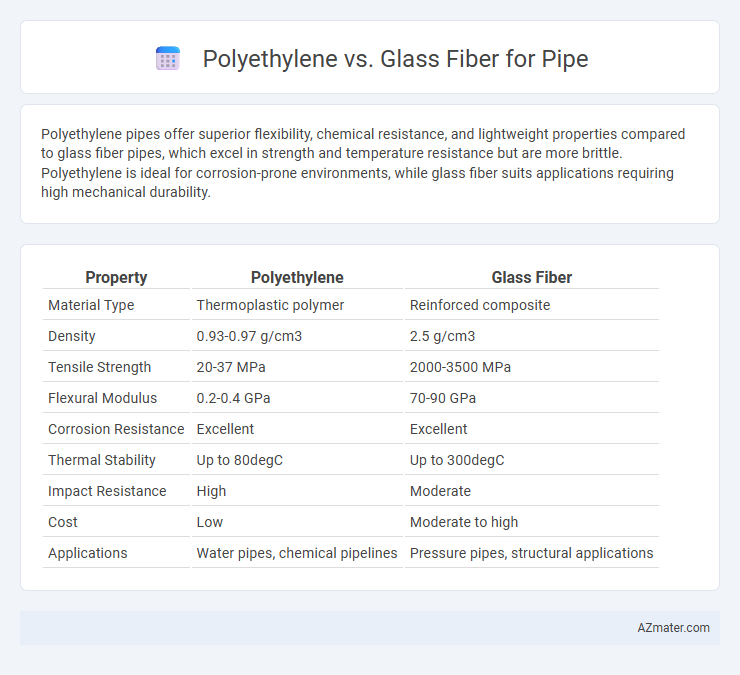
Polyethylene pipes offer superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and lightweight properties compared to glass fiber pipes, which excel in strength and temperature resistance but are more brittle. Polyethylene is ideal for corrosion-prone environments, while glass fiber suits applications requiring high mechanical durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Reinforced composite |
| Density | 0.93-0.97 g/cm3 | 2.5 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 20-37 MPa | 2000-3500 MPa |
| Flexural Modulus | 0.2-0.4 GPa | 70-90 GPa |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 80degC | Up to 300degC |
| Impact Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Cost | Low | Moderate to high |
| Applications | Water pipes, chemical pipelines | Pressure pipes, structural applications |
Overview of Polyethylene and Glass Fiber Pipes
Polyethylene pipes are lightweight, flexible, and resistant to corrosion and chemicals, making them ideal for water supply and gas distribution systems. Glass fiber pipes offer superior strength, high temperature resistance, and excellent durability, commonly used in industrial applications requiring high pressure and structural integrity. Both materials provide distinct advantages, with polyethylene excelling in ease of installation and glass fiber preferred for heavy-duty performance in harsh environments.
Material Composition and Structure
Polyethylene pipes consist of long chains of ethylene molecules, forming a flexible, lightweight thermoplastic with excellent chemical resistance and low permeability. Glass fiber pipes are reinforced composites made by embedding fine glass fibers within a polymer matrix, providing high tensile strength, rigidity, and enhanced durability against mechanical stress. The molecular arrangement in polyethylene ensures flexibility and corrosion resistance, while the glass fiber reinforcement significantly improves the structural integrity and impact resistance of the pipe.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Glass fiber pipes exhibit significantly higher mechanical strength compared to polyethylene pipes, making them suitable for high-pressure and load-bearing applications. Polyethylene pipes offer flexibility and impact resistance but have lower tensile and compressive strength relative to glass fiber-reinforced alternatives. Mechanical strength parameters such as tensile modulus and burst pressure clearly favor glass fiber composites, ensuring enhanced durability under demanding conditions.
Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
Polyethylene pipes offer superior corrosion resistance due to their inert nature, making them highly effective in handling aggressive chemicals and preventing rust formation. Glass fiber pipes provide excellent chemical resistance as well but can be susceptible to damage from highly acidic or alkaline environments if not properly coated or maintained. Polyethylene's flexibility and non-reactivity make it more resilient against a wide range of corrosive agents compared to the structural rigidity and potential brittleness of glass fiber pipes.
Durability and Lifespan
Polyethylene pipes exhibit excellent resistance to corrosion, chemical exposure, and environmental stress cracking, resulting in a lifespan that often exceeds 50 years under optimal conditions. Glass fiber reinforced pipes (GRP) offer superior mechanical strength and enhanced resistance to abrasion and high temperatures, extending their durability in demanding industrial applications. While polyethylene excels in flexibility and impact resistance, glass fiber pipes provide greater structural integrity and longevity in aggressive environments, making the choice dependent on specific durability requirements and operational conditions.
Installation and Handling Differences
Polyethylene pipes offer significant ease in installation due to their lightweight, flexibility, and ability to be joined through heat fusion, reducing labor time and costs on-site. Glass fiber pipes, while providing high strength and corrosion resistance, require careful handling because of their brittleness and often need specialized equipment for cutting and joining. The difference in durability during transport and on-site handling makes polyethylene more suitable for applications demanding quick, less labor-intensive installation, whereas glass fiber pipes are preferred when mechanical strength and chemical resistance are critical.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Polyethylene pipes generally offer lower upfront costs compared to glass fiber-reinforced pipes, making them a cost-effective option for many applications with minimal installation expenses due to their flexibility and lightweight nature. Glass fiber pipes, while more expensive initially, provide enhanced durability and resistance to corrosion, potentially reducing long-term maintenance and replacement costs in harsh environments. Economic considerations should weigh the initial investment against lifecycle costs, including anticipated service life, environmental factors, and maintenance frequency for optimal budget allocation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyethylene pipes exhibit lower environmental impact due to their recyclability and reduced energy consumption during production compared to glass fiber pipes. Glass fiber pipes, while offering greater durability and strength, involve higher embodied energy and challenges in recycling, contributing to increased carbon footprint. Sustainable pipeline systems favor polyethylene for its balance of longevity, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and ease of recycling.
Application Suitability and Industry Use
Polyethylene pipes excel in water supply, irrigation, and gas distribution due to their flexibility, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation, making them ideal for underground and low-pressure applications. Glass fiber reinforced pipes offer superior strength, chemical resistance, and high-temperature tolerance, suitable for industrial processes, chemical transport, and marine environments requiring structural durability. Industries such as agriculture, municipal water systems, and residential plumbing favor polyethylene, while petrochemical, marine, and manufacturing sectors predominantly utilize glass fiber piping for demanding operational conditions.
Maintenance and Long-Term Performance
Polyethylene pipes offer superior corrosion resistance and require minimal maintenance due to their flexibility and chemical inertness, making them ideal for long-term performance in varied environments. Glass fiber reinforced pipes, while strong and durable, may need periodic inspections to monitor for potential delamination or fiber degradation under harsh conditions. Over extended use, polyethylene maintains consistent structural integrity, reducing repair frequency and associated costs compared to glass fiber alternatives.
Infographic: Polyethylene vs Glass fiber for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com