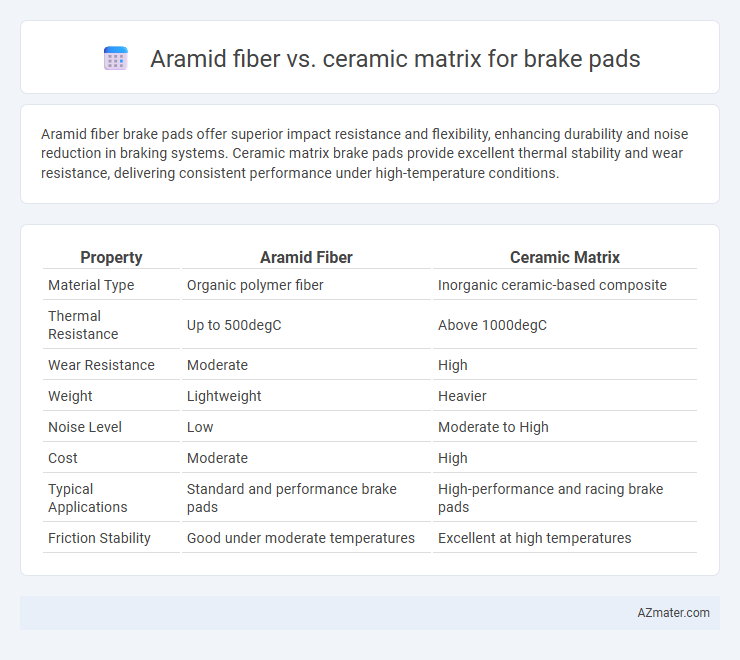
Aramid fiber brake pads offer superior impact resistance and flexibility, enhancing durability and noise reduction in braking systems. Ceramic matrix brake pads provide excellent thermal stability and wear resistance, delivering consistent performance under high-temperature conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aramid Fiber | Ceramic Matrix |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Organic polymer fiber | Inorganic ceramic-based composite |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 500degC | Above 1000degC |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Noise Level | Low | Moderate to High |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
| Typical Applications | Standard and performance brake pads | High-performance and racing brake pads |
| Friction Stability | Good under moderate temperatures | Excellent at high temperatures |
Introduction to Brake Pad Materials
Brake pad materials are critical for effective vehicle braking performance, with aramid fiber and ceramic matrix representing two advanced options. Aramid fiber composites offer high tensile strength and excellent heat resistance, providing enhanced durability and noise reduction. Ceramic matrix brake pads combine ceramic fibers and bonding agents to deliver superior thermal stability, longer lifespan, and reduced wear on rotors.
Overview of Aramid Fiber
Aramid fiber is a high-strength synthetic fiber known for its excellent heat resistance, impact durability, and lightweight properties, making it ideal for brake pad applications requiring superior friction performance and wear resistance. It offers enhanced thermal stability and flexibility compared to ceramic matrix materials, allowing for efficient energy absorption and reduced noise during braking. Aramid fiber brake pads typically provide consistent stopping power and longevity in various driving conditions, especially under high-load and high-temperature scenarios.
Overview of Ceramic Matrix
Ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) in brake pads offer superior thermal stability and wear resistance compared to aramid fiber materials. These composites enable higher operating temperatures and improved braking performance under extreme conditions due to their low thermal expansion and excellent hardness. Enhanced durability and reduced brake fade make ceramic matrix brake pads a preferred choice in high-performance and heavy-duty applications.
Performance Comparison: Aramid Fiber vs Ceramic Matrix
Aramid fiber brake pads offer superior impact resistance and excellent noise reduction, making them highly effective in everyday driving conditions. Ceramic matrix brake pads provide enhanced thermal stability and longer wear life, excelling in high-performance and heavy-duty applications. Both materials deliver reliable stopping power, but aramid fibers prioritize comfort and noise control, whereas ceramic matrices emphasize durability and high-temperature performance.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Stability
Aramid fiber brake pads exhibit excellent heat resistance up to approximately 500degC, maintaining structural integrity and consistent friction performance under moderate thermal stress. Ceramic matrix brake pads offer superior thermal stability, withstanding temperatures beyond 800degC without significant degradation, providing enhanced performance during high-speed or heavy-duty braking conditions. The higher melting point and thermal conductivity of ceramic matrices reduce brake fade and extend pad lifespan in extreme heat environments compared to aramid fiber composites.
Wear and Longevity
Aramid fiber brake pads exhibit high wear resistance due to their toughness and ability to absorb energy, resulting in prolonged service life under moderate braking conditions. Ceramic matrix brake pads offer superior longevity with excellent heat resistance and minimal wear, maintaining stable friction performance even under high-temperature, heavy-duty braking scenarios. The ceramic matrix materials outperform aramid fibers in durability, making them ideal for applications demanding consistent wear resistance and extended operational lifespan.
Noise and Dust Production
Aramid fiber brake pads produce less noise due to their excellent damping properties, resulting in quieter braking compared to ceramic matrix pads. Ceramic matrix brake pads generate minimal dust, as their composition resists wear and produces finer particles that settle quickly, while aramid fiber pads tend to produce more noticeable dust. Selecting ceramic matrix pads is preferred for maintaining cleaner wheels and reducing brake dust-related maintenance.
Cost and Availability
Aramid fiber brake pads offer a cost-effective solution due to lower raw material expenses and wide industrial availability, making them accessible for mass production. Ceramic matrix brake pads, though more expensive, provide superior performance but suffer from higher manufacturing costs and limited availability of advanced raw materials. The cost-efficiency and widespread supply of aramid fibers often make them preferable for standard applications, while ceramic matrix composites are reserved for high-performance or specialty vehicles.
Environmental Impact
Aramid fiber brake pads generate lower particulate emissions and are less abrasive on brake rotors, contributing to reduced environmental pollution during use. Ceramic matrix brake pads offer superior wear resistance and produce finer, less harmful dust particles, minimizing airborne contaminants and improving air quality. Both materials provide eco-friendly alternatives to traditional metal-based pads by reducing toxic metal emissions and enhancing recyclability in brake system applications.
Choosing the Best Material for Your Brake Pads
Aramid fiber brake pads offer superior impact resistance and excellent thermal stability, making them ideal for high-performance vehicles requiring durability and noise reduction. Ceramic matrix brake pads excel in heat dissipation and generate less dust, ensuring cleaner wheel surfaces and consistent braking performance under extreme conditions. Selecting the best material depends on balancing factors like thermal tolerance, noise preference, and driving style to optimize brake pad longevity and efficiency.
Infographic: Aramid fiber vs Ceramic matrix for Brake pad
 azmater.com
azmater.com