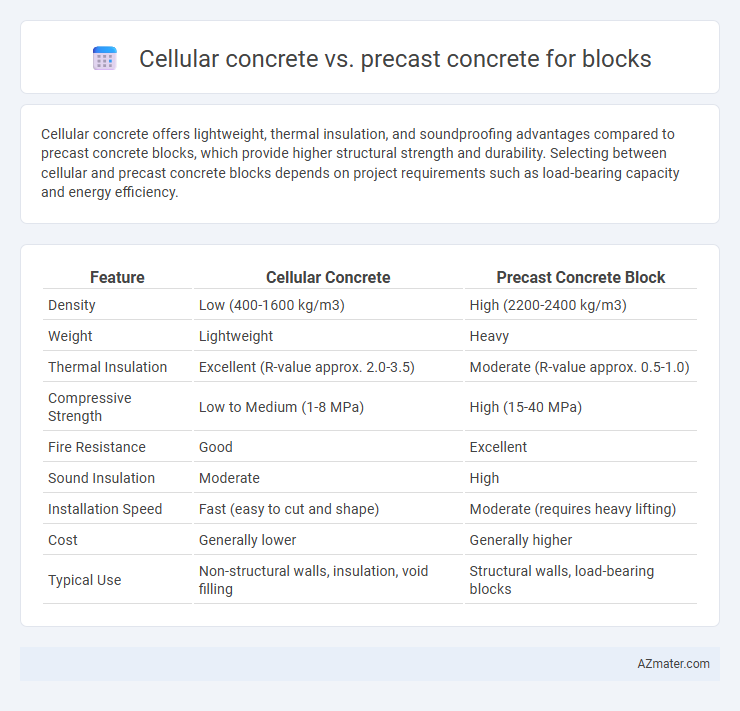
| Feature | Cellular Concrete | Precast Concrete Block |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low (400-1600 kg/m3) | High (2200-2400 kg/m3) |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavy |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent (R-value approx. 2.0-3.5) | Moderate (R-value approx. 0.5-1.0) |
| Compressive Strength | Low to Medium (1-8 MPa) | High (15-40 MPa) |
| Fire Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Sound Insulation | Moderate | High |
| Installation Speed | Fast (easy to cut and shape) | Moderate (requires heavy lifting) |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Typical Use | Non-structural walls, insulation, void filling | Structural walls, load-bearing blocks |
Introduction to Cellular and Precast Concrete Blocks
Cellular concrete blocks are lightweight, made using aerated cement mixtures that enhance thermal insulation and reduce structural load. Precast concrete blocks are manufactured in controlled factory settings, ensuring consistent quality, high strength, and rapid installation on site. Both types offer distinct advantages in construction, with cellular blocks favored for energy efficiency and precast blocks preferred for durability and precision.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Cellular concrete consists of cement, water, and a foaming agent that introduces air bubbles, resulting in a lightweight, porous material with excellent thermal insulation properties. Precast concrete blocks are made from a mixture of cement, aggregates like sand and gravel, and water, cured in controlled factory conditions to achieve high strength and durability. The manufacturing process for cellular concrete involves mixing and curing at ambient temperatures with foam integration, while precast concrete requires molds and often steam curing for rapid strength gain.
Structural Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity
Cellular concrete exhibits lower structural strength and load-bearing capacity compared to precast concrete blocks due to its lightweight, porous nature designed primarily for insulation and ease of installation. Precast concrete blocks offer superior compressive strength and durability, making them ideal for load-bearing walls and heavy structural elements in construction. Engineers often select precast concrete for foundational applications where high load tolerance and long-term stability are critical.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation due to its porous structure, which significantly reduces heat transfer compared to dense precast concrete blocks. Acoustic insulation is enhanced in cellular concrete by its lightweight and air-filled cavities that effectively absorb sound waves, outperforming the denser precast concrete in noise reduction. Precast concrete blocks, while providing structural strength, have lower thermal and acoustic insulation values, making cellular concrete a preferred choice for energy-efficient and soundproof building applications.
Installation and Construction Speed
Cellular concrete offers faster installation and curing times compared to precast concrete blocks due to its lightweight nature and ability to be poured directly into molds or forms on-site, reducing transportation and handling requirements. Precast concrete blocks, although manufactured under controlled conditions ensuring quality, require more time for delivery and positioning during construction, potentially slowing down the build process. The reduced weight and ease of forming cellular concrete accelerate construction timelines, especially in projects where speed and efficiency are critical.
Durability and Longevity
Cellular concrete offers enhanced durability due to its lightweight, porous structure, which provides excellent freeze-thaw resistance and reduces cracking over time. Precast concrete blocks exhibit high compressive strength and durability, benefiting from factory-controlled curing processes that enhance longevity and structural integrity. Both materials provide long-lasting performance, but cellular concrete is advantageous in applications requiring thermal insulation and reduced weight, while precast concrete excels in strength-intensive uses.
Cost Comparison and Budget Considerations
Cellular concrete offers a lower material cost compared to precast concrete blocks due to its lightweight composition and reduced cement usage, making it more budget-friendly for large-scale projects. Precast concrete blocks, while more expensive upfront, provide superior strength and durability that can lower long-term maintenance expenses. Budget considerations should weigh initial investment against lifecycle costs, including installation speed and structural requirements, to determine the most cost-effective option for specific construction needs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cellular concrete significantly reduces environmental impact by incorporating air bubbles, lowering raw material usage and enhancing insulation properties, thereby improving energy efficiency in construction. Precast concrete blocks, while durable and consistent in quality, typically involve higher embodied energy due to manufacturing processes and transportation emissions. Sustainable construction practices favor cellular concrete for its lighter weight, reduced carbon footprint, and superior thermal performance compared to conventional precast concrete blocks.
Applications and Suitable Use Cases
Cellular concrete offers excellent thermal insulation and lightweight properties, making it ideal for non-load-bearing walls, partitions, and void filling in residential and commercial construction. Precast concrete blocks provide superior strength and durability, suitable for load-bearing walls, infrastructure projects, and industrial buildings requiring high structural performance. While cellular concrete excels in energy efficiency and ease of installation, precast concrete is preferred for applications demanding enhanced mechanical strength and longevity.
Maintenance Requirements and Future Trends
Cellular concrete blocks require less frequent maintenance due to their lightweight and insulating properties that reduce cracking and moisture damage compared to traditional precast concrete. Precast concrete blocks, while more durable and load-bearing, may need periodic inspections for joint integrity and surface wear in high-traffic or harsh environmental conditions. Emerging trends include integrating advanced additives in cellular concrete for enhanced strength and sustainability, and the increased use of automation and 3D printing in precast block manufacturing to optimize structural performance and reduce carbon footprint.
Infographic: Cellular concrete vs Precast concrete for Block
 azmater.com
azmater.com